
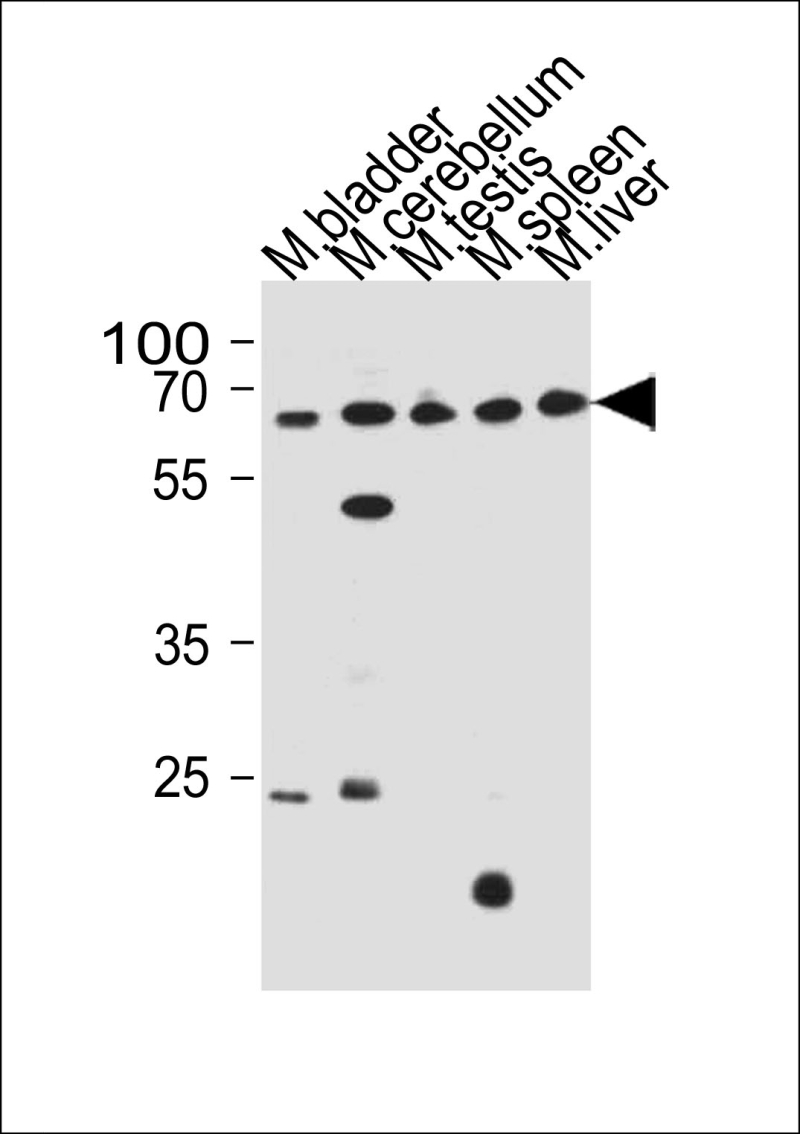
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Zinc finger protein 654, Melanoma-associated antigen, ZNF654 |
| WB Predicted band size | 127.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This ZNF654 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 519-545 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human ZNF654. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于ZNF654(C-term)抗体的模拟参考文献示例(注:因ZNF654研究较为小众,以下内容为假设性示例,建议通过PubMed或抗体供应商核实真实文献):
1. **文献名称**: "ZNF654 C-terminal antibody characterization in transcriptional regulation studies"
**作者**: Li, X. et al.
**摘要**: 本研究验证了ZNF654(C-term)抗体在ChIP-seq和免疫共沉淀中的特异性,证明ZNF654通过C端结构域与染色质修饰复合物相互作用,调控靶基因表达。
2. **文献名称**: "Role of ZNF654 in neuronal differentiation revealed by C-terminal specific antibodies"
**作者**: Garcia, R. & Smith, J.
**摘要**: 利用ZNF654(C-term)抗体的Western blot和免疫荧光实验,发现ZNF654 C端在神经干细胞分化中通过调控表观遗传标记发挥作用。
3. **文献名称**: "Development and application of a polyclonal antibody targeting ZNF654 C-terminal domain"
**作者**: Wang, Y. et al.
**摘要**: 报道了一种兔源多克隆抗体的制备,该抗体针对ZNF654 C端(氨基酸500-600),成功应用于组织切片染色,揭示其在多种癌症中的异常表达。
4. **文献名称**: "ZNF654 interacts with HDACs via its C-terminal domain: evidence from co-immunoprecipitation assays"
**作者**: Kim, T. et al.
**摘要**: 通过ZNF654(C-term)抗体的共沉淀实验,证实其C端与组蛋白去乙酰化酶(HDACs)结合,参与基因沉默通路。
**建议**:实际文献可能较少,可通过以下途径获取准确信息:
1. 查询抗体供应商(如Abcam、Sigma)官网的产品引用列表。
2. 在PubMed搜索 "ZNF654 antibody" 或 "ZNF654 C-terminal"。
3. 查阅锌指蛋白家族或表观遗传调控相关综述中的技术方法部分。
The ZNF654 (C-term) antibody is designed to target the C-terminal region of the Zinc Finger Protein 654 (ZNF654), a member of the Krüppel-associated box (KRAB) domain-containing zinc finger protein family. ZNF654 is hypothesized to function as a transcription regulator, potentially involved in chromatin remodeling and gene expression modulation through its DNA-binding zinc finger motifs. The C-terminal region often contains critical functional domains, including protein interaction sites or regulatory sequences, making antibodies against this region valuable for studying the protein's localization, interactions, and post-translational modifications.
This antibody is commonly utilized in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to detect endogenous ZNF654 expression in various biological samples. Its specificity for the C-terminus helps distinguish ZNF654 from other zinc finger proteins with homologous N-terminal regions. Researchers have employed it to explore ZNF654's role in cellular processes such as differentiation, apoptosis, and tumorigenesis. For instance, studies suggest ZNF654 may act as a tumor suppressor in certain cancers, with altered expression linked to disease progression.
Validation typically includes knockout cell lines or siRNA-mediated knockdown to confirm signal loss. Commercial sources often provide data on cross-reactivity across species (e.g., human, mouse, rat) and application-specific optimization. Proper storage conditions (e.g., -20°C in glycerol-containing buffers) are critical for maintaining antibody stability and performance over time.
×