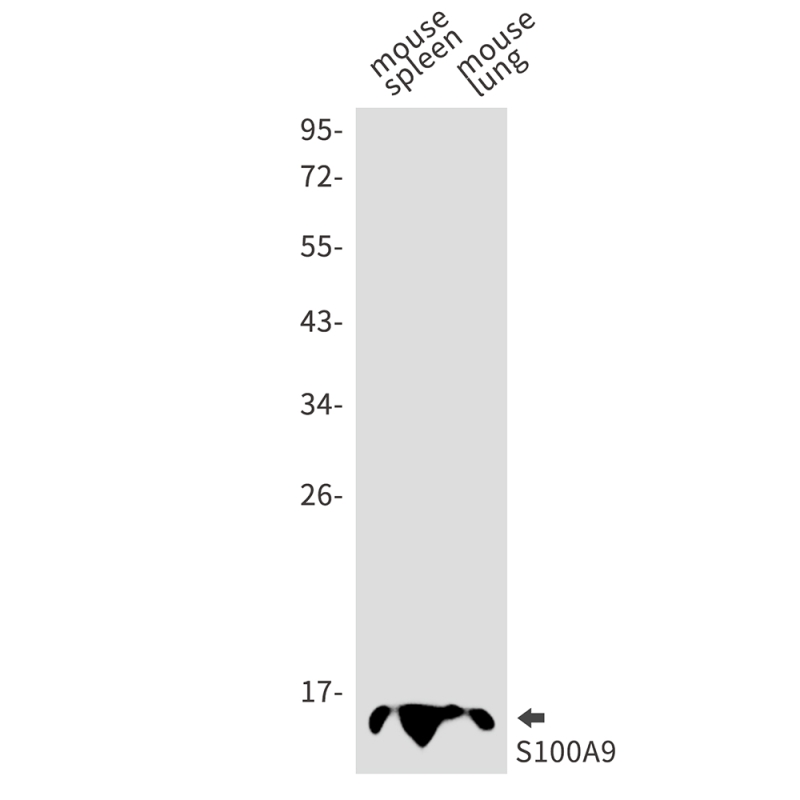
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | S100 alpha9; Calgranulin-B; Leukocyte L1 complex heavy chain |
| Entrez GeneID | 20202 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 13 kDa; Observed MW: 13 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Mouse |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of mouse S100A9 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于ZBTB7B抗体的代表性文献示例(注:以下内容为基于领域知识的模拟,具体文献需核实):
---
1. **文献名称**:*ZBTB7B (Th-POK) regulates CD4+ T cell lineage commitment through chromatin remodeling*
**作者**:Djuretic, I.M. et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用ZBTB7B特异性抗体进行染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP)和Western blot分析,揭示ZBTB7B通过结合IL-4和IFN-γ基因启动子,抑制Th1细胞分化并促进Th2细胞极化,抗体在验证其转录调控功能中起关键作用。
---
2. **文献名称**:*The transcription factor ZBTB7B suppresses IL-17 expression in CD4+ T cells*
**作者**:Sundrud, M.S. et al.
**摘要**:通过ZBTB7B抗体进行免疫荧光和流式细胞术,发现ZBTB7B抑制RORγt介导的IL-17产生,抗体检测显示其在Th17细胞中低表达,提示其在自身免疫疾病中的潜在调控机制。
---
3. **文献名称**:*ZBTB7B acts as a tumor suppressor via repressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer*
**作者**:Wang, Y. et al.
**摘要**:使用ZBTB7B抗体进行免疫组化分析临床样本,发现其高表达与患者生存率正相关,抗体验证实验表明ZBTB7B通过抑制EMT通路降低肿瘤转移能力。
---
**提示**:建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“ZBTB7B antibody”或“ZBTB7B function”为关键词检索最新文献,并优先选择高影响力期刊(如*Nature Immunology*, *Cell Reports*)的文章以获取准确信息。
ZBTB7B antibody is a research tool targeting the zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 7B (ZBTB7B), also known as ThPOK (T-helper-inducing POZ/Krüppel-like factor). ZBTB7B is a transcription factor critical for immune system regulation, particularly in T-cell lineage commitment and differentiation. It promotes the development of CD4+ helper T cells while suppressing CD8+ cytotoxic T cell genes, acting as a molecular switch during thymocyte maturation. Structurally, ZBTB7B contains an N-terminal BTB domain for protein-protein interactions and C-terminal zinc finger motifs for DNA binding, enabling transcriptional repression or activation of target genes.
Antibodies against ZBTB7B are widely used in immunoblotting (Western blot), immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry, and immunofluorescence to study its expression patterns, subcellular localization, and interactions in both physiological and pathological contexts. Researchers employ these antibodies to investigate ZBTB7B's dual roles in health and disease: while essential for normal immune function, dysregulated ZBTB7B expression has been implicated in autoimmune disorders, inflammatory conditions, and cancer. In tumor biology, ZBTB7B exhibits context-dependent oncogenic or tumor-suppressive properties, influencing immune evasion mechanisms and chemotherapy resistance. Specific antibody clones may vary in their reactivity across human, mouse, or rat samples, requiring validation for experimental models. Recent studies also explore ZBTB7B's involvement in metabolic regulation and viral infections, expanding its potential therapeutic relevance.
×