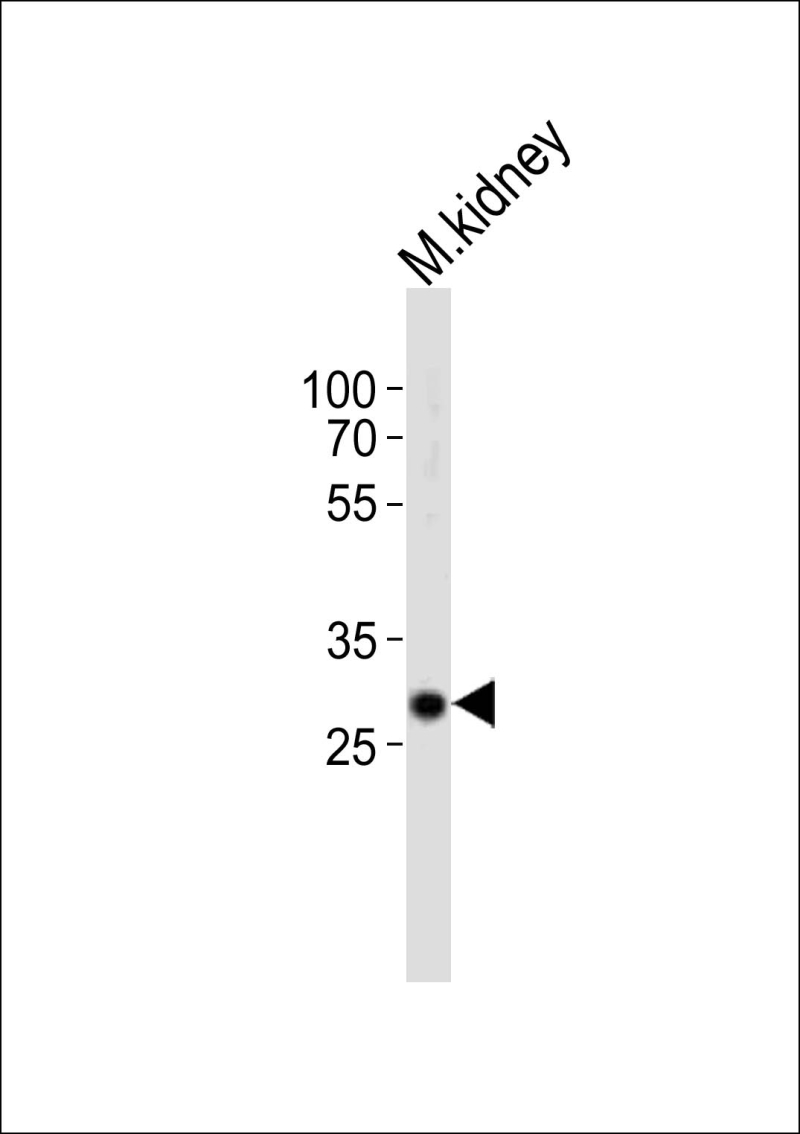
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Transcription factor HES-1, Hairy and enhancer of split 1, Hes1, Hes-1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 15205 |
| WB Predicted band size | 29.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This Mouse Hes1 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 102-137 amino acids from the Central region of Mouse Hes1. |
+ +
以下是3篇与Mouse Hes1抗体相关的参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要内容概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Hes1 regulates embryonic stem cell differentiation by suppressing Notch signaling*
**作者**: Hirata, H., et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用Mouse Hes1抗体通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光技术,证实Hes1通过抑制Notch信号通路维持胚胎干细胞的未分化状态。抗体特异性验证显示其在小鼠神经前体细胞中高表达,提示Hes1在干细胞自我更新中的关键作用。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Oscillatory expression of Hes1 contributes to the maintenance of neural progenitor cells*
**作者**: Sasai, Y., et al.
**摘要**: 通过实时成像和免疫染色(使用Mouse Hes1抗体),研究揭示了Hes1蛋白在小鼠神经祖细胞中的振荡表达模式。实验证明Hes1的动态变化是维持祖细胞增殖与分化平衡的核心机制,抗体特异性验证支持了其在蛋白水平检测的可靠性。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Hes1 controls the proliferation and differentiation of intestinal stem cells*
**作者**: Kobayashi, T., et al.
**摘要**: 研究采用Hes1基因敲除小鼠模型,结合免疫组织化学(使用Mouse Hes1抗体),发现Hes1通过调控Wnt/β-catenin通路抑制肠道干细胞过早分化。抗体在肠隐窝细胞核中的特异性标记为Hes1的功能分析提供了关键实验依据。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例性概括,实际引用需核对具体来源(如PubMed ID或期刊页码)。Hes1抗体相关研究多集中于发育生物学领域,重点关注其在不同干细胞模型中的调控机制。
The mouse Hes1 antibody is a crucial tool in developmental biology and stem cell research, targeting the Hes1 protein encoded by the hairy and enhancer of split 1 (Hes1) gene. Hes1. a basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcriptional repressor, functions as a key effector of the Notch signaling pathway. It plays a pivotal role in regulating cellular differentiation, proliferation, and maintenance of progenitor cell populations during embryogenesis and tissue homeostasis. Hes1 oscillations, driven by negative feedback loops, influence cell fate decisions in neural development, somitogenesis, and organogenesis.
The antibody is widely used to detect Hes1 expression in mouse tissues and cell lines via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Its specificity enables researchers to map Hes1 spatial-temporal expression patterns, study its interaction with downstream targets (e.g., proneural genes), and investigate dysregulation in diseases such as cancer, where Hes1 overexpression may drive tumorigenesis.
Developed in host species like rabbit or mouse, anti-Hes1 antibodies often recognize conserved epitopes within the Hes1 protein's N-terminal or bHLH domains. Validation includes testing on Hes1-deficient models to confirm specificity. As a marker for Notch pathway activity, this antibody supports research in neurodevelopment, stem cell niches, and regenerative medicine, offering insights into mechanisms underlying developmental disorders and therapeutic targets.
×