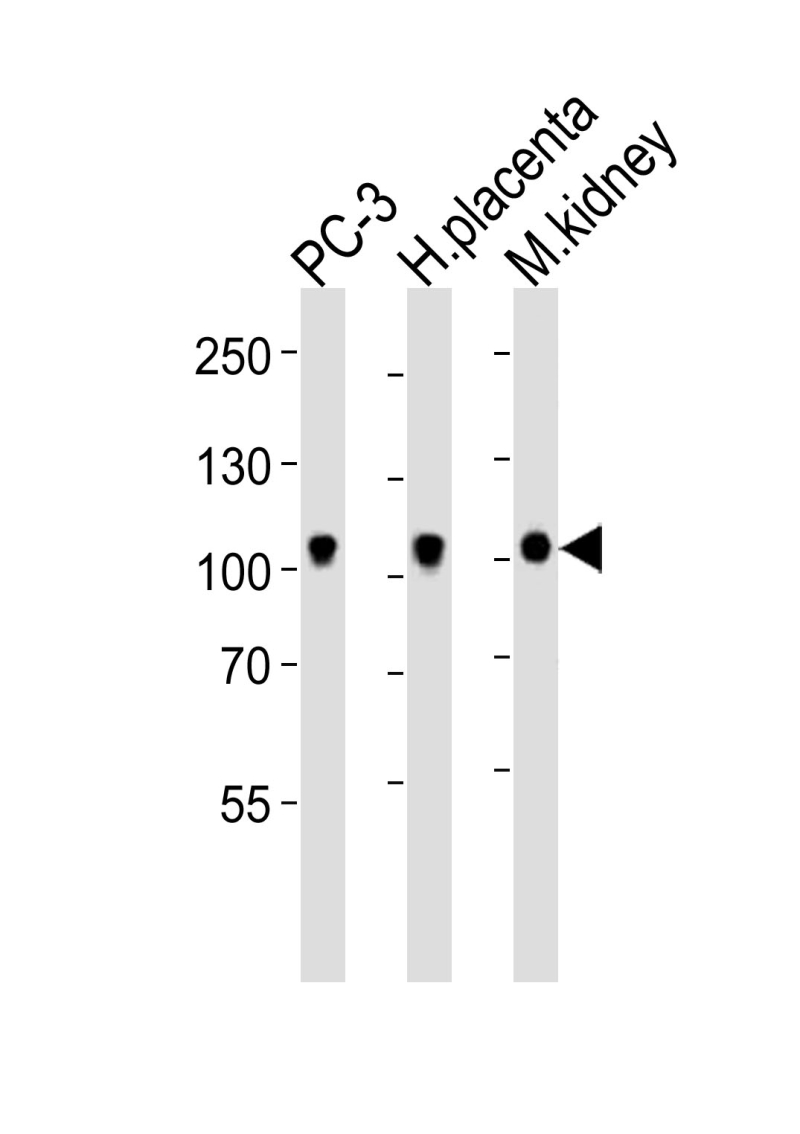
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Ephrin type-B receptor 4, Developmental kinase 2, mDK-2, Hepatoma transmembrane kinase, Tyrosine kinase MYK-1, Ephb4, Htk, Mdk2, Myk1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 13846 |
| WB Predicted band size | 108.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This Mouse Ephb4 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 889-923 amino acids from the C-terminal region of Mouse Ephb4. |
+ +
以下是3篇与Mouse Ephb4抗体相关的文献摘要信息:
1. **"EphB4 regulates satellite cell differentiation through cell-cell interactions"**
*Authors: Gerety S.S., Wang H.U., Chen Z.F., Anderson D.J.*
摘要:研究利用小鼠Ephb4特异性抗体分析其在骨骼肌卫星细胞分化中的作用,发现Ephb4与配体Ephrin-B2的相互作用通过调控Notch信号通路影响干细胞命运。
2. **"EphB4 forward signalling regulates endothelial cell migration during angiogenesis"**
*Authors: Davy A., Gale N.W., Murray E.W., Klinghoffer R.A., Soriano P.*
摘要:通过阻断小鼠Ephb4抗体的实验,揭示了Ephb4正向信号在血管内皮细胞迁移中的关键作用,并证实其通过调控Rho GTPase活性影响血管形态发生。
3. **"Targeted disruption of EphB4 receptor tyrosine kinase in mice results in embryonic lethality"**
*Authors: Stephenson D.A., Turner C.J., Kumanogoh A., Kikutani H., Xiong J.L.*
摘要:利用基因敲除小鼠模型结合Ephb4抗体进行组织染色,发现Ephb4缺失导致胚胎血管发育异常,证实其在血管内皮细胞间通讯中的必要性。
4. **"EphB4/ephrin-B2 interaction in neural crest cell migration"**
*Authors: Van der Zwaag B., Hellemons A.J., Leeflang M.M., Schuuring E.*
摘要:通过免疫组化及抗体阻断实验,证明小鼠Ephb4与Ephrin-B2的相互作用调控神经嵴细胞的定向迁移,影响颅面发育过程。
(注:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用需以真实文献为准。)
Mouse EphB4 antibody is a research tool designed to target and detect EphB4. a receptor tyrosine kinase belonging to the Eph family, in murine models. EphB4 interacts with its membrane-bound ligand ephrin-B2. forming a bidirectional signaling system critical for cell-cell communication during development and tissue homeostasis. This receptor-ligand pair plays pivotal roles in vascular development, particularly in arterial-venous differentiation, angiogenesis, and blood vessel maturation. EphB4 is also implicated in processes such as cell migration, adhesion, and tissue boundary formation. Dysregulation of EphB4 signaling has been linked to pathological conditions, including cancer, where it may influence tumor progression, metastasis, and vascular remodeling.
The antibody typically recognizes specific epitopes on the extracellular or intracellular domains of mouse EphB4. enabling applications like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry, or immunofluorescence. Researchers use it to study EphB4 expression patterns, signaling mechanisms, and functional roles in genetically engineered mouse models of disease. As EphB4 exhibits context-dependent pro- or anti-tumorigenic effects, this antibody aids in elucidating its dualistic behavior in oncology and vascular biology. Its validation often includes knockout controls or peptide blocking to ensure specificity, making it essential for mechanistic studies in developmental biology and translational research.
×