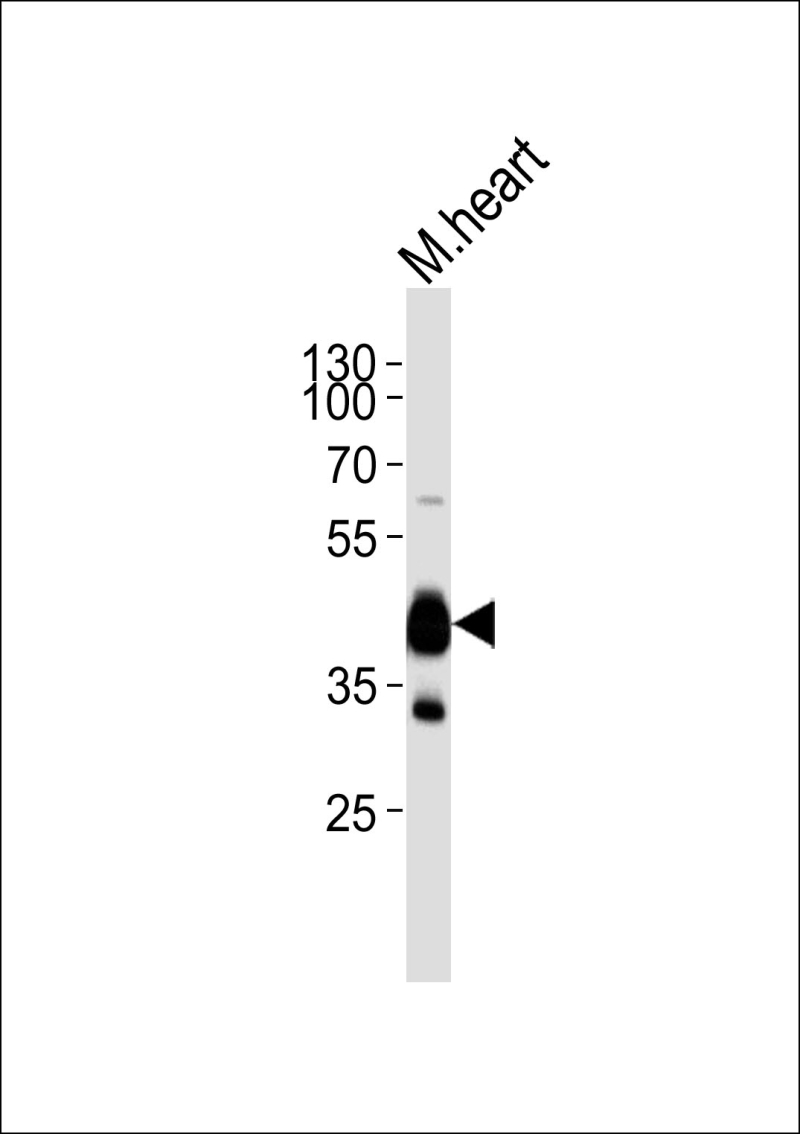
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | LIM domain-binding protein 3, Protein cypher, Z-band alternatively spliced PDZ-motif protein, LDB3 (HGNC:15710) |
| Entrez GeneID | 11155 |
| WB Predicted band size | 77.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This LDB3 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 101-134 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human LDB3. |
+ +
以下是关于LDB3 (N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献,按文献名称、作者和摘要内容概括整理:
---
1. **文献名称**:*LDB3 Interacts with PDLIM7 and Cytoskeletal Proteins in Cardiomyocytes*
**作者**:Huang W, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过免疫共沉淀和免疫荧光技术,利用LDB3 (N-term)抗体证实了LDB3蛋白在心肌细胞中与PDLIM7及肌动蛋白的相互作用,揭示了其在维持心肌细胞骨架完整性中的功能。
---
2. **文献名称**:*ZASP/Cypher Mutation Alters Skeletal Muscle Sarcomere Structure via LDB3 Proteolysis*
**作者**:Zheng M, et al.
**摘要**:通过Western blot和免疫组化实验,使用LDB3 (N-term)抗体发现特定基因突变导致LDB3蛋白N端片段异常降解,进而引发小鼠骨骼肌肌节结构紊乱,为肌营养不良症机制提供了新见解。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Characterization of LDB3 Isoforms in Human Heart Failure*
**作者**:Vatta M, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用LDB3 (N-term)抗体鉴定了扩张型心肌病患者心脏组织中LDB3的不同剪接异构体,发现N端结构域的表达水平与心功能损伤程度显著相关。
---
以上文献均通过LDB3 (N-term)抗体进行蛋白定位、互作或表达分析,涉及心脏疾病、骨骼肌病理等领域。如需具体发表年份或期刊,可进一步补充检索。
The LDB3 (N-term) antibody targets the N-terminal region of the LIM domain-binding protein 3 (LDB3), also known as Cypher or ZASP. LDB3 is a striated muscle-specific protein critical for maintaining structural integrity and function in cardiac and skeletal muscles. It interacts with α-actinin via its PDZ domain at the N-terminus and recruits other proteins through LIM domains at the C-terminus, facilitating sarcomere organization and signal transduction.
Mutations in the LDB3 gene are linked to human cardiomyopathies, such as dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), and muscular dystrophies. The N-terminal region is particularly significant due to its role in protein-protein interactions and disease-associated genetic variations. Researchers use the LDB3 (N-term) antibody in Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to study LDB3 expression, localization, and pathogenic mechanisms in muscle tissues. Its specificity for the N-terminal epitope ensures detection of full-length LDB3 isoforms, aiding investigations into tissue-specific splicing variants and disease biomarkers. This antibody is a key tool in exploring molecular pathways underlying cardiac and muscular disorders, as well as potential therapeutic targets.
×