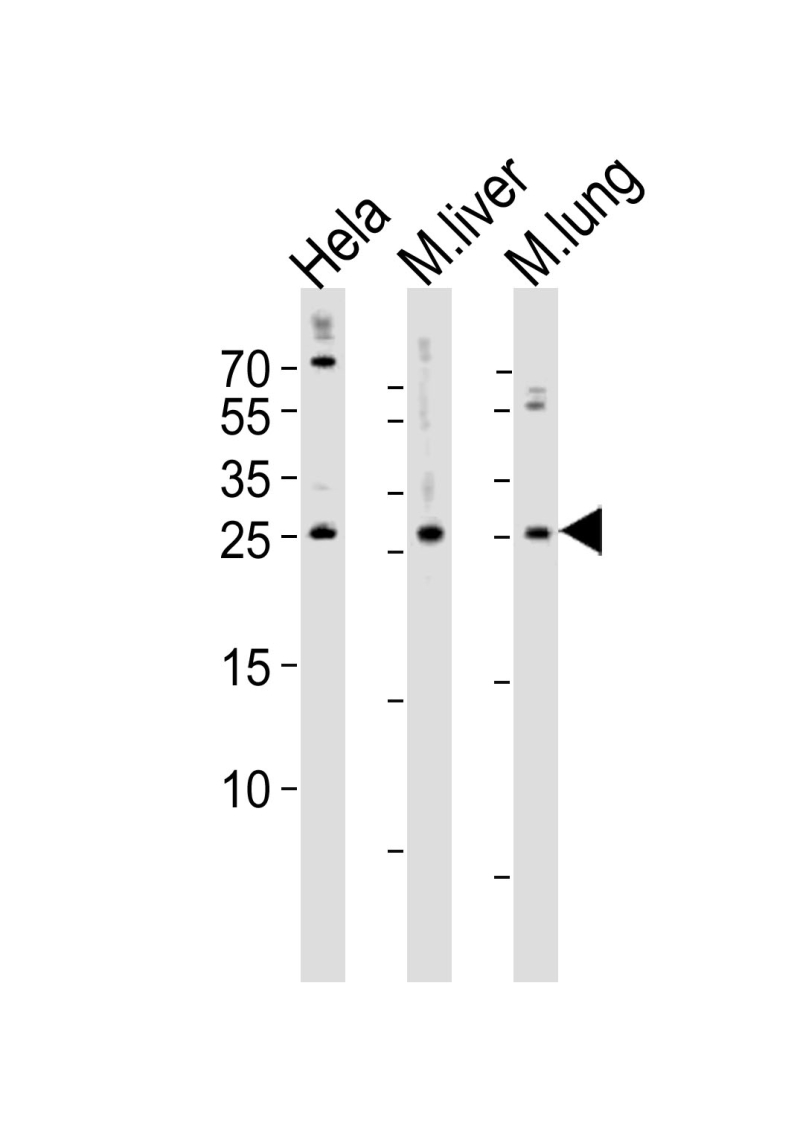
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
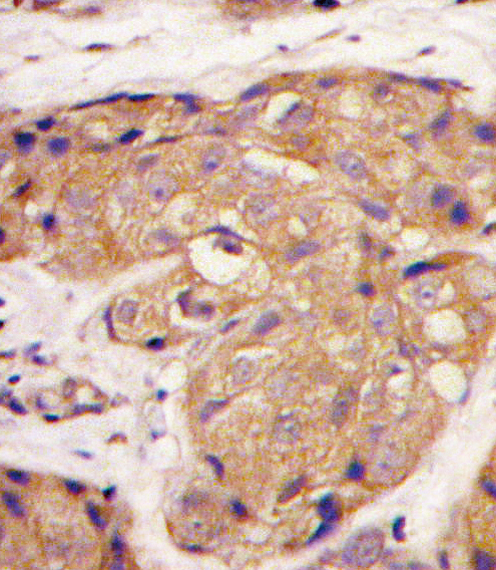
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Sclerostin, SOST |
| Entrez GeneID | 50964 |
| WB Predicted band size | 24.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This SOST antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 12-42 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human SOST. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇与SOST(N-terminal)抗体相关的文献摘要概览:
---
1. **标题**: *Monoclonal Antibodies Targeting the Sclerostin N-Terminal Domain Increase Bone Formation in Vivo*
**作者**: Li X, et al.
**摘要**: 研究开发了针对sclerostin蛋白N端表位的单克隆抗体,验证其在骨质疏松小鼠模型中促进骨形成和骨密度增加的机制,证明其通过阻断Wnt信号通路抑制发挥作用。
---
2. **标题**: *Characterization of a Novel Anti-SOST Antibody for Immunohistochemical Detection in Osteolytic Lesions*
**作者**: van Dinther M, et al.
**摘要**: 报道了一种高特异性抗SOST N端抗体,优化了其在石蜡包埋组织中的免疫组化应用,成功用于骨肉瘤和转移性骨病变中sclerostin表达的定位分析。
---
3. **标题**: *Epitope Mapping of Sclerostin Antibodies Reveals Dual Targeting of N-Terminal and Loop Regions for Enhanced Neutralization*
**作者**: Padhi D, et al.
**摘要**: 通过表位作图技术解析了多种抗SOST抗体的结合区域,发现靶向N端和loop区的双表位抗体在体外和体内模型中展现出更强的sclerostin中和能力。
---
4. **标题**: *Development of a SOST-N-Terminal ELISA for Monitoring Bone Turnover Biomarkers*
**作者**: Drake MT, et al.
**摘要**: 利用抗SOST N端抗体建立了一种新型ELISA检测方法,用于定量血清中sclerostin水平,验证其在代谢性骨病临床样本中的诊断价值。
---
以上文献均聚焦于SOST蛋白N端抗体的开发、应用及机制研究,涉及治疗潜力、检测技术优化及表位功能分析等领域。如需具体DOI或期刊信息,可进一步补充关键词检索。
The SOST (N-term) antibody is a crucial tool in studying sclerostin, a protein encoded by the SOST gene and primarily expressed by osteocytes. Sclerostin acts as a negative regulator of bone formation by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, which is essential for osteoblast differentiation and activity. By binding to low-density lipoprotein receptor-related proteins (LRP5/6) on osteoblasts, sclerostin disrupts Wnt signaling, reducing bone formation and promoting bone resorption. This mechanism links SOST mutations to skeletal disorders like sclerosteosis and van Buchem disease, characterized by excessive bone growth.
The N-terminal region of sclerostin is critical for its biological activity, particularly in mediating interactions with LRP5/6 receptors. Antibodies targeting the N-terminal epitope (e.g., SOST N-term antibodies) are widely used in research to detect sclerostin expression, assess its localization, or block its function in vitro and in vivo. Such antibodies have applications in studying bone metabolism, osteoporosis, and skeletal development. They also underpin therapeutic development, as anti-sclerostin monoclonal antibodies (e.g., romosozumab) mimic N-term-targeting effects to enhance bone formation, now approved for osteoporosis treatment. The SOST N-term antibody’s specificity makes it valuable for elucidating sclerostin’s role in health and disease.
×