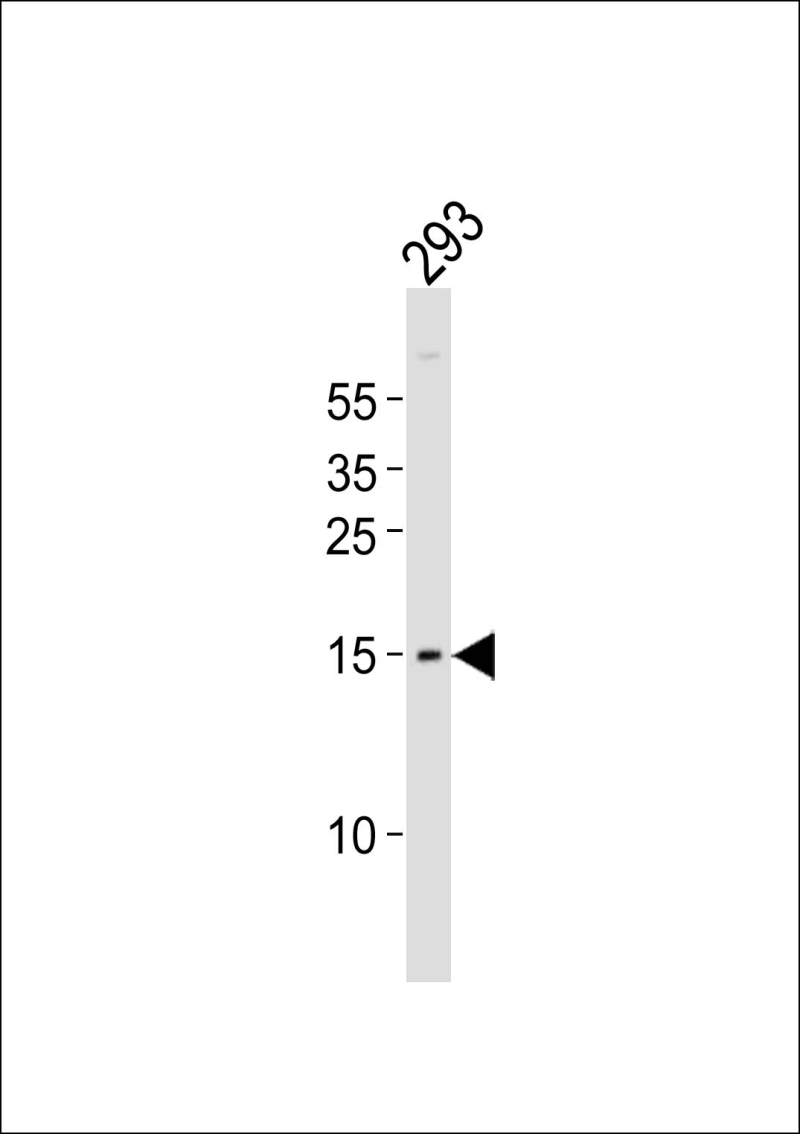
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Basic leucine zipper transcriptional factor ATF-like, B-cell-activating transcription factor, B-ATF, SF-HT-activated gene 2 protein, SFA-2, BATF |
| Entrez GeneID | 10538 |
| WB Predicted band size | 14.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This BATF antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 7-35 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human BATF. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于BATF (N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要内容概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"BATF regulates Th17 differentiation through cooperation with IRF4"*
**作者**:Murphy, T.L., et al. (2013)
**摘要**:该研究利用BATF (N-term)抗体进行ChIP-seq实验,揭示BATF与IRF4在Th17细胞分化中的协同作用,证明其通过结合靶基因启动子区域调控炎症反应。
2. **文献名称**:*"BATF acts as an essential regulator of IL-25-responsive ILC2s in allergic lung inflammation"*
**作者**:Li, P., et al. (2018)
**摘要**:通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术使用BATF N端抗体,发现BATF在ILC2细胞中高表达,并调控过敏性肺部炎症中IL-25信号通路的关键基因表达。
3. **文献名称**:*"Transcriptional regulation of follicular T-helper (Tfh) cells by BATF and IRF4"*
**作者**:Glasmacher, E., et al. (2016)
**摘要**:研究采用BATF (N-term)抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,证实BATF与IRF4共同结合DNA复合物,调控滤泡辅助T细胞(Tfh)的分化和功能。
---
以上文献均聚焦于BATF蛋白N端结构域的功能研究,涉及免疫细胞分化及疾病机制,实验方法中明确使用了靶向N端的特异性抗体。如需具体实验细节,建议查阅原文方法部分。
The BATF (Basic Leucine Zipper ATF-Like Transcription Factor) protein, a member of the AP-1 transcription factor family, plays a critical role in immune regulation, cellular differentiation, and oncogenesis. The BATF (N-term) antibody specifically targets the N-terminal region of the BATF protein, which is essential for its dimerization and DNA-binding activity. BATF forms heterodimers with other AP-1 family members (e.g., Jun proteins) or interacts with IRF4 to regulate gene expression in immune cells, particularly T lymphocytes, B cells, and dendritic cells. It is involved in Th17 cell differentiation, antibody class switching, and tumor microenvironment modulation.
This antibody is widely used in research to investigate BATF's functional mechanisms in diseases such as autoimmune disorders, infections, and cancers. By detecting BATF expression via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, or flow cytometry, researchers can explore its role in transcriptional networks and signaling pathways. Studies have linked BATF overexpression to poor prognosis in certain cancers, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target. The N-terminal specificity of the antibody ensures recognition of full-length BATF, avoiding cross-reactivity with truncated isoforms. Its applications extend to preclinical models, aiding in the development of strategies to modulate immune responses or inhibit oncogenic pathways involving BATF.
×