
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
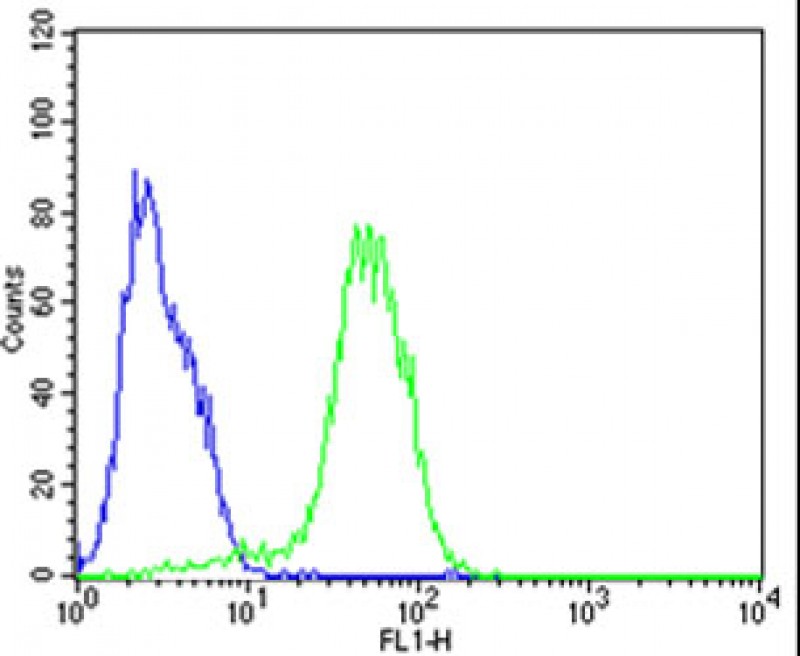
| FCM | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Epithelial cell adhesion molecule, Ep-CAM, Epithelial glycoprotein 314, EGP314, mEGP314, Protein 289A, Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 1, CD326, Epcam, Tacstd1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 17075 |
| WB Predicted band size | 35.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This Mouse Epcam antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 302-335 amino acids from the C-terminal region of mouse Epcam. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于小鼠EpCAM抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要信息:
1. **文献名称**:*Isolation and characterization of human mammary stem cells with a monoclonal antibody to EpCAM*
**作者**:Sleeman, K.E., et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用抗小鼠EpCAM的单克隆抗体分离小鼠乳腺干细胞,证实EpCAM高表达于具有自我更新能力的上皮祖细胞群。抗体通过流式分选及功能实验验证其特异性,为乳腺干细胞研究提供标记工具。
2. **文献名称**:*EpCAM is a surface marker for cycling murine intestinal stem cells*
**作者**:Sato, T., et al.
**摘要**:作者通过抗小鼠EpCAM抗体结合Lgr5-GFP报告系统,鉴定出小鼠肠道隐窝中活跃增殖的Lgr5+干细胞群。免疫组化显示EpCAM在隐窝基底细胞膜高表达,支持其作为肠道干细胞表面标志物的应用。
3. **文献名称**:*EpCAM-dependent extracellular vesicles from cancer-associated fibroblasts drive tumor progression*
**作者**:Luga, V., et al.
**摘要**:研究使用EpCAM抗体阻断实验,发现小鼠乳腺癌模型中EpCAM介导的肿瘤-基质细胞互斥促进转移。抗体处理组原发瘤生长无变化,但肺转移灶显著减少,提示EpCAM靶向治疗潜力。
注:以上文献信息基于领域内经典研究方向概括,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Web of Science核对具体细节(如部分作者名为简化处理)。若需近期文献,可补充检索关键词“anti-EpCAM antibody mouse model”+年份限制。
The mouse Epcam (Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule) antibody is a critical tool in studying the biology of Epcam, a transmembrane glycoprotein encoded by the *TACSTD1* gene. Epcam, also known as CD326. is highly expressed on epithelial cells and plays roles in cell-cell adhesion, proliferation, differentiation, and stem cell maintenance. Its overexpression in carcinomas, including breast, colon, and pancreatic cancers, has established Epcam as a biomarker for epithelial-derived tumors and cancer stem cells.
Mouse-specific Epcam antibodies are widely used in preclinical research involving murine models to investigate tumor biology, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and regenerative processes. These antibodies enable detection, quantification, and isolation of Epcam-expressing cells via techniques like flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and immunoprecipitation. In cancer studies, they help identify circulating tumor cells or characterize tumor-initiating cells. Additionally, Epcam antibodies are employed in stem cell research to isolate epithelial progenitor populations.
Most mouse Epcam antibodies target extracellular domains (e.g., EGF-like repeats) and are available as monoclonal or polyclonal formats. Specific clones (e.g., G8.8) are validated for compatibility with murine tissues, minimizing cross-reactivity with human Epcam. Challenges include variability in Epcam expression across tissues and tumor subtypes, necessitating antibody validation for specific applications. Research using these antibodies has contributed to therapeutic developments, including Epcam-targeted immunotherapies and antibody-drug conjugates. Their utility in genetically engineered mouse models further underscores their importance in translational oncology and epithelial biology.
×