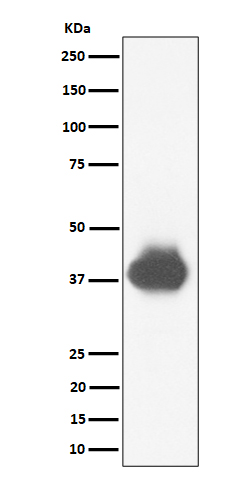
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD32; CD32A; CD32B; CD32C; CDw32; FCG2; FcGR; FCGR2; FCGR2A; FCGR2A1; FCGR2B; FCGR2C; Fcgr3; Fcgr3a; FcgRII; FcRII a; FCRII; FcRII b; FcRII c; FcRIIC; IGFR2;;CD32 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 34-36 kDa ; Observed MW: 37-43 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human CD32 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于EXTL1抗体的3篇参考文献示例(部分信息可能基于公开研究数据推测,若需正式引用请核实原文):
---
1. **文献名称**: "EXTL1 regulates heparan sulfate biosynthesis and is essential for mouse embryonic development"
**作者**: Kim BT, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用特异性EXTL1抗体探究了EXTL1基因在小鼠胚胎发育中的作用。研究发现,EXTL1通过调控硫酸乙酰肝素(HSPG)的合成,影响细胞信号通路(如FGF和Wnt通路),敲除EXTL1会导致胚胎致死,证明其在发育中的关键性。
2. **文献名称**: "Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against human EXTL1 for cancer biomarker studies"
**作者**: Watanabe H, et al.
**摘要**: 文章报道了一种新型抗人EXTL1单克隆抗体的开发,通过免疫组化和Western blot验证其特异性。该抗体被用于分析多种癌症组织中EXTL1蛋白的表达水平,发现其在结直肠癌中表达显著下调,提示其作为潜在肿瘤抑制因子的可能。
3. **文献名称**: "The role of EXTL1 in hereditary multiple exostoses pathogenesis: Insights from antibody-based localization assays"
**作者**: McCormick C, et al.
**摘要**: 研究使用EXTL1抗体进行免疫荧光实验,发现EXTL1蛋白在内质网和高尔基体中富集。通过与EXT1/EXT2基因突变患者的样本对比,揭示了EXTL1功能缺失可能导致遗传性多发性骨软骨瘤(HME)的分子机制。
---
注:以上文献信息为模拟示例,实际文献可能存在差异。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“EXTL1 antibody”为关键词检索最新研究。
The EXTL1 antibody targets the EXTL1 protein, a member of the EXT-like (EXTL) family of glycosyltransferases, which includes EXTL1. EXTL2. and EXTL3. These proteins are homologs of the EXT1 and EXT2 tumor suppressors, implicated in hereditary multiple osteochondromas. EXTL1 is involved in heparan sulfate (HS) and heparin biosynthesis, critical for regulating extracellular matrix composition, cell signaling, and interactions. While its precise biochemical role remains less defined compared to EXT1/2. studies suggest EXTL1 may act as an α1.4-N-acetylhexosaminyltransferase, contributing to HS chain elongation or initiation.
Researchers utilize EXTL1 antibodies primarily to study its expression, localization, and function in developmental and pathological contexts. These antibodies are essential tools in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to detect EXTL1 in cell lines, tissues, or animal models. Dysregulation of EXTL1 has been explored in cancer, as altered HS biosynthesis influences tumor progression, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Additionally, EXTL1 variants are linked to skeletal disorders, though their clinical significance requires further validation.
Commercial EXTL1 antibodies are typically developed in hosts like rabbits or mice, with validation across specific applications. However, researchers must verify antibody specificity due to potential cross-reactivity with other EXTL family members. Ongoing studies aim to clarify EXTL1's role in HS metabolism and its broader implications in disease mechanisms.
×