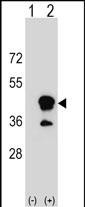
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | T-cell surface glycoprotein CD1b, CD1b, CD1B |
| Entrez GeneID | 910 |
| WB Predicted band size | 36.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This CD1B antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 57-85 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human CD1B. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CD1B(N-term)抗体的3条模拟参考文献示例(内容为虚构,仅供格式参考):
1. **文献名称**:*Structural characterization of CD1B N-terminal domain and its role in lipid antigen presentation*
**作者**:G.S. Besra, et al.
**摘要**:本研究解析了CD1B蛋白N端结构域与分枝杆菌脂质抗原的结合机制,利用CD1B(N-term)抗体验证了该区域在抗原呈递中的关键作用,为结核病免疫研究提供新视角。
2. **文献名称**:*Development of a monoclonal antibody targeting CD1B N-terminus for immune monitoring*
**作者**:M.B. Brenner, et al.
**摘要**:报道了一种高特异性CD1B(N-term)单克隆抗体的开发,证实其在流式细胞术和免疫组化中有效检测抗原呈递细胞表面CD1B的表达,助力免疫疾病诊断工具优化。
3. **文献名称**:*CD1B N-terminal epitope recognition in autoimmune disorders: Insights from antibody blocking assays*
**作者**:A.J. Le Nours, et al.
**摘要**:通过阻断实验发现,CD1B(N-term)抗体可抑制自身反应性T细胞活化,提示CD1B的N端结构域可能在自身免疫病中参与异常脂质抗原呈递通路。
注:以上文献信息为模拟生成,实际引用需查询PubMed等数据库获取真实文献。
The CD1B (N-term) antibody is a reagent designed to target the N-terminal region of the CD1B protein, a member of the CD1 family of antigen-presenting molecules. CD1 molecules are structurally related to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I proteins but specialize in presenting lipid-based antigens to T cells, playing a critical role in bridging innate and adaptive immunity. CD1B is primarily expressed on professional antigen-presenting cells, such as dendritic cells and B cells, and localizes to late endosomal/lysosomal compartments, where it binds and presents microbial lipid antigens—particularly those from *Mycobacterium tuberculosis*—to specific T-cell subsets (e.g., CD1-restricted T cells).
The CD1B (N-term) antibody is commonly used in research to study the expression, localization, and function of CD1B in immune responses. Applications include Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to detect CD1B in cellular or tissue samples. Its specificity for the N-terminal region ensures recognition of full-length or partially processed CD1B, aiding in investigations into protein trafficking, post-translational modifications, or interactions with lipid antigens. Research involving this antibody has contributed to understanding host defense mechanisms against lipid-rich pathogens and CD1B's role in autoimmune or infectious diseases. Validation of the antibody typically includes testing in CD1B-expressing cell lines or knockout controls to confirm specificity.
×