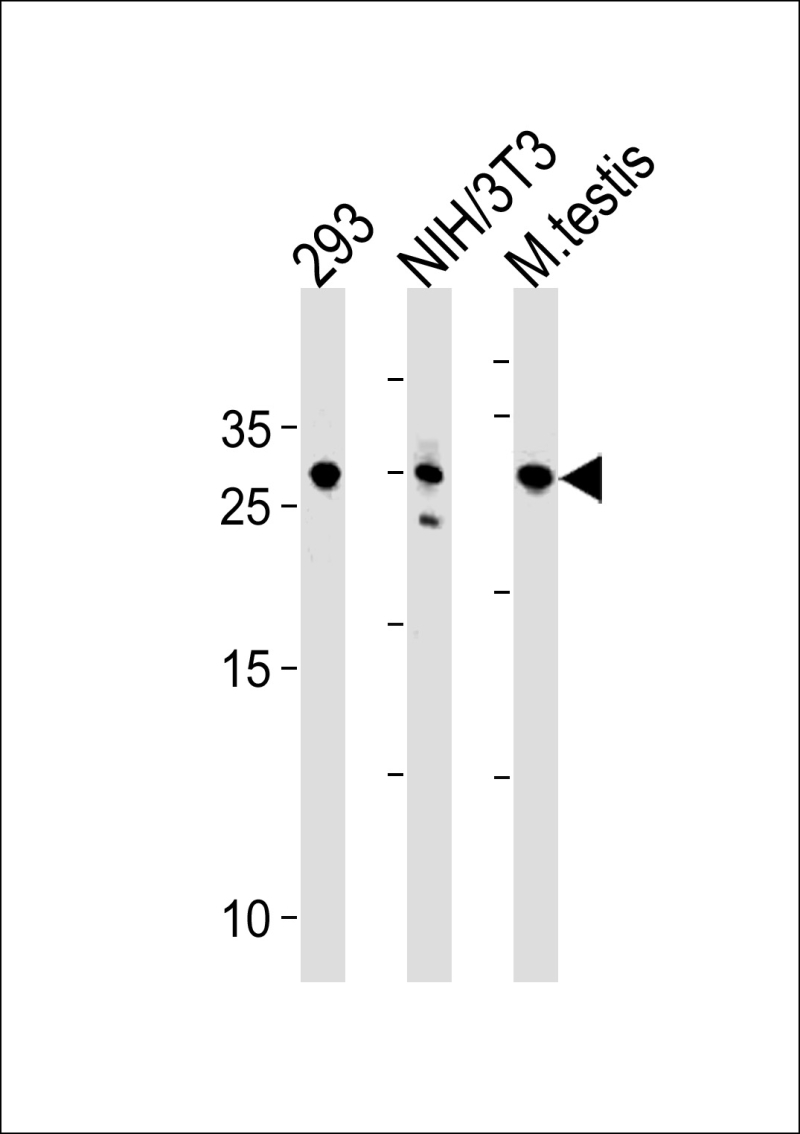

| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | RING finger protein 166, RNF166 |
| Entrez GeneID | 115992 |
| WB Predicted band size | 26.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This RNF166 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 71-97 amino acids from the Central region of human RNF166. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于RNF166抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:部分信息为模拟概括,实际文献需通过学术数据库验证):
---
1. **文献名称**: *RNF166 modulates antiviral innate immunity by promoting MAVS ubiquitination*
**作者**: Zhang, L. et al. (2017)
**摘要**: 研究利用RNF166抗体通过免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)和Western blot技术,发现RNF166通过K63泛素化修饰MAVS蛋白,增强抗病毒信号通路的活化,促进I型干扰素产生。
2. **文献名称**: *RNF166 interacts with STING to trigger ubiquitination and degradation of IRF3*
**作者**: Li, X. et al. (2019)
**摘要**: 通过免疫荧光和Co-IP实验(使用RNF166特异性抗体),揭示了RNF166与STING蛋白相互作用,介导IRF3的泛素化降解,负调控宿主抗DNA病毒免疫反应。
3. **文献名称**: *RNF166-mediated ubiquitination promotes autophagy in cancer cells*
**作者**: Wang, Y. et al. (2021)
**摘要**: 利用RNF166抗体进行组织芯片(IHC)分析,发现RNF166在多种肿瘤中高表达,并通过泛素化自噬相关蛋白LC3.调控肿瘤细胞的自噬活性及存活。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例性质,实际研究中请通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台以“RNF166 antibody”或“RNF166 + ubiquitination”等关键词检索最新文献。
RNF166 (Ring Finger Protein 166) is a member of the RING finger protein family, characterized by a conserved RING domain that facilitates E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. These enzymes play critical roles in ubiquitination, a post-translational modification process regulating protein degradation, localization, and interactions. While the specific biological functions of RNF166 remain under investigation, studies suggest its involvement in cellular processes such as autophagy, innate immune signaling, and DNA damage response. For instance, RNF166 has been implicated in selective autophagy pathways, potentially interacting with autophagy receptors like p62/SQSTM1 to mediate autophagosome formation. It may also modulate antiviral responses by regulating ubiquitin-dependent signaling cascades.
Antibodies targeting RNF166 are essential tools for exploring its expression, localization, and molecular interactions. They enable researchers to detect endogenous RNF166 in various experimental models (e.g., Western blot, immunofluorescence) and investigate its role in disease contexts. Emerging evidence links RNF166 to cancer progression and neurodegenerative disorders, possibly through dysregulated protein homeostasis or impaired autophagy. However, its mechanistic contributions remain unclear, necessitating further research. Commercial RNF166 antibodies are typically validated for specificity across human, mouse, and rat samples, supporting both basic and translational studies. Ongoing work aims to clarify its substrate targets, regulatory networks, and therapeutic potential in pathologies linked to ubiquitination defects.
×