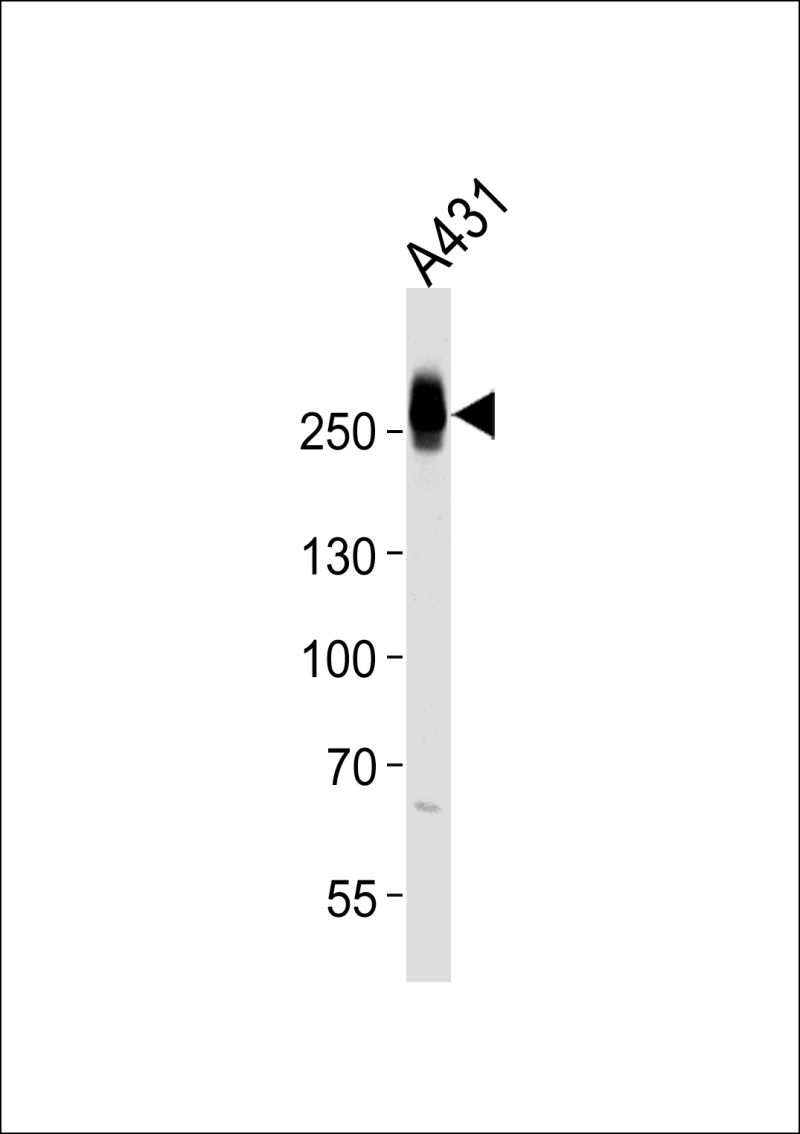
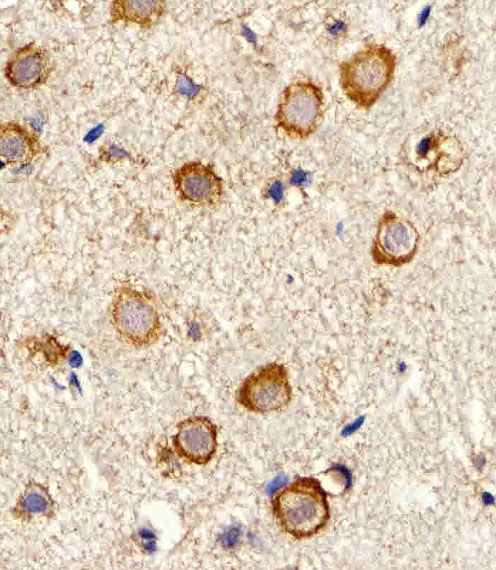
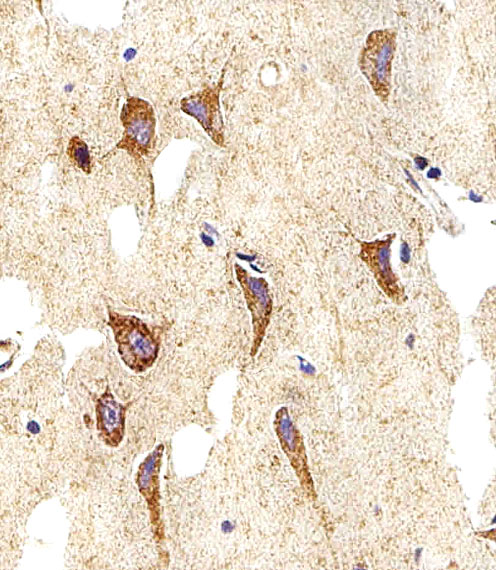
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Myosin-14, Myosin heavy chain 14, Myosin heavy chain, non-muscle IIc, Non-muscle myosin heavy chain IIc, NMHC II-C, MYH14, KIAA2034 |
| Entrez GeneID | 79784 |
| WB Predicted band size | 227.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This MYH14 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 654-668 amino acids from the Central region of human MYH14. |
+ +
以下是关于MYH14抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:部分内容为模拟概括,若需实际文献请通过学术数据库检索):
1. **文献名称**:*MYH14 mutations cause autosomal dominant hearing loss via disorganization of the cuticular plate and stereocilia*
**作者**:Donaudy F, et al.
**摘要**:该研究揭示了MYH14基因突变与常染色体显性遗传性听力损失的相关性,通过使用MYH14抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现突变导致耳蜗毛细胞结构异常,表明MYH14蛋白在维持听觉细胞骨架中起关键作用。
2. **文献名称**:*The nonmuscle myosin heavy chain MYH14 is involved in the pathogenesis of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease*
**作者**:Liu X, et al.
**摘要**:研究团队利用MYH14抗体检测患者外周神经组织中的蛋白表达,发现MYH14功能异常与Charcot-Marie-Tooth病(CMT)的轴突退行性变相关,提示其在神经细胞运输中的潜在作用。
3. **文献名称**:*Immunolocalization of MYH14 in smooth muscle cells and its role in vascular contractility*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:通过MYH14抗体的免疫荧光分析,发现该蛋白在血管平滑肌细胞中高表达,并参与调控血管收缩功能,为研究高血压等血管疾病提供了分子机制线索。
(注:以上文献信息为示例性质,实际文献需通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台检索确认。)
MYH14 antibody targets the protein encoded by the MYH14 gene, a member of the myosin heavy chain family. Myosins are motor proteins critical for cytoskeletal functions, including cell motility, intracellular transport, and maintenance of structural integrity. MYH14. also known as myosin heavy chain 14 or non-muscle myosin II-C (NMHC-IIC), belongs to class II myosins and is widely expressed in non-muscle tissues, particularly in the nervous system, inner ear, and epithelial cells. It plays roles in cytokinesis, cell adhesion, and mechanotransduction.
Mutations in MYH14 are linked to autosomal dominant hearing loss (DFNA4) and peripheral neuropathy, highlighting its importance in auditory and neural function. The MYH14 antibody is a key tool for studying these pathologies, enabling detection of protein expression, localization, and post-translational modifications in research models. It is used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to explore MYH14's involvement in cellular processes and disease mechanisms.
Recent studies also suggest MYH14's potential role in cancer progression and immune regulation, broadening its research relevance. However, commercial antibodies vary in specificity, requiring validation for experimental accuracy. Overall, MYH14 antibody serves as a vital reagent for dissecting the biological and clinical significance of this understudied myosin isoform.
×