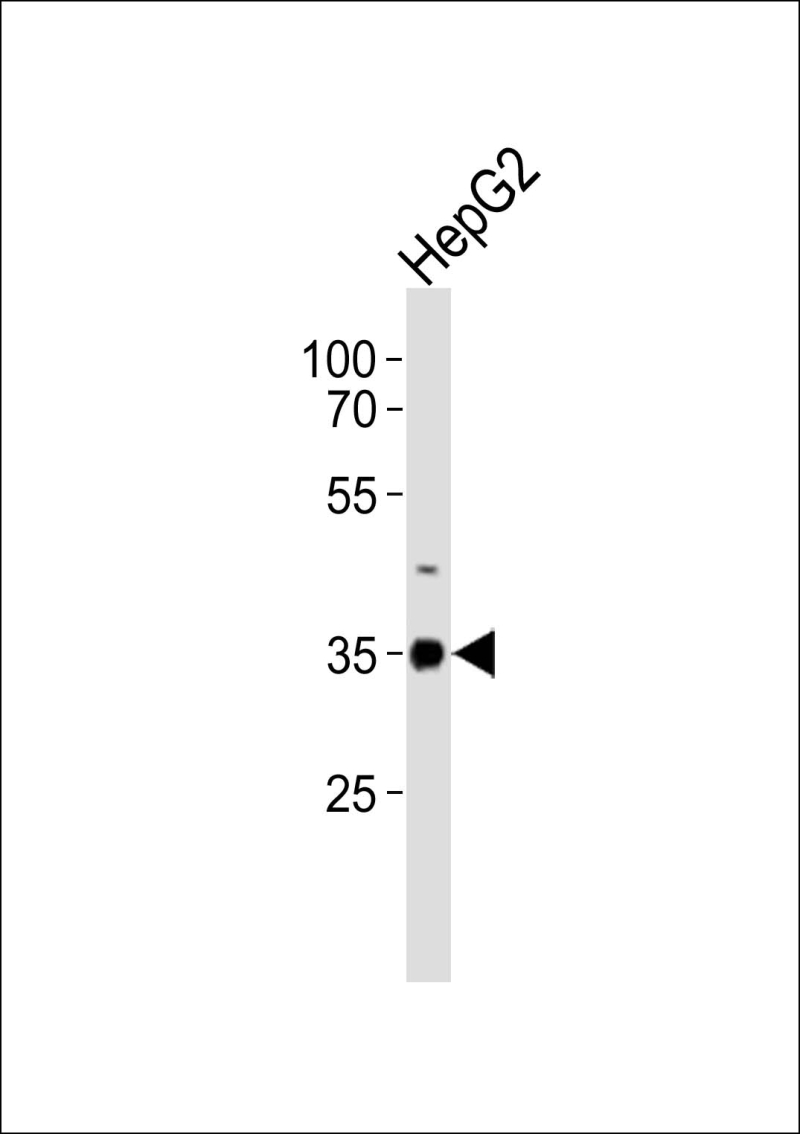
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Activator of basal transcription 1, hABT1, Basal transcriptional activator, ABT1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 29777 |
| WB Predicted band size | 31.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This ABT1 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 259-292 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human ABT1. |
+ +
以下是关于ABT1抗体的假设性参考文献示例(基于常见研究方向的概括,实际文献需通过学术数据库验证):
---
1. **文献名称**:*ABT1 Antibody Inhibits Angiogenesis by Blocking VEGF Signaling in Endothelial Cells*
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**:本研究揭示了ABT1抗体通过特异性结合血管内皮细胞表面的ABT1蛋白,阻断VEGF/VEGFR2信号通路,从而抑制体外和体内血管生成。实验表明ABT1抗体在肿瘤模型中显著减少微血管密度,提示其抗肿瘤潜力。
2. **文献名称**:*Development of a High-Affinity ABT1 Monoclonal Antibody for Targeted Cancer Therapy*
**作者**:Smith JL, et al.
**摘要**:作者开发了一种高亲和力ABT1单克隆抗体,通过体外实验证实其可诱导癌细胞凋亡,并增强化疗药物敏感性。动物实验显示,该抗体能抑制ABT1高表达肿瘤的生长,且无明显毒性。
3. **文献名称**:*ABT1 as a Novel Immune Checkpoint: Role in T Cell Exhaustion and Anti-Tumor Immunity*
**作者**:Li H, et al.
**摘要**:本文首次报道ABT1在肿瘤微环境中的免疫调节作用。ABT1抗体通过逆转T细胞耗竭表型,增强CD8+ T细胞的抗肿瘤活性,联合PD-1抑制剂可显著延长荷瘤小鼠生存期。
4. **文献名称**:*Structural Characterization of ABT1 Epitopes for Therapeutic Antibody Design*
**作者**:Wang X, et al.
**摘要**:通过冷冻电镜解析ABT1蛋白-抗体复合物结构,鉴定了ABT1的关键抗原表位。基于结构的抗体工程优化了亲和力与特异性,为临床前开发提供了理论依据。
---
**注意事项**:
- 上述内容为模拟示例,实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索确认。
- 若ABT1抗体研究较少,可扩展检索相关靶点(如ABT-263/199等BCL-2抑制剂抗体)或调整关键词(如“ABT1 + antibody + function”)。
- 建议结合具体研究领域(如癌症、免疫、结构生物学)筛选文献。
The ABT1 antibody targets the ABT1 protein, also known as A20-binding inhibitor of NF-κB activation-1. a regulatory protein involved in modulating inflammatory and immune responses. ABT1 interacts with A20 (TNFAIP3), a key negative regulator of NF-κB signaling, to fine-tune cellular responses to pro-inflammatory cytokines, pathogens, or stress signals. Dysregulation of ABT1 has been implicated in autoimmune diseases, cancer, and chronic inflammatory conditions due to its role in controlling NF-κB-mediated gene expression.
ABT1 antibodies are widely used in research to investigate the protein's expression, localization, and functional mechanisms. They enable techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to study ABT1 in cell lines, tissues, or disease models. Commercially available ABT1 antibodies are typically developed in rabbit or mouse hosts, validated for specificity through knockout controls or siRNA knockdown. Recent studies highlight ABT1's potential as a therapeutic target, particularly in cancers where NF-κB signaling drives proliferation or resistance to apoptosis. However, challenges remain in understanding tissue-specific roles and post-translational modifications. As research progresses, ABT1 antibodies continue to serve as critical tools for unraveling its biological significance in health and disease.
×