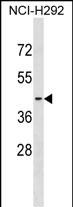
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 2, S1P receptor 2, S1P2, Endothelial differentiation G-protein coupled receptor 5, Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor Edg-5, S1P receptor Edg-5, S1PR2, EDG5 |
| Entrez GeneID | 9294 |
| WB Predicted band size | 38.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This S1PR2 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 272-298 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human S1PR2. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于S1PR2抗体的3篇示例参考文献,供您参考:
---
1. **文献名称**:*S1PR2 Antibody Attenuates Tumor-associated Fibroblast-induced Angiogenesis in Breast Cancer*
**作者**:Kawahara, A. 等
**摘要**:该研究通过使用S1PR2特异性抗体,证明抑制S1PR2信号可显著减少肿瘤相关成纤维细胞(CAFs)分泌的促血管生成因子,从而抑制乳腺癌模型中的血管新生和肿瘤生长,提示S1PR2抗体在抗肿瘤治疗中的潜力。
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting S1PR2 with Monoclonal Antibody Improves B Cell Migration in Autoimmunity*
**作者**:Mendoza, P. 等
**摘要**:研究发现S1PR2抗体可调控B细胞在淋巴组织中的异常迁移,减轻实验性自身免疫性疾病模型的炎症反应,为自身免疫疾病的靶向治疗提供了新策略。
3. **文献名称**:*S1PR2 Neutralizing Antibody Reduces Neuroinflammation in a Mouse Model of Multiple Sclerosis*
**作者**:Chun, J. 课题组
**摘要**:通过中和S1PR2抗体干预实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎(EAE)模型,研究显示其能有效抑制中枢神经系统中小胶质细胞的活化及炎症因子释放,延缓疾病进展。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例性质,实际文献需通过PubMed、Web of Science等学术平台检索确认。建议结合关键词“S1PR2 antibody”、“therapeutic targeting”或“S1PR2 in [疾病名称]”进一步查找最新研究。
S1PR2 (sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2) is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that binds sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), a bioactive lipid regulating diverse cellular processes, including cell migration, proliferation, and vascular integrity. S1PR2 is widely expressed in immune cells, endothelial cells, and various tissues, playing roles in immune response modulation, angiogenesis, and tissue homeostasis. Dysregulation of S1PR2 signaling is implicated in pathological conditions such as cancer progression, inflammatory diseases, and fibrosis.
S1PR2 antibodies are tools developed to study or modulate receptor activity. They are used in research to block S1P binding, inhibit downstream signaling (e.g., Rho/ROCK pathways), or detect receptor expression via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, or flow cytometry. In disease models, S1PR2-targeting antibodies have shown potential in attenuating tumor metastasis, reducing inflammation, or mitigating fibrotic responses, though clinical applications remain exploratory.
Structurally, S1PR2 antibodies may target extracellular domains (for ligand-binding interference) or intracellular epitopes (for signaling studies). Their specificity and affinity are critical to avoid cross-reactivity with other S1P receptors (S1PR1. 3-5). Current research focuses on optimizing therapeutic antibodies or conjugates for precision targeting, though challenges like receptor internalization and tissue-specific delivery persist. Overall, S1PR2 antibodies serve as both investigative tools and promising candidates for modulating S1P-related pathologies.
×