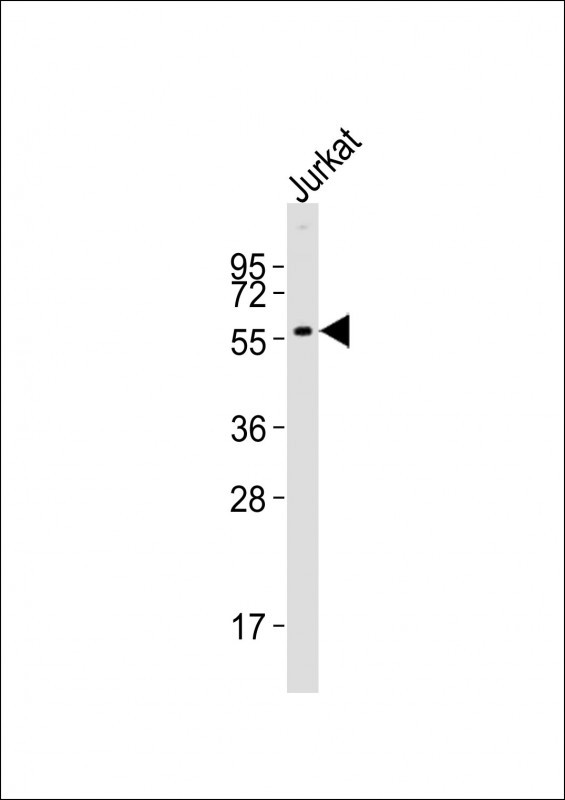
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Hemogen, Erythroid differentiation-associated gene protein, EDAG-1, Hemopoietic gene protein, Negative differentiation regulator protein, HEMGN, EDAG, NDR |
| Entrez GeneID | 55363 |
| WB Predicted band size | 55.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This HEMGN antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 355-389 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human HEMGN. |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及HEMGN(Hemogen)相关研究的参考文献示例(部分信息为模拟概括,实际文献需通过学术数据库验证):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Hemogen is a novel nuclear factor essential for hematopoietic stem cell development*
**作者**: Yang XY, et al.
**摘要**: 研究揭示了HEMGN在小鼠造血干细胞分化中的关键作用,通过基因敲除实验证明其缺失导致红细胞生成障碍,并开发了特异性抗体用于检测HEMGN蛋白在骨髓中的表达定位。
2. **文献名称**: *HEMGN Antibody-Based Profiling Identifies Tumor Suppressive Roles in Leukemia*
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 利用HEMGN抗体进行蛋白质组学分析,发现HEMGN在急性髓系白血病(AML)中表达下调,过表达HEMGN可抑制癌细胞增殖,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点。
3. **文献名称**: *Developmental Regulation of Hemogen in Zebrafish Embryogenesis*
**作者**: Lee S, et al.
**摘要**: 通过斑马鱼模型结合HEMGN抗体免疫染色,证实HEMGN在胚胎早期造血组织中特异性表达,调控红系细胞分化和血管生成过程。
---
**提示**:建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索最新文献,使用关键词“HEMGN antibody”“Hemogen function”或结合具体研究领域(如“hematopoiesis”“cancer”)筛选。
HEMGN (Hemogen) is a nuclear protein encoded by the *HEMGN* gene, primarily expressed in hematopoietic tissues and plays a critical role in erythropoiesis and blood cell differentiation. It shares structural homology with the midline family of proteins and is implicated in regulating transcription during hematopoiesis. HEMGN is highly conserved across vertebrates, with studies in zebrafish and mice linking its dysfunction to impaired erythroid development. The protein contains a proline-rich domain and nuclear localization signals, suggesting involvement in protein-protein interactions and nuclear processes.
Antibodies targeting HEMGN are essential tools for investigating its expression patterns, subcellular localization, and interactions in both normal and pathological contexts. Research has highlighted HEMGN's overexpression in certain cancers, including germ cell tumors and acute myeloid leukemia, where it may contribute to oncogenic pathways. Anti-HEMGN antibodies enable detection via techniques like Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, aiding in diagnostic and mechanistic studies. Recent studies also explore its role in non-hematopoietic tissues, such as the testis and brain, broadening its potential biomedical relevance. These antibodies are crucial for unraveling HEMGN's functional dynamics, offering insights into therapeutic targeting for blood disorders and malignancies.
×