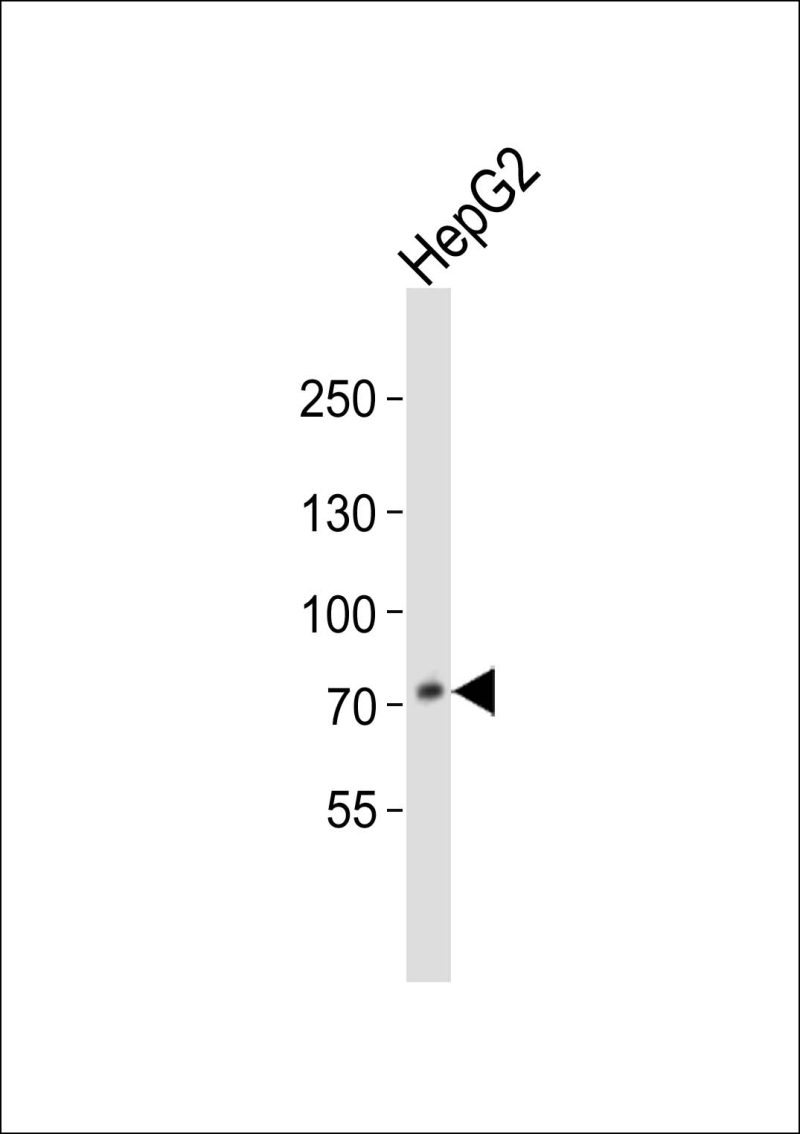



| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
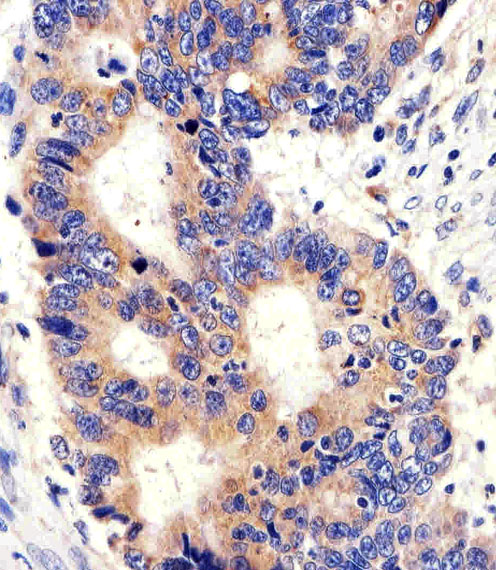
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
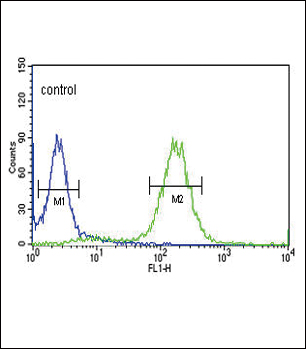
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9, 3421-, Neural apoptosis-regulated convertase 1, NARC-1, Proprotein convertase 9, PC9, Subtilisin/kexin-like protease PC9, PCSK9, NARC1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 255738 |
| WB Predicted band size | 74.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This PCSK9 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 479-508 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human PCSK9. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是3篇关于PCSK9抗体的重要文献概览:
1. **文献名称**:Evolocumab and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Cardiovascular Disease
**作者**:Sabatine MS et al.
**摘要**:FOURIER临床试验显示,PCSK9抑制剂evolocumab联合他汀治疗可显著降低LDL-C水平,并使心血管事件(心梗、卒中)风险降低15-20%(N Engl J Med, 2017)。
2. **文献名称**:Alirocumab and Cardiovascular Outcomes after Acute Coronary Syndrome
**作者**:Schwartz GG et al.
**摘要**:ODYSSEY Outcomes试验证实,急性冠脉综合征患者使用alirocumab强化降脂治疗,可使全因死亡风险降低15%,且LDL-C水平降低至25-50 mg/dL(N Engl J Med, 2018)。
3. **文献名称**:PCSK9: A Key Modulator of Cardiovascular Health
**作者**:Seidah NG et al.
**摘要**:基础研究揭示PCSK9通过结合LDL受体促进其降解,单克隆抗体通过阻断该作用提升肝细胞对LDL的清除能力(Nat Rev Cardiol, 2014)。
4. **文献名称**:Efficacy and Safety of PCSK9 Inhibitors
**作者**:Garza CA et al.
**摘要**:综述指出PCSK9抗体可降低LDL-C达50-60%,安全性良好(注射部位反应<5%),为家族性高胆固醇血症患者提供新选择(J Am Coll Cardiol, 2015)。
注:以上为典型研究范例,实际引用需核对原文及DOI编号。
PCSK9 (proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9) antibodies represent a breakthrough in cardiovascular disease management, targeting a key regulator of cholesterol metabolism. Discovered in 2003. PCSK9 binds to hepatic LDL receptors (LDLR), promoting their degradation and reducing LDL cholesterol (LDL-C) clearance. Genetic studies revealed that gain-of-function PCSK9 mutations cause hypercholesterolemia, while loss-of-function variants correlate with low LDL-C and reduced cardiovascular risk. This established PCSK9 inhibition as a therapeutic strategy.
Monoclonal antibodies like alirocumab and evolocumab, approved by the FDA in 2015. bind circulating PCSK9. preventing its interaction with LDLR. This preserves LDLR recycling, enhancing LDL-C uptake by liver cells and lowering serum LDL-C by up to 60%. These agents are used adjunctively with statins for familial hypercholesterolemia or statin-intolerant patients, demonstrating ~15% reduction in major cardiovascular events in trials.
Despite efficacy, barriers include high costs and subcutaneous administration. Research continues into oral PCSK9 inhibitors, siRNA therapies (e.g., inclisiran), and gene-editing approaches. PCSK9 antibodies exemplify translational success from genetic discovery to clinical application, offering a precision medicine tool for atherosclerosis management while highlighting challenges in drug accessibility and long-term safety monitoring.
×