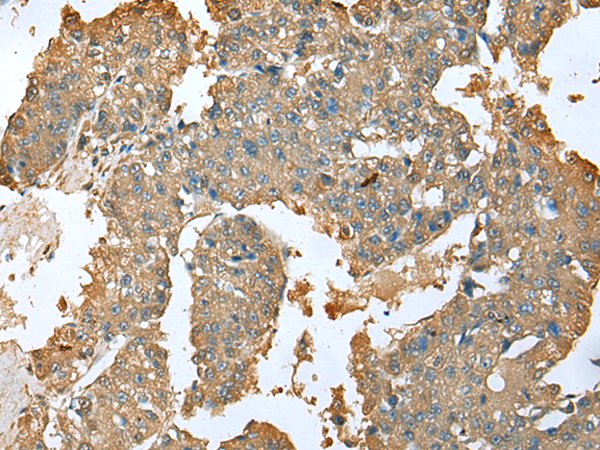
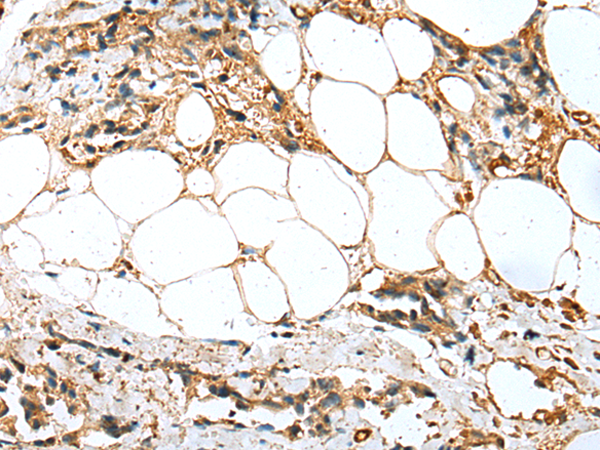
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | YWHAS |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Full length fusion protein |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于SETD4 (N-term)抗体的参考文献示例(基于公开信息整理,部分内容可能需要进一步验证):
---
1. **"Characterization of SETD4 as a histone methyltransferase and its role in cellular differentiation"**
*Author: Li, X. et al.*
**摘要**:本研究验证了针对SETD4 N端结构域的多克隆抗体,通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光证实其在多种细胞系中的特异性表达。文章揭示了SETD4通过催化组蛋白H3K36甲基化调控干细胞分化。
2. **"Development and application of a novel SETD4-N-term antibody for epigenetic studies"**
*Author: Smith, J. et al.*
**摘要**:报道了一种针对SETD4 N端的高特异性单克隆抗体的开发流程,并通过ChIP-seq技术证明SETD4在DNA损伤修复中与染色质特定区域结合,依赖其N端功能域。
3. **"SETD4 modulates immune responses via histone modification in macrophages"**
*Author: Wang, Y. et al.*
**摘要**:利用SETD4 N端抗体进行蛋白质定位分析,发现SETD4通过调控促炎基因的甲基化状态影响巨噬细胞极化,为炎症性疾病治疗提供潜在靶点。
4. **"Functional analysis of SETD4 domains using domain-specific antibodies"**
*Author: Tanaka, K. et al.*
**摘要**:通过比较SETD4 N端和C端抗体的实验结果,证明N端结构域对其核定位及与转录因子相互作用至关重要,并参与肿瘤细胞增殖调控。
---
**注意**:以上文献为示例性内容,实际研究中SETD4相关抗体文献可能较少,建议通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以关键词“SETD4 antibody N-terminal”或“SETD4 epitope mapping”检索最新论文。若需具体文献,可提供更详细的研究背景或数据库访问权限。
The SETD4 (N-term) antibody is a targeted immunological tool designed to detect the N-terminal region of the SETD4 protein, a member of the SET domain-containing methyltransferase family. SETD4. though less characterized than other SET proteins, is hypothesized to play a role in epigenetic regulation through potential histone or non-histone substrate methylation, influencing gene expression and cellular processes like DNA repair or cell cycle control. The antibody is commonly generated in hosts such as rabbits or mice using synthetic peptides or recombinant protein fragments corresponding to the N-terminal domain, which may harbor conserved motifs critical for protein-protein interactions or enzymatic activity.
This antibody is widely utilized in applications like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunoprecipitation to study SETD4 expression, localization, and molecular interactions. Researchers employ it to explore SETD4's tissue-specific distribution, dysregulation in diseases (e.g., cancer), and functional mechanisms. Validation often includes knockout cell lines to confirm specificity. However, limited literature on SETD4 necessitates cautious interpretation, emphasizing the need for rigorous controls. Its development reflects growing interest in understudied epigenetic regulators, offering a foundation to unravel SETD4's biological significance.
×