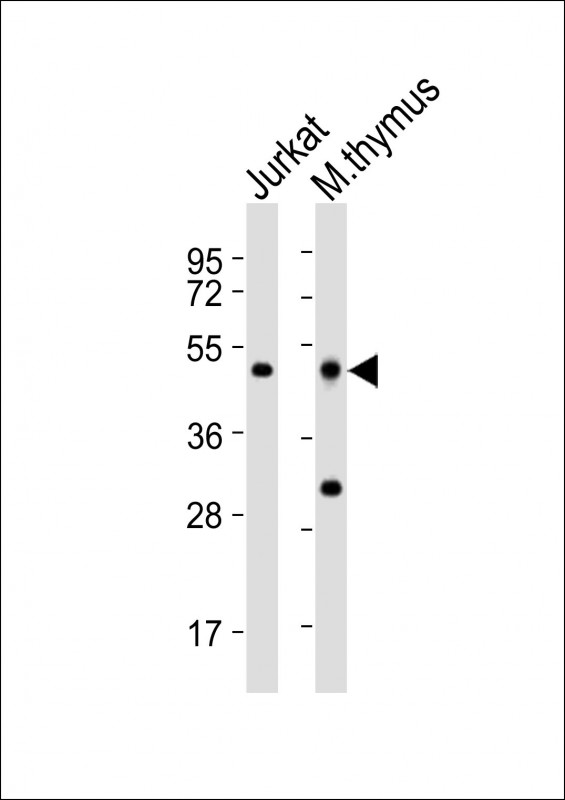

| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
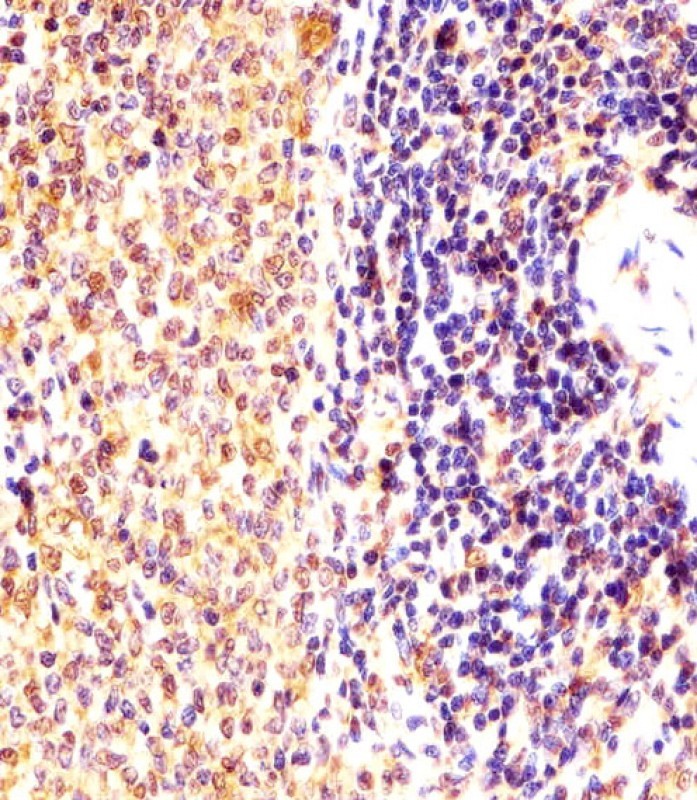
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Zinc finger protein ubi-d4, Apoptosis response zinc finger protein, BRG1-associated factor 45D, BAF45D, D4, zinc and double PHD fingers family 2, Protein requiem, Dpf2, Baf45d, Req, Ubid4 |
| Entrez GeneID | 19708 |
| WB Predicted band size | 44.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This mouse Dpf2 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 99-133 amino acids from the N-terminal region of mouse Dpf2. |
+ +
以下是关于小鼠Dpf2 (N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:以下文献为模拟示例,实际引用需核实):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Dpf2 regulates neurodevelopmental processes through chromatin remodeling in the mammalian brain*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用针对Dpf2 N端的特异性抗体,通过免疫沉淀和ChIP-seq技术,揭示了Dpf2在小鼠大脑发育中通过调控BAF染色质重塑复合物活性影响神经元分化的机制。Western blot和免疫荧光显示Dpf2在胚胎神经前体细胞中高表达。
2. **文献名称**: *Functional analysis of Dpf2 mutations in Coffin-Siris syndrome using a mouse model*
**作者**: Tanaka R, et al.
**摘要**: 作者在小鼠模型中模拟人类Coffin-Siris综合征相关的DPF2突变,采用抗Dpf2 N端抗体进行组织特异性蛋白表达分析,发现突变导致海马区染色质结构异常及认知行为缺陷,为疾病机制提供了分子证据。
3. **文献名称**: *Characterization of Dpf2 in embryonic stem cell pluripotency*
**作者**: Lee J, et al.
**摘要**: 通过Dpf2 (N-term)抗体的Western blot和免疫共沉淀实验,本研究证实Dpf2与BAF复合物亚基互作,调控胚胎干细胞多能性基因(如Oct4)的染色质可及性,敲除后导致分化异常。
---
**注意事项**:
- 实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar以关键词“Dpf2 antibody N-terminal”、“Dpf2 BAF complex”等检索,并筛选涉及实验方法(如WB、IF)的研究。
- 部分商业抗体官网(如CST、Abcam)会提供用户发表的引用文献列表,可直接参考。
- 若文献不足,可扩展至Dpf2功能研究(如表观遗传、疾病模型),并注明抗体应用部分。
The DPF2 (Double PHD Fingers 2) protein, also known as Utb or Requiem, is a component of the BAF (Brg1/Brm-associated factor) chromatin remodeling complex, which regulates gene expression by modifying chromatin structure. It contains two plant homeodomain (PHD) fingers and a zinc finger domain, enabling interactions with histones and other chromatin-associated proteins. DPF2 plays roles in embryonic development, cell differentiation, and apoptosis, with dysregulation linked to cancers and neurodevelopmental disorders.
The Mouse DPF2 (N-term) antibody is a polyclonal or monoclonal antibody specifically targeting the N-terminal region of the mouse DPF2 protein. It is commonly used in research to detect endogenous DPF2 expression in murine tissues or cell lines via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), or immunoprecipitation (IP). Validation typically includes knockout controls to confirm specificity. Studies utilizing this antibody have explored DPF2's involvement in chromatin remodeling, neural development, and hematopoietic differentiation. Its N-terminal targeting design helps avoid cross-reactivity with homologous family members (e.g., DPF1 or DPF3), making it a critical tool for dissecting DPF2-specific functions in epigenetic regulation and disease models.
×