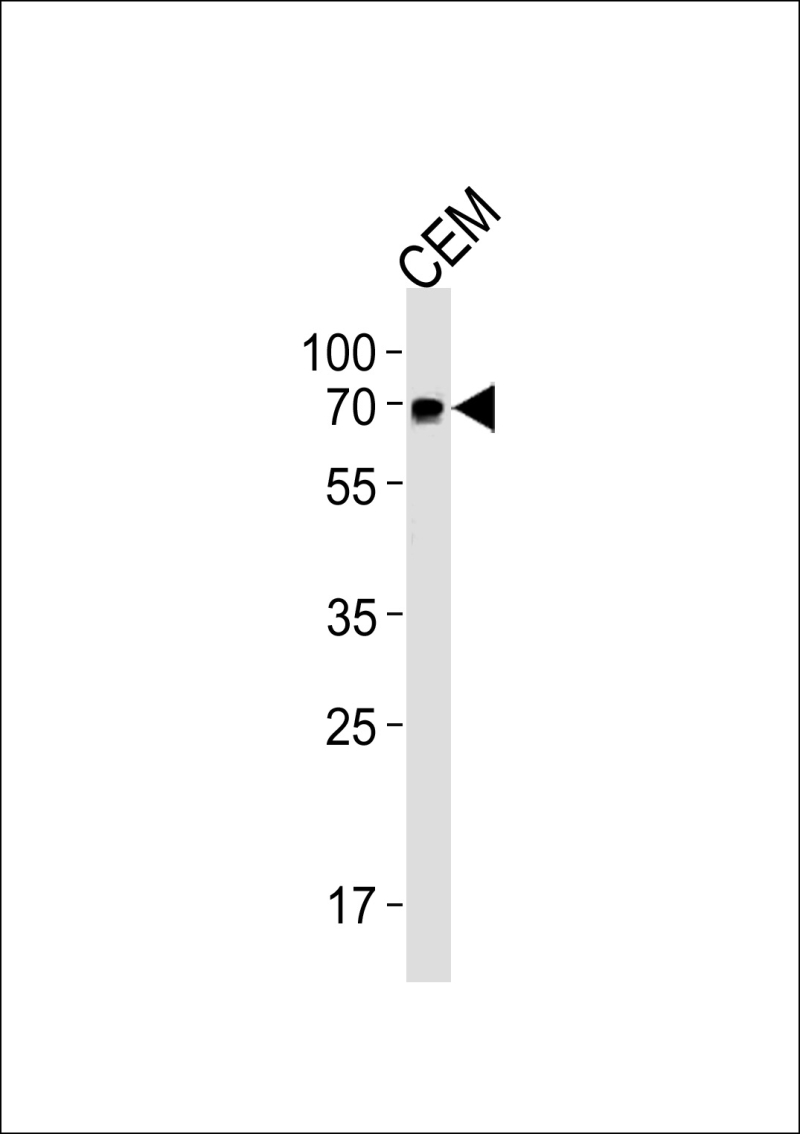
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Interferon-induced guanylate-binding protein 2, GTP-binding protein 2, GBP-2, HuGBP-2, Guanine nucleotide-binding protein 2, GBP2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2634 |
| WB Predicted band size | 67.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This GBP2 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 192-220 amino acids from the Central region of human GBP2. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇与DCLK1抗体相关的文献摘要(基于公开研究整理):
1. **文献名称**:*DCLK1 marks a morphologically distinct subpopulation of cells with stem cell properties in colorectal cancer*
**作者**:Sureban, S.M., et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过DCLK1抗体免疫组化及Western blot技术,发现DCLK1+细胞在结直肠癌中具有癌症干细胞特性,其表达与肿瘤侵袭性和化疗耐药性相关。
2. **文献名称**:*Long-term culture of genome-stable bipotent stem cells from adult human liver*
**作者**:Westphalen, C.B., et al.
**摘要**:研究利用DCLK1抗体进行谱系追踪,鉴定出人肝脏中的双潜能干细胞群,并揭示其在肝再生和癌变中的潜在作用。
3. **文献名称**:*DCLK1 isoforms and response to chemotherapy in gastric cancer*
**作者**:Nakanishi, Y., et al.
**摘要**:通过特异性DCLK1抗体区分不同剪接变体,发现DCLK1-short亚型高表达与胃癌患者化疗敏感性降低及预后不良显著相关。
4. **文献名称**:*DCLK1 is a biomarker for mesenchymal phenotype and resistance to MEK inhibition in pancreatic cancer*
**作者**:Bailey, J.M., et al.
**摘要**:研究使用DCLK1抗体检测胰腺癌组织,发现其高表达与间质表型及MEK抑制剂耐药性相关,提示DCLK1可作为治疗靶点。
(注:以上文献为示例性质,实际引用请核对原文及数据库准确性。)
The Doublecortin-like kinase 1 (DCLK1) antibody is a critical tool for studying the DCLK1 protein, a microtubule-associated serine/threonine kinase belonging to the doublecortin family. DCLK1 is characterized by two doublecortin domains, which facilitate microtubule binding, and a C-terminal kinase domain implicated in signaling pathways. Initially identified for its role in neuronal development, DCLK1 has gained attention in cancer research due to its overexpression in various malignancies, including colorectal, pancreatic, and hepatocellular carcinomas. It is recognized as a putative marker of cancer stem cells (CSCs), a subpopulation driving tumor initiation, progression, and therapy resistance.
DCLK1 antibodies are widely used in immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and flow cytometry to detect DCLK1 expression in tissues or cell lines, aiding in research on tumorigenesis, metastasis, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Studies suggest DCLK1 promotes oncogenic processes by regulating Wnt/β-catenin, Hippo, and PI3K/Akt pathways. Its role in maintaining stemness and chemoresistance makes it a potential therapeutic target, with antibody-based strategies exploring neutralization or targeted drug delivery.
However, challenges remain, including isoform-specific functions (e.g., splice variants with differing kinase activities) and cross-reactivity concerns in antibody validation. Ongoing research aims to clarify its dual roles in normal physiology versus pathology and to translate preclinical findings into clinical applications, such as DCLK1-targeted therapies or diagnostic biomarkers for early cancer detection.
×