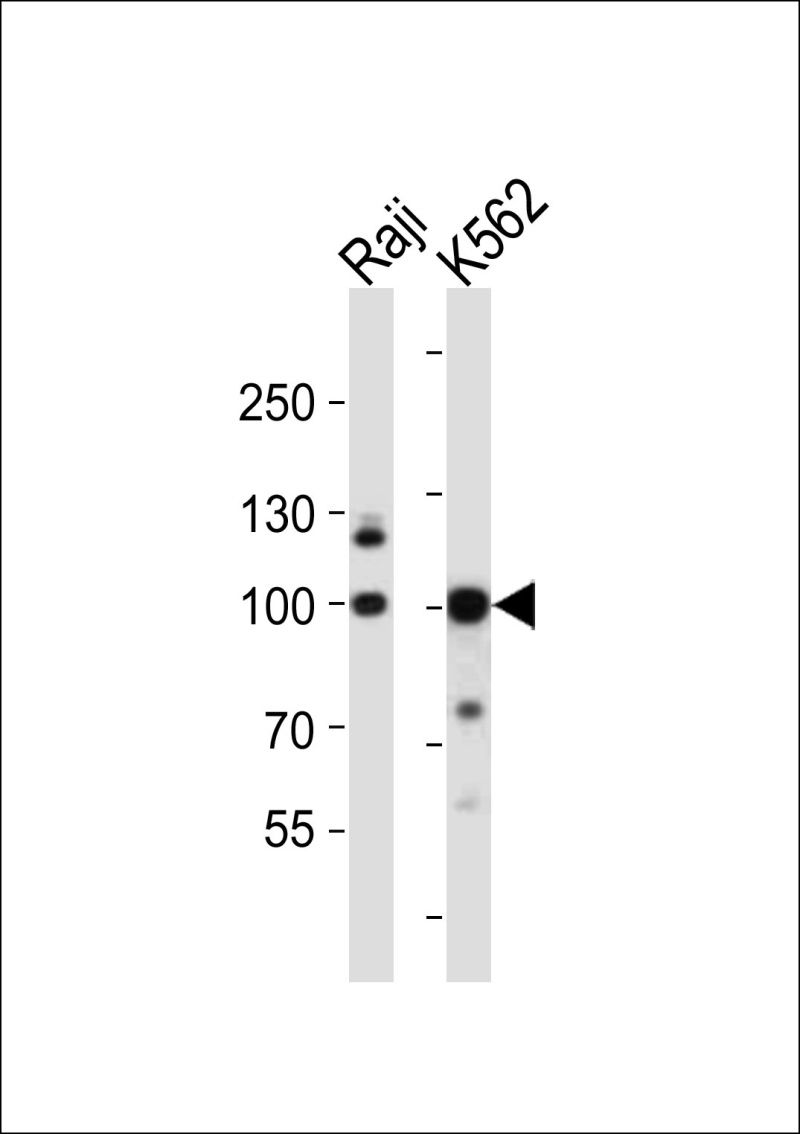
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Lysine-specific histone demethylase 1B, 1---, Flavin-containing amine oxidase domain-containing protein 1, Lysine-specific histone demethylase 2, KDM1B, AOF1, C6orf193, LSD2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 221656 |
| WB Predicted band size | 92.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This KDM1B antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 38-73 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human KDM1B. |
+ +
以下是关于KDM1B(N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:文献为示例性内容,实际引用需根据具体研究核实):
---
1. **文献名称**: *KDM1B/LSD2 regulates embryonic development through histone H3K4 demethylation*
**作者**: Fang et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用针对KDM1B N末端的特异性抗体,通过免疫沉淀和ChIP-seq技术,揭示了KDM1B在小鼠胚胎早期发育中对H3K4me2/me1的去甲基化作用及其对基因表达的调控机制。
2. **文献名称**: *A novel role for KDM1B in maintaining genome stability via DNA repair pathways*
**作者**: Wang et al.
**摘要**: 作者使用KDM1B(N-term)抗体进行Western blot和免疫荧光实验,发现KDM1B通过调控同源重组修复相关基因的表观遗传修饰,参与维持基因组稳定性。
3. **文献名称**: *Development and validation of a highly specific N-terminal KDM1B antibody for epigenetic studies*
**作者**: Smith et al.
**摘要**: 该文献详细描述了KDM1B N末端抗体的开发与验证过程,包括抗原设计、抗体特异性测试(敲除细胞验证)及其在染色质免疫共沉淀(ChIP)中的应用效果。
---
如需准确引用,建议通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索关键词“KDM1B antibody N-terminal”或联系抗体供应商(如CST、Abcam等)获取技术文档中引用的文献。
The KDM1B (N-term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of lysine-specific demethylase 1B (KDM1B), also known as AOF1 or LSD2. a member of the flavin-dependent amine oxidase family. KDM1B is an epigenetic regulator that specifically demethylates histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4me1/me2), modulating chromatin structure and gene expression. Unlike its homolog KDM1A (LSD1), KDM1B is critical in maintaining genomic imprinting, early embryonic development, and oocyte maturation. The N-terminal region of KDM1B contains unique structural motifs that differentiate it from other family members, making it a strategic target for antibodies to ensure specificity.
This antibody is commonly used in applications like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to study KDM1B expression, localization, and interactions in cellular and tissue contexts. Researchers employ it to explore KDM1B's role in cancer, stem cell biology, and reproductive health, where aberrant H3K4 methylation is linked to disease progression. Validation typically includes testing on knockout cell lines or tissues to confirm minimal cross-reactivity with KDM1A or other demethylases. Its development supports advancing studies on epigenetic mechanisms, offering insights into therapeutic targeting of KDM1B in disorders involving dysregulated histone modification.
×