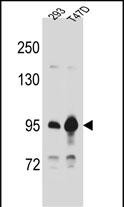
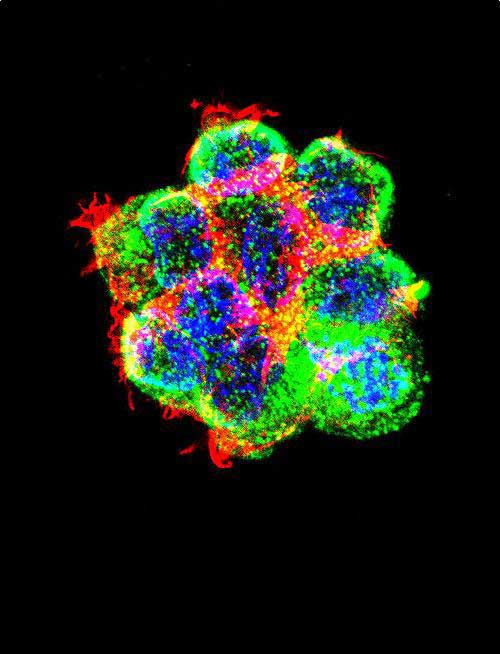
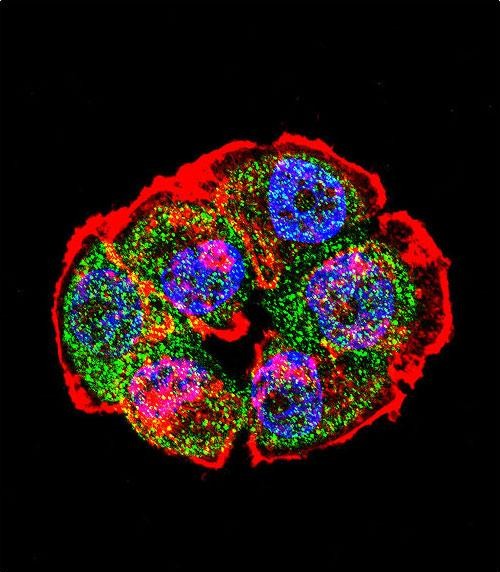
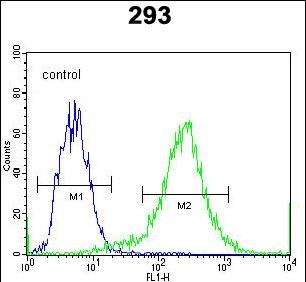

| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Catenin beta-1, Beta-catenin, CTNNB1, CTNNB |
| Entrez GeneID | 1499 |
| WB Predicted band size | 85.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This CTNNB1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 692-721 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human CTNNB1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇与CTNNB1(β-catenin)抗体相关的经典文献及摘要概括:
1. **"Constitutive transcriptional activation by a β-catenin-Tcf complex in APC⁻/⁻ colon carcinoma"**
- **作者**: Korinek, V. et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究通过免疫沉淀(使用CTNNB1抗体)发现APC基因缺失导致β-catenin在结直肠癌细胞核内异常积累,激活Wnt靶基因转录,揭示了APC/β-catenin-Tcf通路在癌症中的作用。
2. **"Activation of β-catenin-Tcf signaling in colon cancer by mutations in β-catenin or APC"**
- **作者**: Morin, P.J. et al.
- **摘要**: 通过Western blot和免疫组化(使用β-catenin抗体)证实结肠癌中CTNNB1基因突变或APC缺失导致β-catenin蛋白稳定性增加,驱动肿瘤发生。
3. **"Wnt/β-catenin signaling and disease"**
- **作者**: Clevers, H. & Nusse, R.
- **摘要**: 综述文章总结了β-catenin在Wnt信号通路中的核心作用,强调其实验工具(如抗体)在检测蛋白定位及活性中的应用,并探讨其在癌症和发育异常中的机制。
4. **"Genome-wide pattern of TCF7L2/TCF4 chromatin occupancy in colorectal cancer cells"**
- **作者**: Hatzis, P. et al.
- **摘要**: 研究通过染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP,使用CTNNB1抗体)揭示结直肠癌细胞中β-catenin与TCF4转录因子共同调控下游致癌基因的全基因组结合模式。
这些文献均涉及CTNNB1抗体的实验应用(如检测表达、定位或互作),并解析β-catenin在疾病中的功能。
The CTNNB1 antibody targets β-catenin, a multifunctional protein encoded by the CTNNB1 gene. β-catenin plays pivotal roles in cell adhesion and Wnt signaling, regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, and tissue homeostasis. In the canonical Wnt pathway, β-catenin acts as a transcriptional co-activator: when Wnt ligands bind receptors, β-catenin escapes degradation, accumulates in the cytoplasm, and translocates to the nucleus to drive target gene expression. Dysregulation of CTNNB1/β-catenin is implicated in cancers (e.g., colorectal, hepatocellular carcinomas) and developmental disorders. Mutations in CTNNB1. often affecting phosphorylation sites, stabilize β-catenin, leading to constitutive pathway activation.
CTNNB1 antibodies are widely used in research to assess β-catenin expression, localization (membrane, cytoplasmic, nuclear), and mutational status. They are critical tools in studying Wnt pathway activity, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and cancer progression. Common applications include Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and co-immunoprecipitation. Specificity varies among antibodies; some recognize total β-catenin, while others detect active (non-phosphorylated) forms or phosphorylation-specific epitopes. Proper validation using controls (e.g., knockout cells, tissue samples with known mutations) is essential, as post-translational modifications, isoforms, or subcellular localization can influence detection. These antibodies also aid in diagnosing diseases with β-catenin abnormalities, such as desmoid tumors or β-cateninopathies.
×