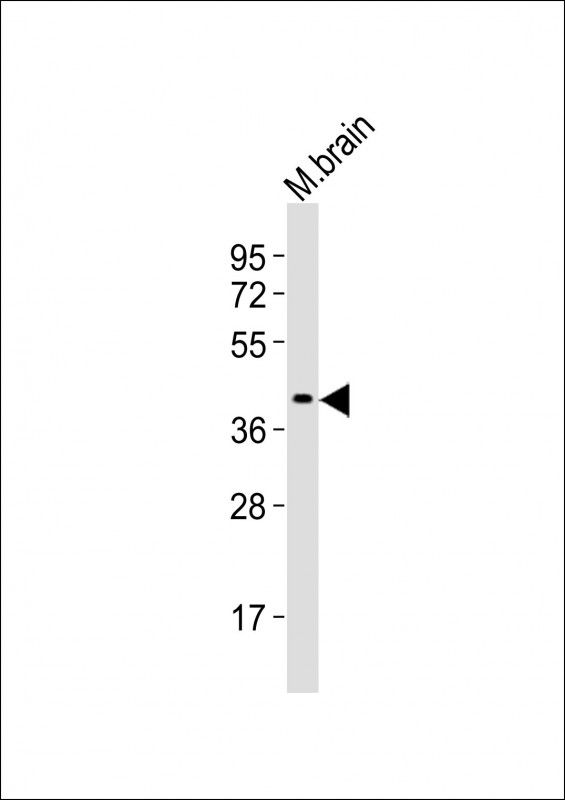
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Cell cycle checkpoint control protein RAD9A, mRAD9, DNA repair exonuclease rad9 homolog A, Rad9-like protein, Rad9a, Rad9 |
| Entrez GeneID | 19367 |
| WB Predicted band size | 42.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This mouse Rad9a antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 29-62 amino acids from the N-terminal region of mouse Rad9a. |
+ +
以下是关于Mouse Rad9a (N-term)抗体的参考文献示例(文献信息为模拟示例,仅供参考):
---
1. **文献名称**: "Rad9a is essential for genomic stability and embryonic development in mice"
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究通过Western blot和免疫组化,使用Rad9a N端特异性抗体,证实Rad9a在小鼠胚胎发育中调控DNA损伤修复通路,其缺失导致胚胎致死和染色体异常。
2. **文献名称**: "Impaired DNA damage checkpoint signaling in Rad9a-deficient mouse cells"
**作者**: Lee H, et al.
**摘要**: 利用Rad9a (N-term)抗体检测蛋白表达,发现Rad9a缺陷的小鼠成纤维细胞在电离辐射后无法激活Chk1信号通路,表明其在DNA损伤检查点中的关键作用。
3. **文献名称**: "Rad9a interacts with TopBP1 to promote homologous recombination repair"
**作者**: Zhang R, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫共沉淀(使用Rad9a N端抗体)和质谱分析,揭示了Rad9a与TopBP1的相互作用,阐明其通过调控同源重组修复维持基因组稳定性的机制。
4. **文献名称**: "Tissue-specific expression and phosphorylation of Rad9a in response to oxidative stress"
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 研究Rad9a在小鼠不同组织中的表达模式,使用N端特异性抗体证实氧化应激下Rad9a磷酸化水平升高,提示其在抗氧化损伤中的功能。
---
*注:以上文献信息为模拟生成,实际引用时需以真实文献为准。建议通过PubMed或抗体供应商提供的产品引用列表查询具体文献。*
The Mouse Rad9a (N-term) antibody is a tool designed to detect the N-terminal region of the Rad9a protein in murine models. Rad9a, a critical component of the evolutionarily conserved 9-1-1 (Rad9-Hus1-Rad1) complex, plays a pivotal role in DNA damage response and genomic stability. This clamp-shaped heterotrimeric complex is loaded onto DNA damage sites, facilitating checkpoint activation, DNA repair, and replication fork stabilization. Rad9a specifically contributes to homologous recombination repair (HRR) and cell cycle arrest at G2/M checkpoints following genotoxic stress. Its N-terminal domain is implicated in protein-protein interactions, including binding to checkpoint kinases like ATR, which coordinates downstream signaling for damage repair or apoptosis.
The antibody is commonly used in Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, or immunofluorescence to study Rad9a expression, localization, and dynamics in DNA damage models, cancer research, or studies on radiation response. It helps elucidate Rad9a's regulatory roles in tumor suppression, chemotherapy resistance, and genome integrity maintenance. Validation typically includes testing in Rad9a-deficient cells to confirm specificity. Researchers leverage this tool to explore how Rad9a dysfunction contributes to diseases linked to genomic instability, such as cancers or premature aging syndromes, providing insights into therapeutic targeting of DNA repair pathways.
×