
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
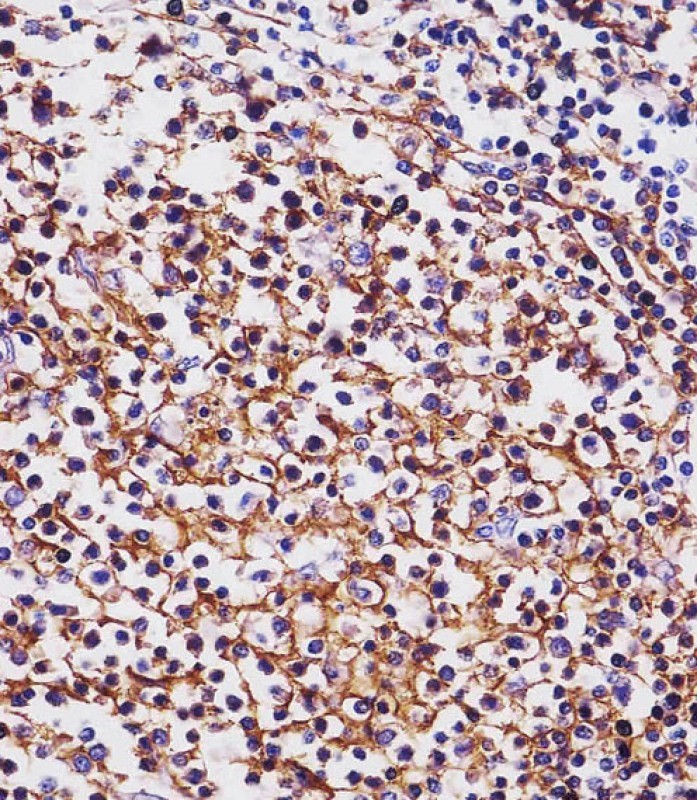
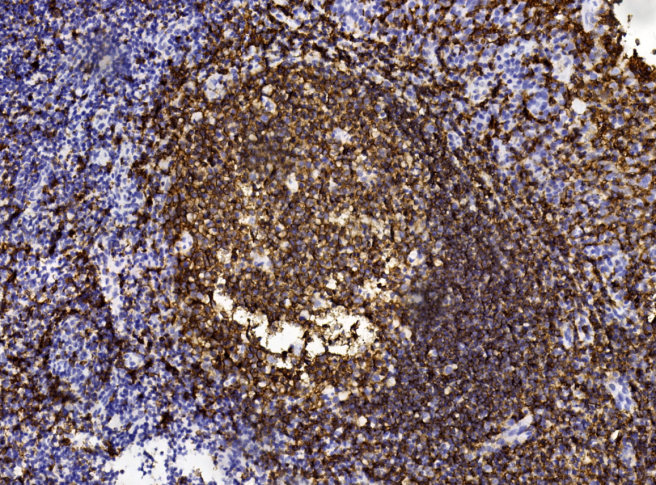
| IHC | 1/100-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | B-lymphocyte antigen CD20, B-lymphocyte surface antigen B1, Bp35, Leukocyte surface antigen Leu-16, Membrane-spanning 4-domains subfamily A member 1, CD20, MS4A1, CD20 |
| Entrez GeneID | 931 |
| WB Predicted band size | 33.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This MS4A1/CD20 antibody is generated from mice immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 266-294 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human MS4A1/CD20. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是关于MS4A1/CD20抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Rituximab (anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody) as single first-line therapy for patients with follicular lymphoma with a low tumor burden: clinical and molecular evaluation*
**作者**:Colombat P, et al.
**摘要**:该研究评估利妥昔单抗(抗CD20单抗)作为低肿瘤负荷滤泡性淋巴瘤患者一线单药治疗的疗效,显示其能诱导高缓解率并延长无进展生存期,同时降低治疗毒性。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Ofatumumab, a human anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis*
**作者**:Taylor PC, et al.
**摘要**:探讨第二代抗CD20抗体Ofatumumab在类风湿性关节炎中的疗效,证明其通过高效结合CD20并增强补体依赖性细胞毒性(CDC),显著改善患者症状和疾病活动度。
---
3. **文献名称**:*CD20 as a target for therapeutic type I and II monoclonal antibodies*
**作者**:Cragg MS, et al.
**摘要**:系统综述CD20作为治疗靶点的机制,比较I型(如利妥昔单抗)和II型(如Obinutuzumab)抗体的作用差异,强调后者通过增强细胞直接杀伤作用(如非凋亡性死亡)提高疗效。
---
如需扩展,可补充耐药机制或新型双特异性抗体研究文献。
MS4A1. also known as CD20. is a cell surface protein encoded by the MS4A1 gene, primarily expressed on mature B lymphocytes and a key marker for B-cell identification. Discovered in the 1980s, CD20 plays a role in regulating calcium influx during B-cell receptor signaling, though its exact physiological function remains partially understood. Its restricted expression on B cells—absent on stem cells or plasma cells—makes it an attractive therapeutic target for B-cell-related disorders.
CD20 antibodies revolutionized oncology and immunology. Rituximab, the first FDA-approved monoclonal anti-CD20 antibody (1997), binds to CD20 and depletes B cells via antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), and direct apoptosis. It became a cornerstone for treating B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHL), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), and autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis. Subsequent generations of anti-CD20 antibodies, such as obinutuzumab (type II, glycoengineered for enhanced ADCC) and ofatumumab (targeting a distinct epitope with improved CDC), were developed to overcome resistance or improve efficacy. More recently, ocrelizumab gained approval for multiple sclerosis, highlighting CD20's role in autoimmune pathology.
Despite their success, anti-CD20 therapies carry risks like infusion reactions and increased infection susceptibility. Ongoing research focuses on optimizing dosing, combination therapies, and novel agents like bispecific antibodies or CAR-T cells targeting CD20. expanding their therapeutic potential.
×