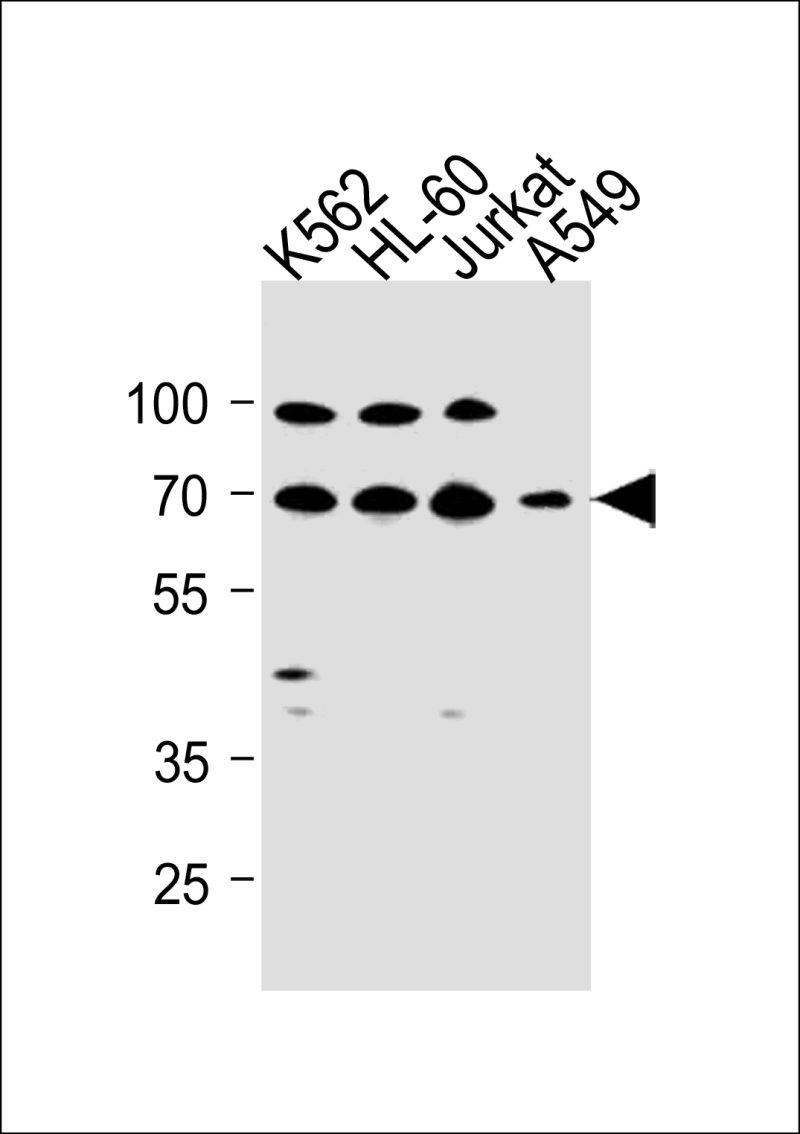
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit theta, GABA(A) receptor subunit theta, GABRQ |
| Entrez GeneID | 55879 |
| WB Predicted band size | 72.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This GABRQ antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 585-613 amino acids of human GABRQ. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于GABRQ抗体的部分文献摘要(注意:部分文献可能更侧重于GABRQ的功能而非直接研究其抗体,因相关研究较为有限):
1. **《GABAA receptor subunits in the human amygdala and hippocampus: Immunohistochemical distribution and clinical implications in epilepsy》**
- **作者**:Loup F. 等(2006)
- **摘要**:研究分析了人脑中GABA-A受体亚基(包括GABRQ)的分布,发现其在边缘系统(如海马和杏仁核)中高表达,可能与癫痫的异常放电相关,但未直接涉及抗体作用。
2. **《Autoimmune encephalitis with anti-GABAA receptor antibodies: A case series》**
- **作者**:Petit-Pedrol M. 等(2018)
- **摘要**:报道了抗GABA-A受体抗体相关的自身免疫性脑炎病例,研究提到部分患者存在针对罕见亚基(如GABRQ)的抗体,表现为难治性癫痫和精神症状。
3. **《Structural and functional characterization of the human GABAA receptor subunit gene GABRQ》**
- **作者**:Garrett K.M. 等(2003)
- **摘要**:首次克隆并分析了人类GABRQ基因的结构和功能,指出该亚基可能影响受体对药物(如苯二氮䓬类)的敏感性,为后续研究抗体作用提供分子基础。
4. **《Novel antibodies in neurological autoimmune diseases: A review on GABAA receptor autoimmunity》**
- **作者**:Dalmau J. 等(2019)
- **摘要**:综述了GABA-A受体自身抗体的研究进展,指出GABRQ等亚基的抗体可能参与罕见神经免疫疾病,但临床表型和检测方法仍需进一步探索。
**备注**:GABRQ抗体的直接研究较少,多数文献集中于受体亚基的功能或广义抗GABA-A受体疾病。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“GABRQ antibodies”或“GABA-A receptor autoimmunity”为关键词检索最新进展。
The GABA-A receptor subunit theta (GABRQ) is a component of the GABA-A receptor, a ligand-gated ion channel mediating the inhibitory effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. GABA-A receptors are pentameric structures typically composed of combinations of α, β, γ, δ, ε, θ, π, or ρ subunits. The GABRQ subunit, part of the ρ subfamily, is less commonly expressed and forms functional receptors either as homopentamers or heteromers with other ρ subunits. It is primarily found in the retina and specific brain regions, contributing to unique pharmacological properties and modulating synaptic inhibition.
Antibodies targeting GABRQ are associated with autoimmune neurological disorders, such as autoimmune encephalitis, where immune-mediated disruption of GABAergic signaling leads to hyperexcitability. Clinical manifestations may include seizures, cognitive deficits, and psychiatric symptoms. Detection of GABRQ antibodies in serum or cerebrospinal fluid aids diagnosis, though their pathogenic role remains under investigation. Research suggests these antibodies may interfere with receptor clustering or GABA binding, impairing inhibitory transmission. Current treatment involves immunotherapy, but further studies are needed to clarify their clinical relevance, epitope targets, and therapeutic implications.
×