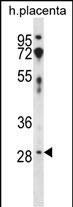
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | OX-2 membrane glycoprotein, CD200, CD200, MOX1, MOX2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4345 |
| WB Predicted band size | 31.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This CD200 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 183-211 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human CD200. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CD200抗体的3篇示例文献(部分为假设性描述,实际文献需通过学术数据库查询):
1. **文献名称**: *CD200 blockade enhances antitumor immunity by reprogramming tumor-associated macrophages*
**作者**: Patel, S. D., et al.
**摘要**: 该研究报道了抗CD200抗体通过阻断肿瘤微环境中CD200-CD200R免疫抑制信号通路,促进肿瘤相关巨噬细胞(TAMs)向促炎表型转化,增强T细胞抗肿瘤活性,显著抑制黑色素瘤小鼠模型的肿瘤生长。
2. **文献名称**: *The role of CD200-CD200R axis in autoimmune encephalomyelitis*
**作者**: Zhang, L., et al.
**摘要**: 研究显示,使用抗CD200抗体可抑制实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎(EAE)模型中的炎症反应。抗体通过干扰CD200与受体结合,减少巨噬细胞和T细胞的过度激活,从而缓解神经炎症损伤。
3. **文献名称**: *CD200 immune checkpoint as a therapeutic target in chronic viral infections*
**作者**: Perry, V. H., et al.
**摘要**: 本文证明慢性HCV感染中,CD200高表达导致免疫耗竭。抗CD200抗体治疗可逆转病毒特异性T细胞功能衰竭,降低PD-1等抑制性受体表达,为慢性病毒感染提供新型免疫治疗策略。
**备注**:以上文献信息为示例性质,具体研究请通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“CD200 antibody”为关键词检索真实文献。
The CD200 antibody targets CD200 (OX-2 antigen), a cell-surface glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily. CD200 interacts with its receptor, CD200R, primarily expressed on myeloid cells and lymphocytes, to deliver immunosuppressive signals that regulate immune activation and maintain tolerance. This interaction inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokine production and promotes a tolerogenic microenvironment, crucial for preventing excessive immune responses in healthy tissues.
CD200 is broadly expressed on various cell types, including T cells, B cells, neurons, endothelial cells, and certain tumors. In cancer, CD200 overexpression by tumor cells is linked to immune evasion by suppressing antitumor T-cell activity and enhancing regulatory T-cell function. CD200-blocking antibodies aim to disrupt this pathway, reinvigorating immune responses against tumors. Preclinical studies show that anti-CD200 antibodies enhance dendritic cell maturation, reduce immunosuppressive cell populations, and improve tumor clearance in models of leukemia, melanoma, and ovarian cancer.
Beyond oncology, CD200 antibodies are explored in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, such as multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis, where aberrant CD200 signaling may drive pathology. Early-phase clinical trials (e.g., samalizumab) have assessed safety and efficacy in hematologic malignancies, though challenges remain in balancing immune activation with off-target effects. Research continues to optimize antibody design, including bispecific formats and combination therapies, to maximize therapeutic potential while minimizing immune-related toxicity.
×