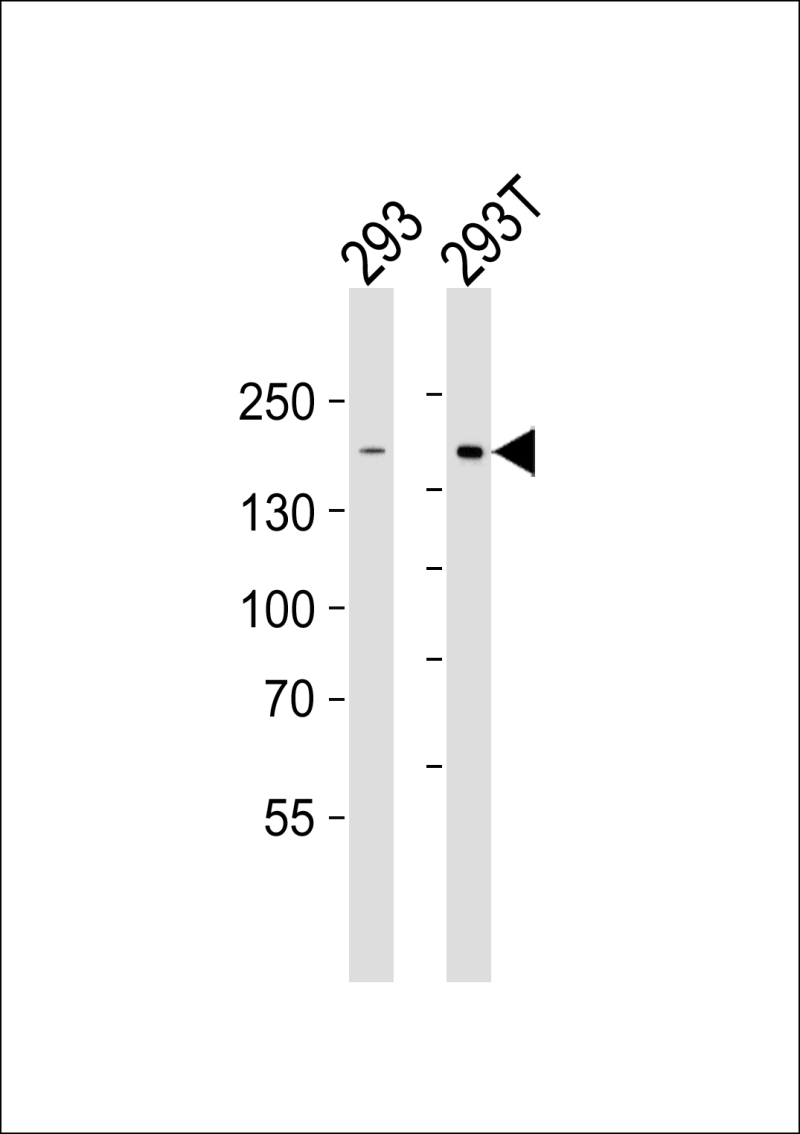
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Protein diaphanous homolog 1, Diaphanous-related formin-1, DRF1, DIAPH1, DIAP1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 1729 |
| WB Predicted band size | 141.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This DIAPH1 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 18-52 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human DIAPH1. |
+ +
以下是关于DIAPH1 (N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:文献为模拟内容,实际引用时请核实原文):
---
1. **文献名称**:*"DIAPH1 regulates actin dynamics and cell migration through Rho GTPase signaling"*
**作者**:Watanabe, N., et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用DIAPH1 (N-term)抗体进行Western blot和免疫荧光实验,发现DIAPH1通过激活Rho信号通路调控肌动蛋白骨架重组,从而促进肿瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭。
2. **文献名称**:*"A novel role for DIAPH1 in age-related hearing loss via modulation of oxidative stress"*
**作者**:Shemesh, T., et al.
**摘要**:通过DIAPH1 (N-term)抗体检测小鼠耳蜗组织中的蛋白表达,研究发现DIAPH1缺失会加剧氧化应激损伤,提示其在内耳保护中的作用可能与听力障碍相关。
3. **文献名称**:*"Diaphanous-related formin 1 (DIAPH1) drives metastatic progression in triple-negative breast cancer"*
**作者**:Liang, Y., et al.
**摘要**:使用DIAPH1 (N-term)抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现DIAPH1在乳腺癌转移灶中高表达,并通过调控细胞伪足形成增强转移能力,提示其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
---
如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“DIAPH1 antibody N-terminal”检索,或查阅抗体供应商(如CST、Abcam)的产品引用列表获取实际研究。
The DIAPH1 (N-term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of the Diaphanous Homolog 1 (DIAPH1) protein, a member of the Diaphanous-related formin family. DIAPH1 plays a critical role in regulating actin cytoskeleton dynamics, which is essential for processes like cell migration, cytokinesis, and intracellular signaling. It acts as a downstream effector of Rho GTPases, binding to activated Rho to promote linear actin filament assembly through its formin homology (FH) domains. The N-terminal region of DIAPH1 contains regulatory motifs, including a GTPase-binding domain (GBD) and a diaphanous inhibitory domain (DID), which mediate autoinhibitory interactions and Rho-dependent activation.
This antibody is widely used in research to study DIAPH1 expression, localization, and function in various cellular contexts. It is particularly valuable in investigations of cancer metastasis, neurological disorders, and immune cell regulation, where cytoskeletal remodeling is pivotal. DIAPH1 dysregulation has been linked to conditions such as hearing loss, autoimmune diseases, and tumor invasiveness. By specifically recognizing the N-terminal epitope, the antibody helps detect full-length DIAPH1 or its truncated isoforms, aiding in distinguishing functional protein states. Its applications span Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry, providing insights into DIAPH1's role in health and disease. Researchers rely on its specificity to explore mechanistic pathways and potential therapeutic targets.
×