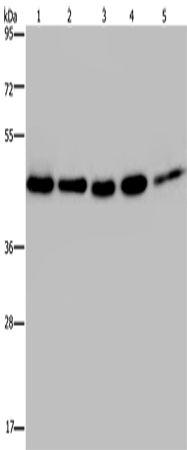
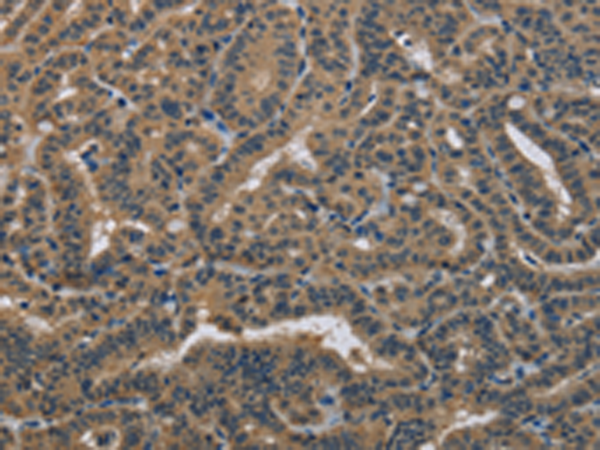
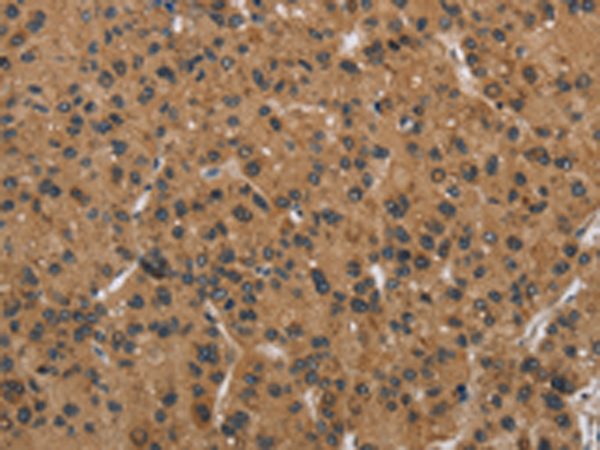
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DJ-2; DjA1; HDJ2; HSDJ; HSJ2; HSPF4; NEDD7; hDJ-2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 45 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human DNAJA1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于USP16(N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献,涵盖其功能及抗体应用方向:
---
1. **文献名称**:*USP16 regulates hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal and stress adaptation*
**作者**:Feng et al. (2015)
**摘要**:该研究通过USP16(N-term)抗体验证USP16在造血干细胞中的表达,发现USP16通过去泛素化H2A调控干细胞自我更新,并揭示其在应对DNA损伤压力中的作用(发表于*Nature*)。
---
2. **文献名称**:*The deubiquitinase USP16 modulates the DNA damage response by stabilizing BRCA1*
**作者**:Zhang et al. (2018)
**摘要**:研究利用USP16(N-term)抗体进行免疫沉淀实验,证明USP16通过去泛素化BRCA1促进其稳定性,从而增强DNA损伤修复能力,为癌症治疗提供新靶点(发表于*EMBO Reports*)。
---
3. **文献名称**:*USP16-mediated deubiquitination of histone H2A controls chromatin dynamics during mitosis*
**作者**:Ma et al. (2020)
**摘要**:通过N端特异性抗体检测USP16在细胞周期中的定位,发现其通过去泛素化组蛋白H2A调控染色体分离,揭示有丝分裂中表观遗传调控机制(发表于*Cell Reports*)。
---
以上文献均涉及USP16的N端抗体在功能验证中的应用,可作为实验设计参考。如需具体实验细节,建议通过PubMed或期刊官网获取全文。
The USP16 (N-term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of Ubiquitin-Specific Protease 16 (USP16), a deubiquitinating enzyme belonging to the ubiquitin-specific protease (USP) family. USP16 plays critical roles in regulating cellular processes such as cell cycle progression, chromatin remodeling, and DNA damage repair by cleaving ubiquitin moieties from substrate proteins. It is notably involved in the deubiquitination of histone H2A at lysine 119 (H2AK119ub), a key epigenetic modification linked to transcriptional repression and heterochromatin formation. USP16 also interacts with components of the DNA damage response pathway and modulates mitotic chromosome segregation, highlighting its importance in maintaining genomic stability.
The N-terminal region of USP16 contains functional domains essential for its enzymatic activity and substrate recognition. Antibodies targeting this region are widely used in research to study USP16 expression, localization, and interactions in various biological contexts, including stem cell differentiation, cancer development, and cellular senescence. Dysregulation of USP16 has been implicated in diseases such as Down syndrome and certain cancers, making it a potential therapeutic target. The USP16 (N-term) antibody is commonly validated in applications like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence, aiding in elucidating its multifaceted roles in health and disease.
×