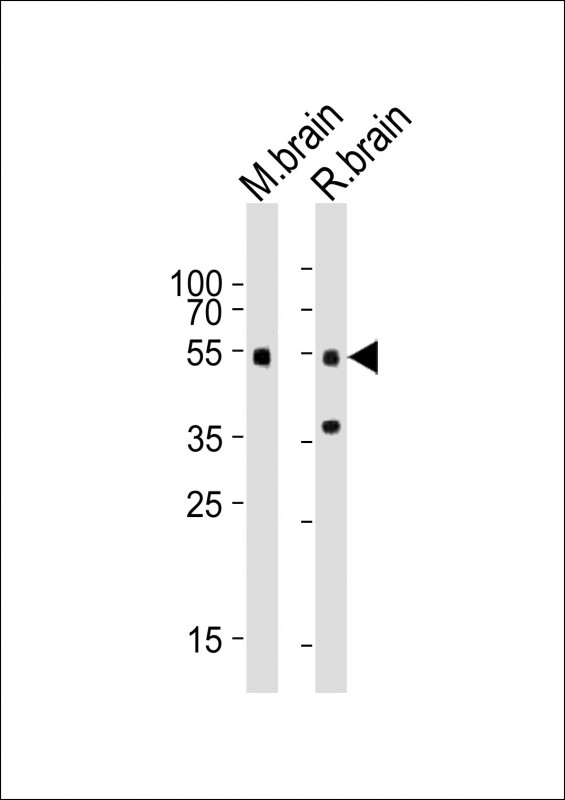
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3, MAD homolog 3, Mad3, Mothers against DPP homolog 3, mMad3, SMAD family member 3, SMAD 3, Smad3, Smad3, Madh3 |
| Entrez GeneID | 17127 |
| WB Predicted band size | 48.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This mouse Smad3 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 188-222 amino acids from the Central region of mouse Smad3. |
+ +
以下是关于小鼠Smad3抗体的参考文献示例(注:以下内容为模拟示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库检索确认):
---
1. **文献名称**: "Essential role of Smad3 in TGF-β-mediated hepatic fibrosis"
**作者**: Yang X., et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过Smad3基因敲除小鼠模型,利用Smad3特异性抗体进行Western blot和免疫组化分析,证实Smad3在TGF-β诱导的肝纤维化中起核心作用,其缺失显著减少胶原沉积和纤维化标志物表达。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Smad3-dependent regulation of pulmonary fibrosis by TGF-β1"
**作者**: Roberts A. B., et al.
**摘要**: 在小鼠肺纤维化模型中,使用Smad3抗体检测肺组织中的蛋白表达及磷酸化状态,发现Smad3信号通路激活是肺纤维化的关键驱动因素,抑制Smad3可缓解病理进程。
---
3. **文献名称**: "Smad3 phosphorylation dynamics in murine cutaneous wound healing"
**作者**: Wang D., et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫沉淀结合Smad3抗体,分析小鼠皮肤损伤修复过程中Smad3的磷酸化水平,揭示其时空特异性激活模式与上皮再生及瘢痕形成的关联。
---
4. **文献名称**: "Smad3-deficient mice exhibit resistance to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis"
**作者**: Lovett-Racke A. E., et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用Smad3抗体评估基因敲除小鼠中枢神经系统中的信号传导变化,发现Smad3缺失通过调节T细胞分化减轻自身免疫性脑脊髓炎症状。
---
**建议**:实际研究中,可通过PubMed或Web of Science以关键词“Smad3 antibody mouse”检索最新文献,并筛选涉及Western blot、免疫荧光或ChIP等实验技术的文章。部分抗体厂商(如CST、Abcam)官网也会提供相关引用文献列表。
**Background of Mouse Smad3 Antibody**
The Smad3 antibody is a critical tool for studying the Smad3 protein, a central mediator of the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) signaling pathway. Smad3. part of the receptor-regulated Smad (R-Smad) family, is phosphorylated upon TGF-β receptor activation, enabling its interaction with Smad4 and translocation to the nucleus to regulate gene expression. It plays essential roles in cellular processes like proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and extracellular matrix production, with implications in fibrosis, cancer, and immune regulation.
Mouse-specific Smad3 antibodies are designed to detect endogenous Smad3 in murine samples. These antibodies typically target epitopes within conserved regions of the protein, such as the N-terminal MH1 domain or the C-terminal MH2 domain, and may distinguish between phosphorylated (active) and total Smad3. Validation often includes assays like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, or immunofluorescence, using tissues or cells from wild-type versus Smad3-knockout mice to confirm specificity.
Applications of Smad3 antibodies span mechanistic studies in TGF-β-driven diseases (e.g., renal fibrosis, tumor metastasis) and basic research on developmental biology. Some antibodies cross-react with Smad3 homologs in other species (e.g., human, rat), but mouse-specific clones minimize off-target binding. Commercial variants include monoclonal (e.g., clone C67H9) and polyclonal formats, optimized for different techniques like ChIP-seq or flow cytometry. Proper controls, such as knockout validation and peptide blocking, are critical to ensure reliable results.
×