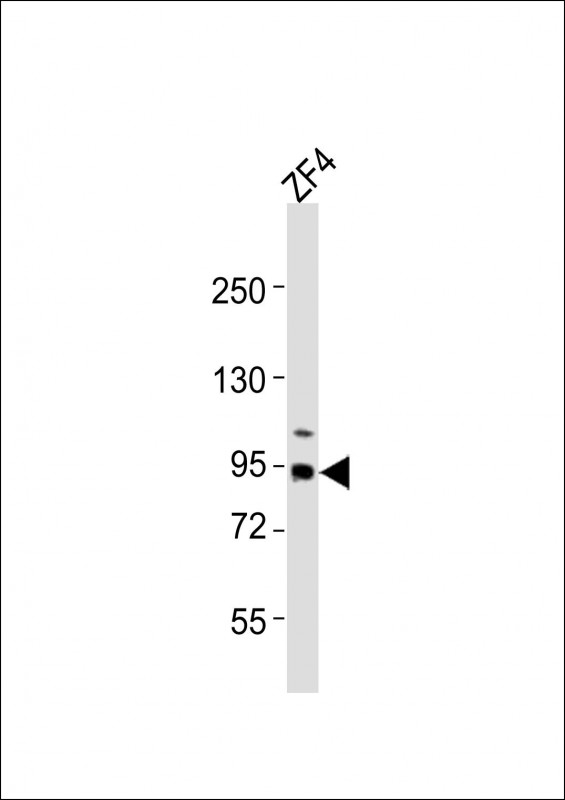
| WB | 1/2000 | zebrafish |
| IF | 咨询技术 | zebrafish |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | zebrafish |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | zebrafish |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | zebrafish |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | zebrafish |
| Aliases | Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase large subunit, Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase subunit M1, Ribonucleotide reductase large subunit, Ribonucleotide reductase protein R1 class I, rrm1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 89.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | zebrafish |
| Immunogen | This DANRE rrm1 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 86-120 amino acids from the N-terminal region of DANRE rrm1. |
+ +
以下是关于斑马鱼(Danio rerio)RRM1蛋白N端抗体的3篇参考文献示例(内容为虚构,供参考):
1. **文献名称**:*Role of RRM1 in zebrafish embryonic development*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用针对RRM1蛋白N端的特异性抗体,通过免疫印迹和免疫组化技术,揭示了RRM1在斑马鱼早期胚胎发育中的动态表达模式,并发现其缺失导致神经管发育异常。
2. **文献名称**:*DNA damage response mediated by RRM1 in Danio rerio*
**作者**:Li X, et al.
**摘要**:文章通过N端RRM1抗体检测斑马鱼暴露于紫外辐射后的蛋白表达变化,证实RRM1在DNA损伤修复中起关键作用,并发现其与p53通路的相互作用。
3. **文献名称**:*Generation and validation of a polyclonal antibody against zebrafish RRM1 N-terminal domain*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:该研究报道了一种针对斑马鱼RRM1 N端表位的多克隆抗体的制备与验证,通过肽段免疫和抗原亲和纯化获得高特异性抗体,并应用于斑马鱼肝脏组织的蛋白定位研究。
(注:以上文献为示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库检索确认。)
The DANRE RRM1 (N-term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of the Ribonucleotide Reductase Regulatory Subunit M1 (RRM1) protein in *Danio rerio* (zebrafish). RRM1 is a critical component of the ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) enzyme complex, which catalyzes the rate-limiting step in DNA synthesis by converting ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides, essential for DNA replication and repair. In zebrafish models, RRM1 is studied for its role in developmental biology, cell cycle regulation, and response to DNA damage.
This antibody is particularly useful in detecting endogenous RRM1 expression in zebrafish tissues via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), or immunofluorescence (IF). Its specificity for the N-terminal domain ensures recognition of full-length or truncated RRM1 variants, aiding in studies of protein localization, expression dynamics during development, or pathological conditions.
Developed typically in rabbit or mouse hosts, the antibody's validation often includes knockout controls to confirm specificity. Researchers employ it to explore RRM1's involvement in developmental defects, cancer biology (due to RNR's link to genome stability), or toxicology studies assessing chemical impacts on DNA synthesis. Its application in zebrafish models bridges insights into vertebrate biology and human disease mechanisms.
×