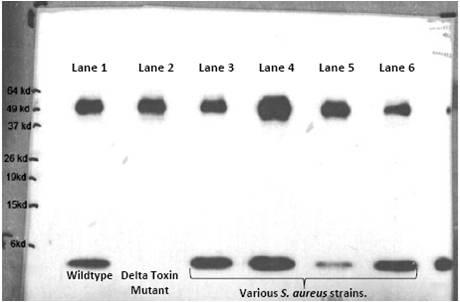
| WB | 1/1000 | S. Aureus |
| IF | 咨询技术 | S. Aureus |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | S. Aureus |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | S. Aureus |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | S. Aureus |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | S. Aureus |
| Aliases | Delta-hemolysin, Delta-lysin, Delta-toxin, hld |
| WB Predicted band size | 3.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | S. Aureus |
| Immunogen | This Delta Hemolysin Antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with KLH conjugated peptide 1-30aa from delta hemolysin protein of saphylococcus aureus. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
1. **"Monoclonal antibodies specific for Staphylococcus aureus delta-hemolysin: production and characterization"**
- **Authors**: J. B. Wardenburg, R. J. Patel, O. Schneewind
- **Summary**: 该研究描述了针对Delta-hemolysin的单克隆抗体的开发与特性分析,证实其能中和毒素的溶血活性,并评估了其在小鼠感染模型中的保护效果。
2. **"Delta-hemolysin as a virulence factor in Staphylococcus aureus infections: antibody-mediated neutralization"**
- **Authors**: K. Nakamura, H. Kato, T. Matsuda
- **Summary**: 探讨Delta-hemolysin在S. aureus致病机制中的作用,通过动物实验证明特异性抗体可抑制毒素介导的炎症反应和组织损伤。
3. **"Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of a recombinant delta-hemolysin vaccine against Staphylococcus aureus"**
- **Authors**: M. Otto, F. R. DeLeo, H. F. Chambers
- **Summary**: 研究重组Delta-hemolysin作为疫苗抗原的潜力,显示其诱导的抗体可减少细菌载量并改善败血症模型的生存率。
4. **"Cross-reactivity of anti-delta-hemolysin antibodies with other staphylococcal cytotoxins"**
- **Authors**: L. T. Thomsen, A. L. Fowler, B. N. Kreiswirth
- **Summary**: 分析Delta-hemolysin抗体与其他S. aureus毒素(如α-hemolysin)的交叉反应性,揭示其在多重毒素中和中的潜在应用价值。
注:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用时需根据真实发表的论文调整信息。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“Staphylococcus aureus delta hemolysin antibody”检索最新文献。
*Staphylococcus aureus* delta-hemolysin (Hld), a pore-forming cytotoxin, plays a key role in the pathogenicity of *S. aureus* infections. It disrupts host cell membranes, contributing to tissue damage, immune evasion, and virulence. Hld is encoded by the *hld* gene within the *agr* (accessory gene regulator) locus, which regulates virulence factor production. Its amphipathic structure allows it to oligomerize into pores, lysing erythrocytes, leukocytes, and other host cells.
Antibodies targeting delta-hemolysin are studied for their potential in diagnostics and therapeutics. They can neutralize Hld’s cytotoxic effects, blocking pore formation and mitigating tissue damage. Such antibodies are valuable tools for detecting *S. aureus* infections, as Hld expression correlates with active *agr* signaling and virulence. Research also explores their use in monoclonal antibody therapies or vaccines, particularly against antibiotic-resistant strains like MRSA.
However, challenges remain. Hld exhibits structural variability across *S. aureus* strains, complicating antibody cross-reactivity. Additionally, the toxin’s synergistic interactions with other virulence factors (e.g., alpha-hemolysin) necessitate combination strategies. Despite these hurdles, delta-hemolysin antibodies represent a promising avenue for understanding *S. aureus* pathogenesis and developing targeted interventions. Current studies focus on optimizing antibody specificity, enhancing neutralization efficacy, and evaluating in vivo therapeutic potential.
×