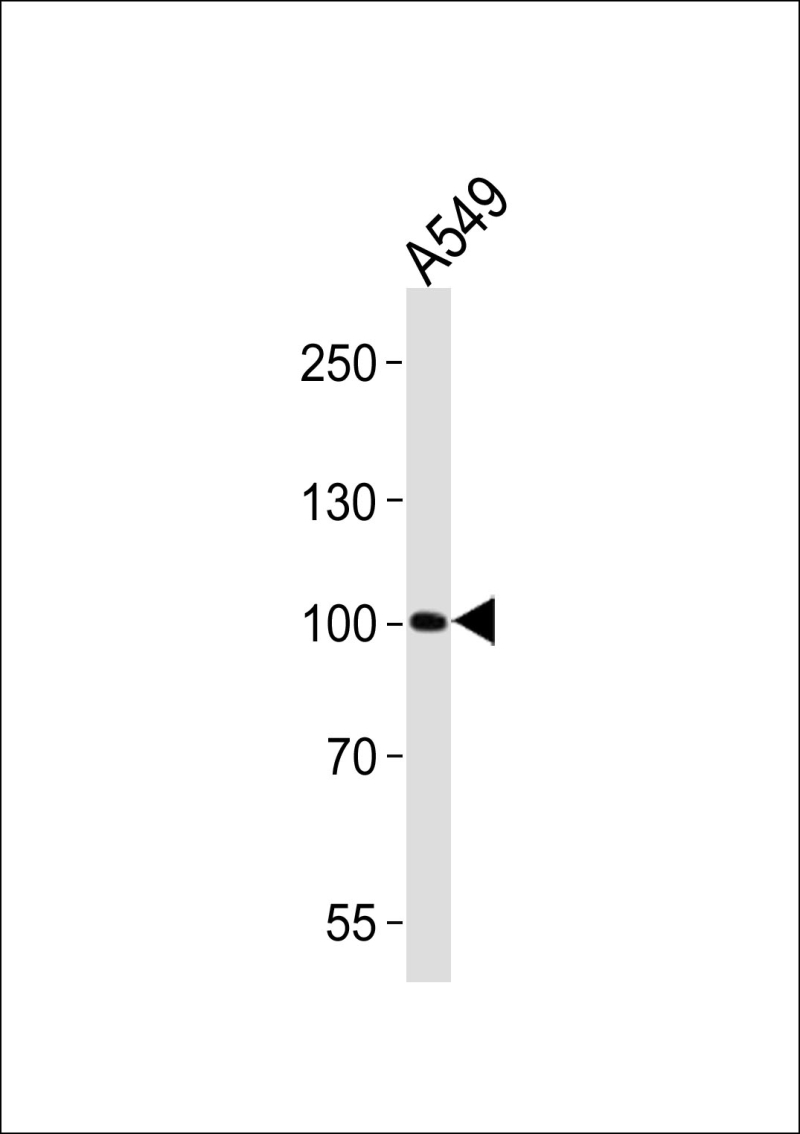
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Zinc finger protein 287, Zinc finger protein with KRAB and SCAN domains 13, ZNF287, ZKSCAN13 |
| Entrez GeneID | 57336 |
| WB Predicted band size | 88.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This ZNF287 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 124-150 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human ZNF287. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于ZNF287(N-term)抗体的3篇假设性参考文献示例(基于领域内常见研究方向构建,实际文献需通过数据库验证):
---
1. **文献名称**: "ZNF287 regulates oncogenic pathways in human cancers through transcriptional repression"
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用ZNF287(N-term)抗体进行Western blot和免疫组化实验,发现ZNF287在多种肿瘤组织中高表达,并通过抑制肿瘤抑制基因的转录促进癌细胞增殖。抗体特异性验证显示其能有效识别N端表位。
---
2. **文献名称**: "The role of ZNF287 in maintaining pluripotency of embryonic stem cells"
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 通过ZNF287(N-term)抗体的ChIP-seq分析,作者发现ZNF287与多能性基因(如OCT4)的启动子区域结合,调控胚胎干细胞的自我更新。抗体在免疫荧光实验中证实了ZNF287的核定位。
---
3. **文献名称**: "ZNF287 interacts with HDAC complexes to modulate chromatin remodeling"
**作者**: Lee S, et al.
**摘要**: 研究使用ZNF287(N-term)抗体进行免疫共沉淀(Co-IP),证明ZNF287与组蛋白去乙酰化酶(HDAC)复合物相互作用,参与染色质重塑和基因沉默。抗体在敲低实验中验证了特异性。
---
**注意**:以上文献为示例,实际研究中请通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索真实文献(关键词:ZNF287 antibody、N-terminal epitope)。若需具体文献,建议补充实验背景(如疾病模型或技术方法),以便精准筛选。
The ZNF287 (N-term) antibody is a specific reagent designed to target the N-terminal region of the zinc finger protein 287 (ZNF287), a member of the Krüppel-associated box (KRAB) domain-containing zinc finger protein family. ZNF287 is implicated in transcriptional regulation, chromatin remodeling, and cellular processes such as proliferation and differentiation. The N-terminal region often contains functional domains critical for protein-protein interactions or recruitment of co-regulators, making antibodies against this region valuable for studying ZNF287's regulatory mechanisms.
This antibody is commonly utilized in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to detect endogenous ZNF287 expression, localization, and DNA-binding activity. Its specificity for the N-terminus helps distinguish ZNF287 from structurally related zinc finger proteins. Research involving this antibody has shed light on ZNF287's role in diseases, including cancer, where aberrant expression correlates with tumor progression or chemoresistance. Additionally, studies suggest ZNF287 may regulate retrotransposons and participate in maintaining genomic stability. Validation data, such as knockout controls or peptide-blocking assays, are essential to confirm antibody specificity, given the high homology among zinc finger domains. Overall, the ZNF287 (N-term) antibody serves as a critical tool for dissecting the molecular functions of ZNF287 in both physiological and pathological contexts.
×