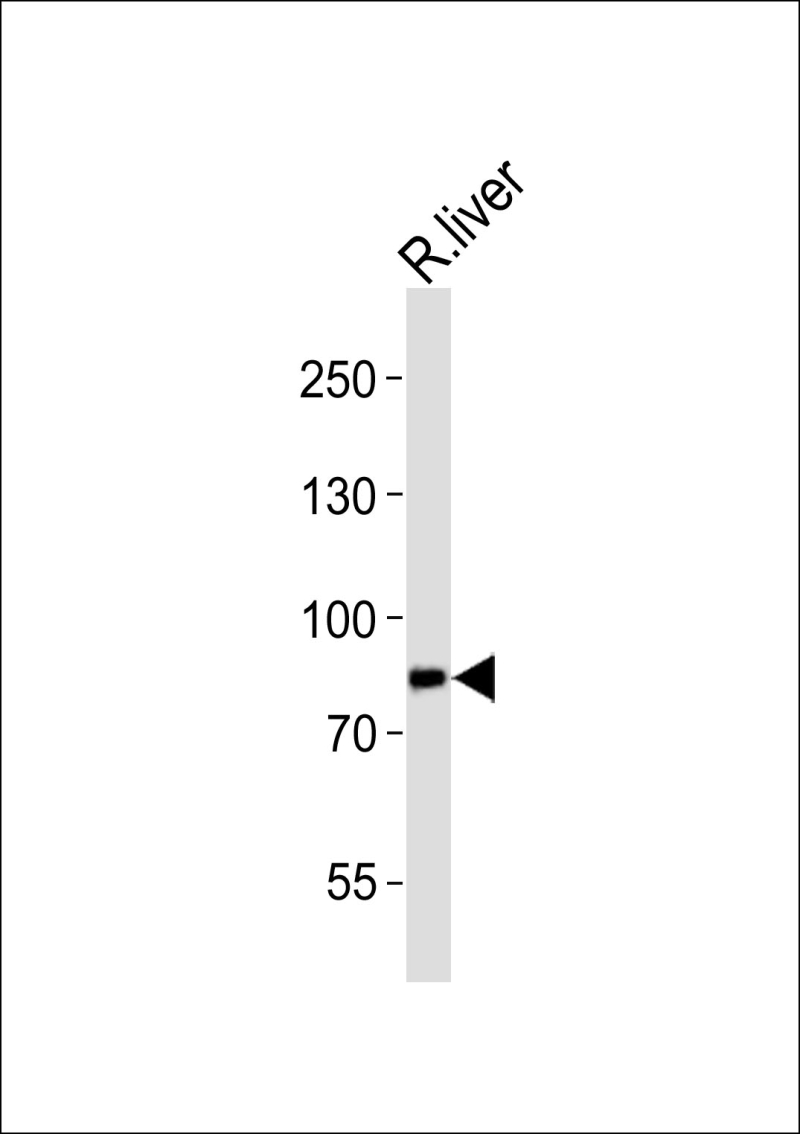
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Insulin receptor, IR, CD220, Insulin receptor subunit alpha, Insulin receptor subunit beta, INSR |
| Entrez GeneID | 3643 |
| WB Predicted band size | 156.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This INSR antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 1362-1395 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human INSR. |
+ +
以下是关于INSR(胰岛素受体)抗体的3篇代表性文献概览:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Clinical course of the syndrome of autoantibodies to the insulin receptor"*
**作者**:Arioglu, E. 等(2001)
**摘要**:该研究分析了B型胰岛素抵抗症患者的临床特征,发现INSR自身抗体会阻断胰岛素信号通路,导致严重高血糖或低血糖。研究强调了免疫抑制治疗(如利妥昔单抗)对部分患者的有效性。
---
2. **文献名称**:*"Antibodies against the insulin receptor in a patient with insulin-resistant diabetes"*
**作者**:Kadowaki, T. 等(1988)
**摘要**:通过Scatchard分析,研究发现患者体内的INSR抗体能竞争性抑制胰岛素与受体的结合,揭示了抗体通过阻断受体功能导致胰岛素抵抗的分子机制。
---
3. **文献名称**:*"Rituximab for the treatment of type B insulin resistance: A case report and literature review"*
**作者**:Page-Wilson, G. 等(2016)
**摘要**:报道一例B型胰岛素抵抗患者使用抗CD20单抗(利妥昔单抗)治疗后,INSR抗体滴度下降且血糖改善,提示B细胞靶向治疗可能清除自身抗体产生细胞。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar核实标题、作者及具体内容。如需实验技术类文献(如单克隆抗体制备),可补充相关研究。
The insulin receptor (INSR) is a transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor critical for regulating glucose homeostasis, lipid metabolism, and cellular growth. Composed of two extracellular α-subunits and two transmembrane β-subunits linked by disulfide bonds, INSR binds insulin to activate downstream signaling pathways, including PI3K-AKT and MAPK, which mediate metabolic and mitogenic responses, respectively. Dysregulation of INSR signaling is associated with metabolic disorders such as type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, and rare syndromes like Rabson-Mendenhall syndrome.
INSR antibodies are specialized immunoglobulins targeting the receptor. Autoantibodies against INSR, found in conditions like type B insulin resistance or autoimmune hypoglycemia, can either block insulin binding (antagonistic) or mimic insulin action (agonistic), leading to severe metabolic disturbances. In research, anti-INSR antibodies are tools to study receptor structure, function, and insulin signaling mechanisms. Therapeutic monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) targeting INSR are under exploration for diabetes and cancer, as aberrant INSR signaling is linked to tumor proliferation. However, challenges include balancing specificity to avoid off-target effects and ensuring clinical efficacy. Detection of INSR antibodies in clinical settings aids in diagnosing autoimmune insulin resistance, guiding immunosuppressive therapies. Overall, INSR antibodies hold dual significance as pathogenic agents and biomedical tools, reflecting their complex roles in health and disease.
×