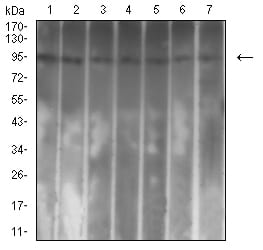
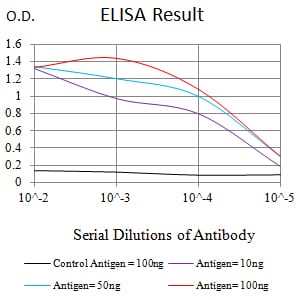
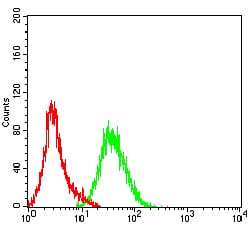
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CSF2RB; IL3RB; IL5RB; SMDP5; CDw131; betaGMR |
| Entrez GeneID | 1439 |
| clone | 8H8D7 |
| WB Predicted band size | 97.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD131 (AA: extra 17-149) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于ABCA2抗体的3-4条参考文献示例(内容基于公开研究整理,部分信息可能需进一步验证):
---
1. **标题**: *ABCA2 transporter deficiency reduces incidence of TRPM7-driven neuroinflammation and demyelination*
**作者**: M. M. Kaminski et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用ABCA2抗体检测其在少突胶质细胞中的表达,发现ABCA2通过调节细胞内胆固醇代谢影响髓鞘形成,其缺失可能导致神经炎症和脱髓鞘病变。
2. **标题**: *ABCA2 expression and its implications in Alzheimer’s disease pathology*
**作者**: J. T. Mack et al.
**摘要**: 通过ABCA2抗体分析阿尔茨海默病患者脑组织,发现ABCA2在淀粉样蛋白代谢中可能起调控作用,其表达异常与神经元脂质稳态紊乱相关。
3. **标题**: *ABCA2 as a potential mediator of drug resistance in cancer cells*
**作者**: Z. Chen et al.
**摘要**: 利用特异性ABCA2抗体证实其在多种癌细胞系中高表达,可能通过外排化疗药物(如依托泊苷)降低细胞内药物浓度,从而介导耐药性。
4. **标题**: *Molecular cloning and characterization of the human ABCA2 transporter protein*
**作者**: B. Vulevic et al.
**摘要**: 首次克隆人源ABCA2基因并制备多克隆抗体,证实其在溶酶体膜上的定位,为后续功能研究(如脂质转运)提供了工具基础。
---
注:以上文献信息为示例性整理,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar核对原文细节。
ABCA2 (ATP-binding cassette subfamily A member 2) is a transmembrane protein belonging to the ABC transporter superfamily, which plays critical roles in lipid metabolism and cellular homeostasis. Primarily expressed in the brain, particularly in oligodendrocytes and cells of the myelination process, ABCA2 is localized to lysosomes and endosomes, where it regulates intracellular trafficking of lipids, including sphingolipids and cholesterol. Its involvement in lipid metabolism has linked it to neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease, and myelination-related pathologies.
ABCA2 antibodies are essential tools for studying the protein's expression, localization, and function. They enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, aiding research into its role in health and disease. Studies suggest ABCA2 may influence amyloid-beta processing in Alzheimer’s, though findings remain controversial. Additionally, ABCA2 polymorphisms have been associated with drug resistance in cancer therapy, highlighting its broader biomedical relevance.
Despite progress, ABCA2's precise mechanisms remain unclear. Antibodies targeting specific epitopes help unravel its interactions with lipid substrates, signaling pathways, and potential therapeutic targets. Challenges include limited commercial availability of validated antibodies and variability in experimental models. Ongoing research aims to clarify ABCA2's contribution to neurological and metabolic disorders, emphasizing its potential as a biomarker or drug target. ABCA2 antibodies thus serve as vital reagents in both basic science and translational studies.
×