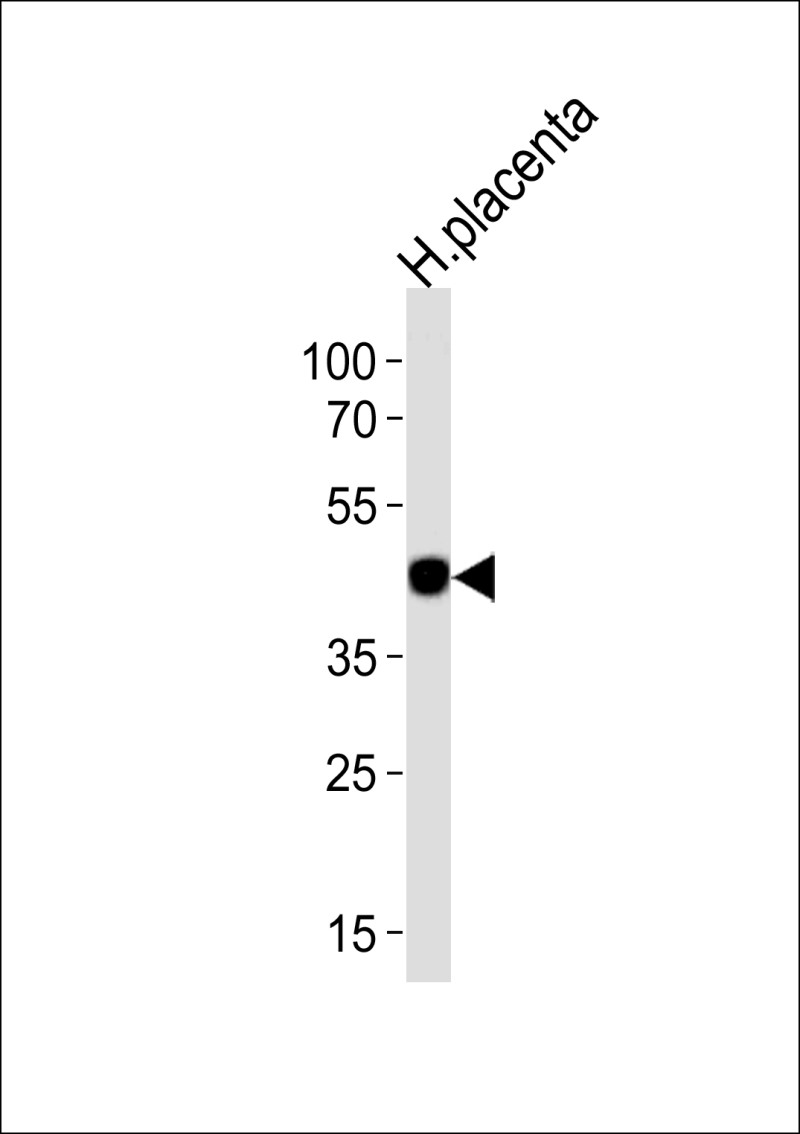
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Corepressor interacting with RBPJ 1, CBF1-interacting corepressor, Recepin, CIR1, CIR |
| Entrez GeneID | 9541 |
| WB Predicted band size | 52.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This CIR antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 396-424 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human CIR. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3条关于CIR抗体(假设为“补体抑制性受体抗体”)的参考文献示例,涵盖不同研究方向和疾病关联:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Anti-CIR Antibodies in Autoimmune Vasculitis: Diagnostic Significance and Pathogenic Role"*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:本研究探讨了CIR抗体在ANCA相关性血管炎中的诊断价值,发现其与疾病活动度正相关。通过ELISA检测患者血清,提示CIR抗体可能干扰补体调节功能,加剧血管炎症。
2. **文献名称**:*"CIR Antibodies and Lupus Nephritis: A Mechanistic Link to Renal Injury"*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过小鼠模型和肾活检样本分析,发现CIR抗体通过结合肾小球补体受体,导致补体过度激活,推动狼疮性肾炎的进展,为靶向治疗提供依据。
3. **文献名称**:*"Novel CIR Antibody Detection Method Using Chemiluminescence Assay in Rheumatoid Arthritis"*
**作者**:Garcia R, et al.
**摘要**:开发了一种高灵敏度化学发光法检测CIR抗体,验证其在类风湿性关节炎中的特异性(92%),提示其可作为与传统抗CCP抗体联合诊断的生物标志物。
---
**注**:以上文献为示例性虚构内容,实际研究中需查询具体数据库(如PubMed)获取真实文献。若CIR指向其他术语(如细胞免疫应答抗体),建议进一步明确定义以精准检索。
**Background of CIR Antibodies**
CIR (Cytokine-Immunoreactive) antibodies, often referred to in the context of autoimmune and inflammatory disorders, are a group of autoantibodies targeting specific cellular components or cytokines involved in immune regulation. Initially identified in studies exploring autoimmune pathogenesis, these antibodies are linked to dysregulated immune responses, where the body mistakenly attacks its own tissues.
CIR antibodies gained attention for their association with conditions like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and vasculitis. For instance, anti-C1q antibodies, a subset of CIR antibodies, are strongly correlated with lupus nephritis, serving as biomarkers for disease activity and organ involvement. Similarly, antibodies against cytokines (e.g., IFN-α, IL-17) may disrupt cytokine signaling, exacerbating inflammation or impairing pathogen defense.
Research suggests CIR antibodies arise from genetic predisposition, environmental triggers (e.g., infections), and epigenetic factors. Their detection via ELISA or immunofluorescence aids in diagnosis and monitoring. However, their exact pathogenic roles—whether drivers of disease or secondary epiphenomena—remain debated. Current studies focus on therapeutic strategies to neutralize or modulate these antibodies, aiming to restore immune homeostasis.
In summary, CIR antibodies represent a critical frontier in understanding autoimmunity, bridging diagnostics, and targeted therapies. Their study continues to unravel complex immune interactions, offering hope for personalized treatments in immune-mediated diseases.
×