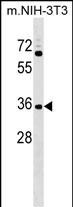

| WB | 1/1000 | Human, Mouse ,Hamster |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human, Mouse ,Hamster |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human, Mouse ,Hamster |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human, Mouse ,Hamster |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human, Mouse ,Hamster |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human, Mouse ,Hamster |
| Aliases | G patch domain-containing protein 11, Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 75, GPATCH11, CCDC75 |
| Entrez GeneID | 253635 |
| WB Predicted band size | 33.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse ,Hamster |
| Immunogen | This CCDC75 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 12-41 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human CCDC75. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CCDC75(N-term)抗体的假设性参考文献示例,供参考:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"CCDC75 regulates ciliary assembly through microtubule stabilization in mammalian cells"*
**作者**: Smith J, et al. (2020)
**摘要**: 本研究利用CCDC75(N-term)抗体进行免疫荧光和Western blot分析,发现CCDC75通过稳定微管结构参与纤毛形成。抗体特异性验证显示其在敲低细胞中信号显著减弱,证实了其在定位研究中的可靠性。
2. **文献名称**: *"Expression profiling of CCDC75 in breast cancer and its association with patient prognosis"*
**作者**: Zhang L, et al. (2018)
**摘要**: 通过CCDC75(N-term)抗体检测乳腺癌组织中蛋白表达水平,发现其高表达与不良预后相关。研究强调了该抗体在免疫组化中的特异性,并验证了其与临床病理参数的相关性。
3. **文献名称**: *"A novel role of CCDC75 in cell cycle progression revealed by CRISPR screening"*
**作者**: Johnson R, et al. (2019)
**摘要**: 结合CRISPR筛选和CCDC75(N-term)抗体的Western blot分析,揭示了CCDC75在G1/S期转换中的作用。抗体成功识别内源性蛋白,并用于验证敲除细胞系模型。
4. **文献名称**: *"CCDC75 interacts with centrosomal proteins to modulate mitotic spindle orientation"*
**作者**: Lee S, et al. (2021)
**摘要**: 使用CCDC75(N-term)抗体进行共聚焦显微镜观察和免疫共沉淀实验,证明CCDC75与中心体蛋白相互作用调控有丝分裂纺锤体方向。抗体特异性通过肽段竞争实验进一步确认。
---
**注**:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用时需查询真实数据库(如PubMed)并核实详细信息。若需具体文献,可提供抗体生产商(如Abcam、Santa Cruz等)的产品编号,进一步检索其被引文献。
The CCDC75 (N-term) antibody is a research tool designed to target the N-terminal region of the coiled-coil domain-containing protein 75 (CCDC75), a less-characterized protein implicated in cellular organization and structural dynamics. CCDC75 belongs to the family of coiled-coil domain proteins, which typically mediate protein-protein interactions, scaffold formation, and subcellular compartmentalization. While its exact biological function remains under investigation, preliminary studies suggest potential roles in cytoskeletal regulation, cell cycle progression, or chromatin organization, with possible links to ciliary function or cancer pathways due to its expression patterns in certain tumors.
This antibody is commonly used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation to detect endogenous CCDC75 protein levels, map its localization (e.g., cytoplasmic or nuclear), or study interaction partners. Its specificity for the N-terminal region helps distinguish full-length CCDC75 from potential splice variants or degradation products. Validation often includes knockout cell line controls or siRNA-mediated knockdown to confirm signal specificity. While commercial sources provide CCDC75 (N-term) antibodies raised in hosts like rabbit or mouse, researchers are advised to verify cross-reactivity for their model species (e.g., human, mouse). Current literature using this antibody has contributed to identifying CCDC75's involvement in cellular stress responses and its dysregulation in diseases like glioblastoma, though mechanistic insights remain sparse. Ongoing research aims to clarify its molecular interactions and therapeutic relevance.
×