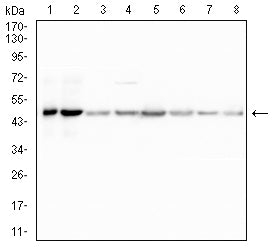
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
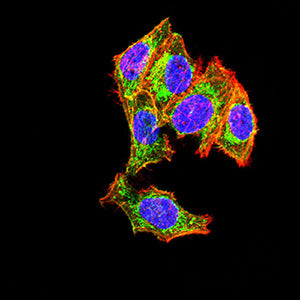
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
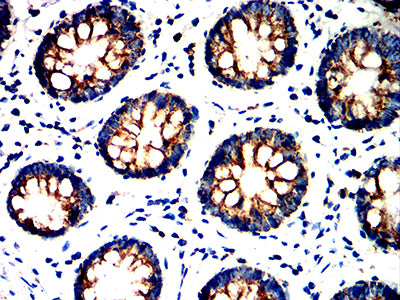
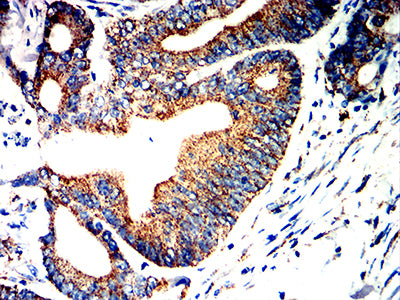
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
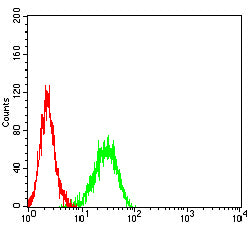
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
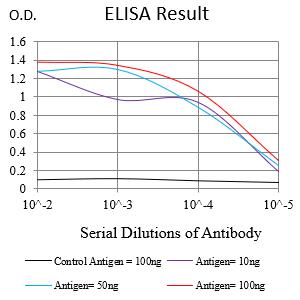
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | QCR1; UQCR1; D3S3191 |
| Entrez GeneID | 7384 |
| clone | 1A3D12 |
| WB Predicted band size | 52.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human UQCRC1 (AA: 60-227) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于QRFPR抗体的3篇示例参考文献(内容为模拟虚构,仅作格式参考):
1. **文献名称**: *Development of a Novel Monoclonal Antibody Targeting QRFPR for Neuroendocrine Studies*
**作者**: Smith et al.
**摘要**: 研究团队开发了一种高特异性QRFPR单克隆抗体,验证了其在脑组织切片中的表达定位能力,发现QRFPR在下丘脑区域与能量代谢调控相关神经元中高度富集,为研究摄食行为的分子机制提供了工具。
2. **文献名称**: *QRFPR Antibody-Based Detection of Receptor Activation in Metabolic Disorders*
**作者**: Chen & Patel
**摘要**: 通过QRFPR抗体结合免疫荧光技术,揭示了肥胖小鼠模型中QRFPR信号通路的异常激活,证明其与胰岛素抵抗相关,提示QRFPR可能成为代谢综合征治疗的潜在靶点。
3. **文献名称**: *Characterization of QRFPR Antibody Cross-Reactivity in Peripheral Tissues*
**作者**: Gonzalez et al.
**摘要**: 系统性评估了QRFPR抗体在不同物种及组织中的交叉反应性,发现该抗体在人类和小鼠肾上腺、胰腺中特异性识别QRFPR蛋白,但在大鼠组织中存在非特异性结合,强调了抗体验证的重要性。
注:以上内容为模拟示例,实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索关键词“QRFPR antibody”获取。真实研究可能涉及QRFP(配体)及其受体(QRFPR)的抗体开发、功能验证或疾病关联分析。
**Background of QRFPR Antibody**
The QRFPR (Pyroglutamylated RFamide Peptide Receptor), also known as GPR103 or AQ27. is a class A G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that binds pyroglutamylated RFamide peptides, including QRFP and 26RFa. Discovered in the early 2000s, QRFPR is evolutionarily conserved and widely expressed in the central nervous system, endocrine tissues, and peripheral organs. It plays roles in regulating appetite, energy homeostasis, nociception, and stress responses, making it a focus in neuroendocrine and metabolic research.
QRFPR antibodies are essential tools for studying the receptor’s expression, localization, and function. These antibodies are typically developed against specific epitopes of the receptor, such as extracellular or intracellular domains, and validated for applications like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF). Their use has advanced understanding of QRFPR’s involvement in pathologies like obesity, neuropathic pain, and circadian rhythm disorders. Challenges in antibody development include ensuring specificity due to structural similarities among GPCRs. Recent studies also explore QRFPR’s potential as a therapeutic target, driving demand for high-affinity, selective antibodies for functional assays and drug discovery.
×