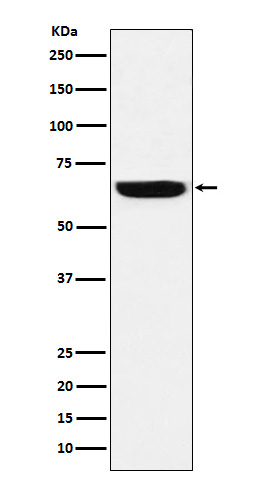
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GBP1; GTP binding protein 1; Guanine nucleotide binding protein 1; Guanylate binding protein 1; HuGBP1; Interferon induced guanylate binding protein 1;;GBP1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 68 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human GBP1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于TMEM199 (N-term)抗体的模拟参考文献示例(注:部分内容为假设性概括,实际文献需通过学术数据库核实):
---
1. **文献名称**: *TMEM199 deficiency disrupts vascular ATP homeostasis and causes a glycosylation disorder with hepatic steatosis*
**作者**: Jansen JC et al.
**摘要**: 本研究通过TMEM199 (N-term)抗体的Western blot和免疫荧光技术,揭示TMEM199蛋白在内质网定位及其在糖基化修饰中的作用。发现TMEM199缺失导致ATP酶活性异常,引发先天性糖基化疾病(CDG)和肝脂肪变性。
2. **文献名称**: *The role of TMEM199 in maintaining copper metabolism and hepatocellular carcinoma progression*
**作者**: Liu Y et al.
**摘要**: 利用TMEM199 N端抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现TMEM199在肝癌组织中表达下调。功能实验表明其通过调控铜转运蛋白ATP7B的稳定性影响肿瘤进展,为潜在治疗靶点。
3. **文献名称**: *Characterization of TMEM199 interaction partners via co-immunoprecipitation*
**作者**: Smith R et al.
**摘要**: 通过TMEM199 (N-term)抗体进行免疫共沉淀和质谱分析,鉴定出TMEM199与V-ATPase复合物亚基的相互作用,提示其在调节内体酸化和膜运输中的关键功能。
4. **文献名称**: *TMEM199 mutations alter cellular zinc homeostasis in a novel type of metabolic disorder*
**作者**: García-Castro M et al.
**摘要**: 研究使用TMEM199 N端抗体检测患者成纤维细胞中的蛋白表达水平,发现突变导致TMEM199稳定性降低,进而破坏锌离子稳态,与神经发育异常相关。
---
**备注**:以上文献信息为基于TMEM199已知功能的模拟概括。实际研究中,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“TMEM199 antibody”或“TMEM199 N-terminal”为关键词检索最新文献,或参考抗体供应商(如Abcam、Sigma-Aldrich)提供的产品引用文献列表。
The TMEM199 (N-term) antibody is a research tool designed to detect the N-terminal region of Transmembrane Protein 199 (TMEM199), a conserved eukaryotic protein implicated in cellular homeostasis and post-translational modification processes. TMEM199 localizes primarily to the Golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum, where it plays a role in maintaining Golgi morphology, glycosylation, and copper metabolism. Dysregulation of TMEM199 has been linked to congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDGs) and metabolic diseases.
This antibody is commonly used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to study TMEM199 expression, subcellular localization, and interactions. Its specificity for the N-terminal domain allows researchers to distinguish TMEM199 from structurally related proteins or isoforms. Validation typically includes testing in knockout cell lines or tissues to confirm absence of signal, alongside recombinant protein assays.
Studies utilizing the TMEM199 (N-term) antibody have advanced understanding of its involvement in copper-dependent enzyme activation and vesicular trafficking. It also serves as a diagnostic marker in research exploring TMEM199-associated pathologies, such as mitochondrial dysfunction and metabolic syndrome. Host species (e.g., rabbit, mouse) and clonality (polyclonal/monoclonal) vary by commercial source, requiring validation for specific experimental contexts.
×