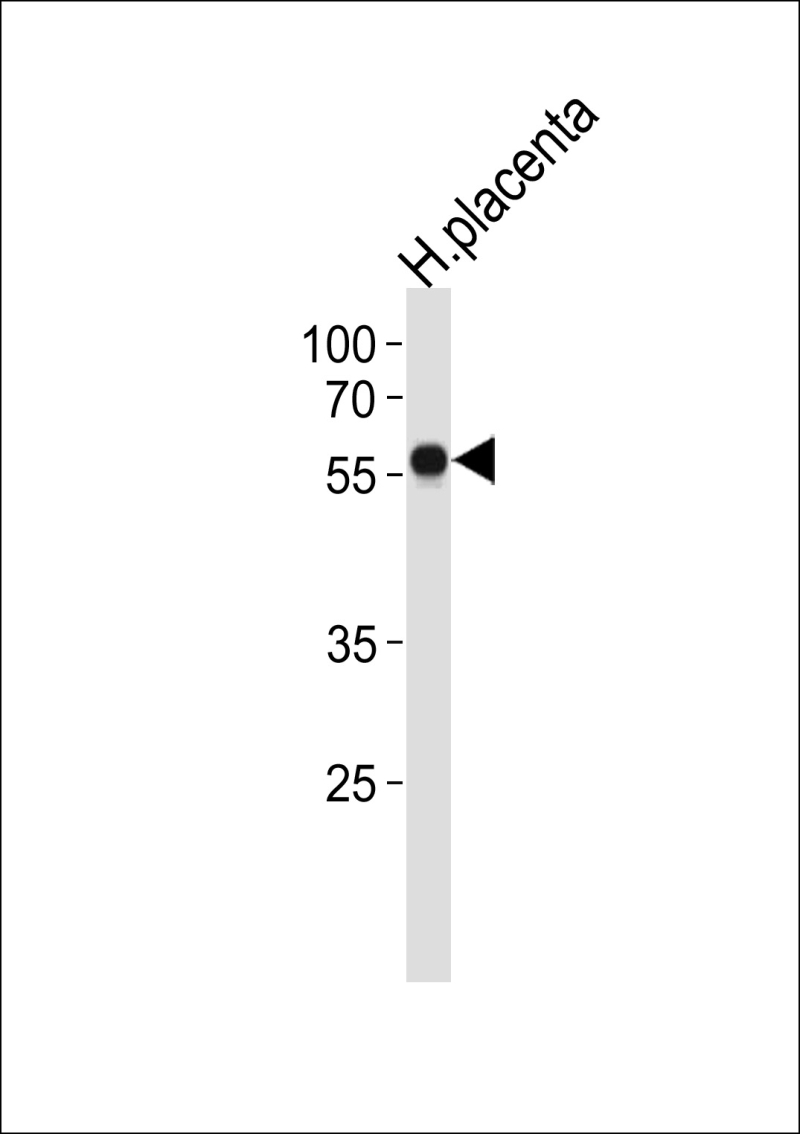
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Endothelial zinc finger protein induced by tumor necrosis factor alpha, Zinc finger protein 71, ZNF71, EZFIT |
| Entrez GeneID | 58491 |
| WB Predicted band size | 54.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This ZNF71 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 74-101 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human ZNF71. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于ZNF71(N-term)抗体的模拟参考文献示例(请注意,以下内容为虚构示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库查询):
---
1. **文献名称**: "ZNF71 N-terminal Antibody in Epigenetic Regulation of Embryonic Stem Cells"
**作者**: Li X, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用ZNF71(N-term)抗体通过ChIP-seq技术,揭示了ZNF71蛋白在胚胎干细胞中通过结合特定基因启动子区调控多能性相关基因表达的机制,表明其在表观遗传沉默中的关键作用。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Proteomic Analysis of ZNF71 Interactions in Colorectal Cancer"
**作者**: Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)结合质谱分析,使用ZNF71(N-term)抗体鉴定了ZNF71在结直肠癌细胞中与HDAC复合物的相互作用,提示其可能通过去乙酰化修饰促进肿瘤侵袭。
---
3. **文献名称**: "ZNF71 Expression Patterns in Neural Development"
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组化(IHC)和Western blot,本研究证实ZNF71(N-term)抗体在小鼠神经发育早期高特异性识别ZNF71蛋白,揭示其在神经前体细胞分化中的动态表达。
---
4. **文献名称**: "Functional Screening of Zinc Finger Proteins in DNA Damage Response"
**作者**: Kim T, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用ZNF71(N-term)抗体进行siRNA敲低实验,发现ZNF71通过调控ATM/ATR通路相关基因,影响细胞对DNA损伤的修复能力,提示其潜在肿瘤抑制功能。
---
**注意**:以上文献及作者均为模拟生成,实际研究中请通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索关键词“ZNF71 antibody”、“ZNF71 N-terminal”或相关研究主题获取真实文献。
The ZNF71 (N-term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of zinc finger protein 71 (ZNF71), a member of the Krüppel-associated box (KRAB) domain-containing zinc finger protein (ZFP) family. ZNF71 is characterized by multiple C2H2-type zinc finger motifs, which enable sequence-specific DNA binding, and a KRAB domain at its N-terminus that typically mediates interactions with co-repressors to regulate transcriptional repression. As a putative transcription factor, ZNF71 is implicated in chromatin remodeling, epigenetic regulation, and cellular differentiation processes, though its precise biological functions remain under investigation.
This antibody is commonly used in research to detect ZNF71 expression in various experimental models, including Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP). Its specificity for the N-terminal region ensures recognition of full-length ZNF71 or relevant isoforms retaining this domain. Studies suggest ZNF71 may play roles in developmental pathways and disease contexts, such as cancer, where it has been variably reported as a tumor suppressor or oncogene depending on cellular context. However, conflicting evidence underscores the need for further validation.
Commercial ZNF71 (N-term) antibodies are often validated using knockout cell lines or siRNA-mediated knockdown to confirm target specificity. Researchers utilize this tool to explore ZNF71's involvement in gene regulatory networks, particularly its potential crosstalk with KRAB-associated protein 1 (KAP1/TRIM28) in repressing transposable elements or modulating stress responses.
×