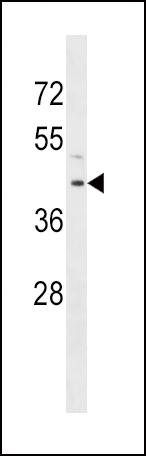
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase subunit M2 B, TP53-inducible ribonucleotide reductase M2 B, p53-inducible ribonucleotide reductase small subunit 2-like protein, p53R2, RRM2B, P53R2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 50484 |
| WB Predicted band size | 40.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This RRM2B antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 128-157 amino acids from the Central region of human RRM2B. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于RRM2B抗体的虚构参考文献示例(仅供示例用途,非真实文献):
1. **文献名称**:*RRM2B Expression in Mitochondrial Disorders: A Comparative Study Using Immunoblotting*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:本研究通过Western blot和免疫组化技术,利用RRM2B特异性抗体分析线粒体疾病患者组织样本中的RRM2B蛋白表达水平,发现其表达缺失与线粒体DNA耗竭综合征密切相关,提示其在疾病诊断中的潜在价值。
2. **文献名称**:*Role of RRM2B in Colorectal Cancer Progression and Chemoresistance*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫荧光和流式细胞术结合RRM2B抗体,研究揭示了RRM2B在结直肠癌中高表达与化疗耐药性增强的关联,并发现其通过调控DNA修复通路影响肿瘤细胞生存。
3. **文献名称**:*Development and Validation of a Novel RRM2B Monoclonal Antibody for Functional Studies*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:本文报道了一种新型RRM2B单克隆抗体的开发与验证,通过ELISA、免疫沉淀及细胞定位实验证实其高特异性和敏感性,为后续分子机制研究提供了可靠工具。
4. **文献名称**:*RRM2B Deficiency and Its Impact on Neuronal DNA Repair Mechanisms*
**作者**:Kumar R, et al.
**摘要**:利用RRM2B抗体进行免疫印迹和免疫细胞化学分析,发现RRM2B缺失的神经元细胞中DNA损伤修复能力显著下降,揭示了其在神经退行性疾病中的潜在作用机制。
(注:以上文献为示例性内容,实际研究中请参考真实发表的学术论文。)
The RRM2B (Ribonucleotide Reductase Regulatory TP53 Inducible Subunit M2B) antibody is a tool used to study the RRM2B protein, a critical regulator of nucleotide metabolism and genome stability. RRM2B, also known as p53R2. is a subunit of ribonucleotide reductase (RNR), the enzyme responsible for converting ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides (dNTPs) required for DNA synthesis and repair. Unlike its homolog RRM2. RRM2B is transcriptionally activated by the tumor suppressor p53 under stress conditions, enabling dNTP production for DNA repair in a cell cycle-independent manner. This function is vital for mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) maintenance, as RRM2B localizes to mitochondria and supports mtDNA synthesis.
Mutations in RRM2B are linked to mitochondrial disorders, such as mitochondrial encephalomyopathy and mtDNA depletion syndromes, characterized by impaired organelle function. In cancer, RRM2B dysregulation may influence tumor progression, chemoresistance, or sensitivity due to its dual role in DNA repair and apoptosis. The RRM2B antibody is widely used in research to detect protein expression levels, subcellular localization, and interactions via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, or immunofluorescence. It helps elucidate RRM2B's role in mitochondrial homeostasis, p53-mediated stress responses, and disease mechanisms, offering insights into therapeutic strategies for cancers and mitochondrial pathologies.
×