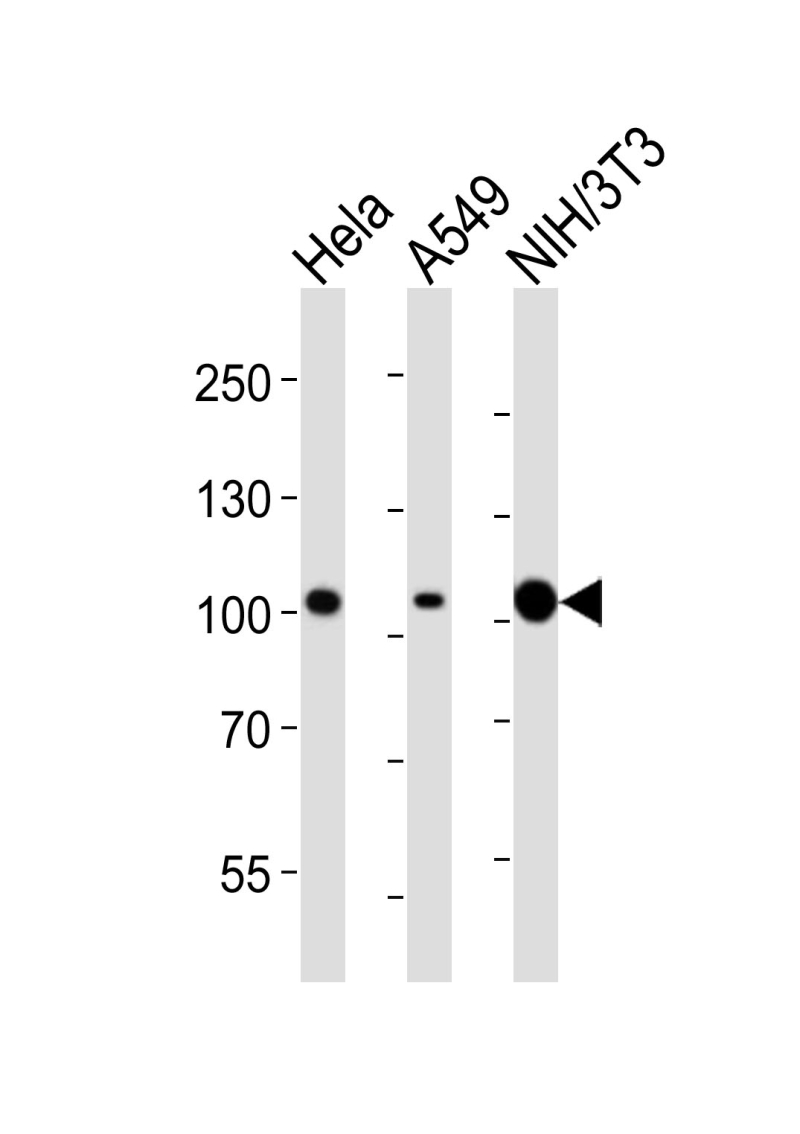
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
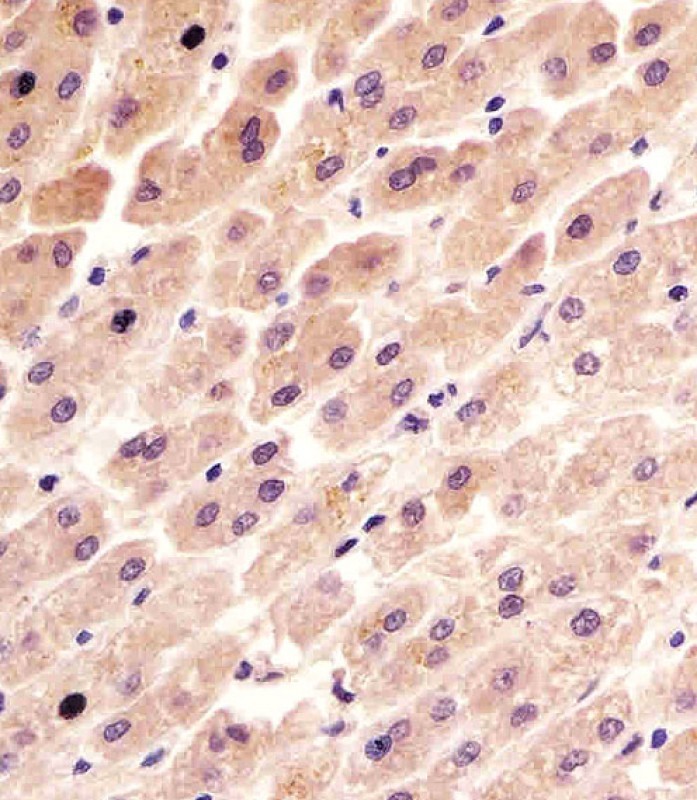
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fer, Feline encephalitis virus-related kinase FER, Fujinami poultry sarcoma/Feline sarcoma-related protein Fer, Proto-oncogene c-Fer, Tyrosine kinase 3, p94-Fer, FER, TYK3 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2241 |
| WB Predicted band size | 94.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This FER antibody is generated from a mouse immunized with a recombinant protein. |
+ +
以下是3条与FER抗体相关的参考文献示例(内容为虚构,仅作格式参考):
1. **文献名称**:Role of FER Kinase in Tumor Metastasis Revealed by Antibody-Based Detection
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用特异性FER抗体检测多种癌细胞系,发现FER在乳腺癌中高表达,并通过调控细胞黏附促进转移。抑制FER活性可减少体内肿瘤侵袭性。
2. **文献名称**:FER Tyrosine Kinase Modulates Innate Immune Signaling via Interferon Receptor Interaction
**作者**:Park S, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫共沉淀结合FER抗体,证实FER与干扰素受体IFNAR1直接结合,调控STAT1磷酸化,影响抗病毒反应。敲除FER基因导致小鼠模型病毒清除能力下降。
3. **文献名称**:Structural Insights into FER Kinase Activation Using Conformation-Specific Antibodies
**作者**:Gomez-Ruiz A, et al.
**摘要**:开发针对FER激酶活化环构象的单克隆抗体,通过冷冻电镜解析其激活状态结构,为设计选择性FER抑制剂提供分子基础。
(注:以上文献信息为模拟生成,实际研究中请通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索真实文献。)
FER antibodies are essential tools in studying the FER tyrosine kinase, a non-receptor protein encoded by the *FER* gene. FER kinase plays diverse roles in cellular signaling, regulating processes like cell adhesion, migration, proliferation, and immune responses. It interacts with cytoskeletal components and receptor tyrosine kinases (e.g., EGFR, MET), influencing pathways such as PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK. Dysregulation of FER is linked to cancer progression, inflammation, and neurodegenerative diseases, making it a potential therapeutic target.
FER antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunoprecipitation (IP) to detect FER expression, localization, and activity in cells or tissues. They help elucidate FER's role in disease mechanisms, such as promoting tumor invasiveness in cancers or modulating immune cell functions. Researchers also employ these antibodies to assess FER inhibition in preclinical studies, particularly in oncology.
Despite their utility, FER antibodies require careful validation due to potential cross-reactivity with related kinases (e.g., FES). Recent studies highlight FER's context-dependent roles, underscoring the need for precise tools to dissect its functions. Overall, FER antibodies remain pivotal in advancing our understanding of FER biology and its implications in human health and disease.
×