
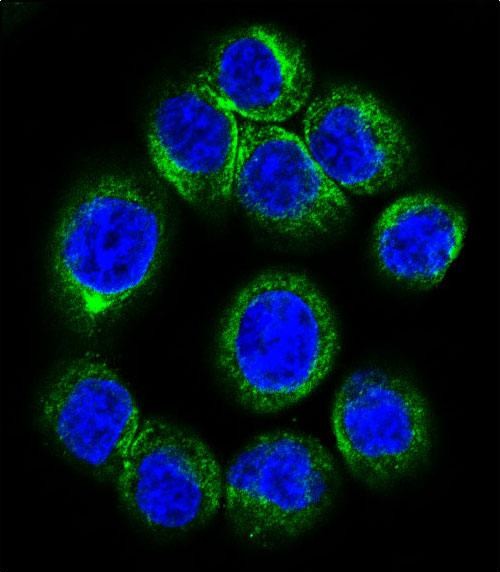
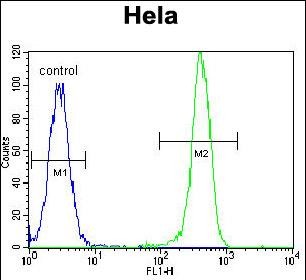
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Erythropoietin receptor, EPO-R, EPOR |
| Entrez GeneID | 2057 |
| WB Predicted band size | 55.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This EPOR antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 329-357 amino acids from the Central region of human EPOR. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于EPOR抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**: *Erythropoietin receptor: Structure, signaling and targeted therapies*
**作者**: Jelkmann W.
**摘要**: 综述了EPOR的结构、信号传导机制及其在贫血治疗中的作用,探讨了靶向EPOR的抗体药物在调节红细胞生成和癌症治疗中的潜在应用,并强调了受体激活异常与肿瘤进展的关联。
2. **文献名称**: *Crystal structure of human erythropoietin complexed with its receptor*
**作者**: Syed RS 等.
**摘要**: 通过X射线晶体学解析了EPO与EPOR胞外结构域的复合物结构,揭示了抗体结合的关键表位区域,为开发靶向EPOR的抗体药物(如拮抗剂或激动剂)提供了结构基础。
3. **文献名称**: *Anti-EPOR antibodies as a cause of pure red cell aplasia*
**作者**: Casadevall N 等.
**摘要**: 报道了接受重组EPO治疗的患者体内产生抗EPOR自身抗体,导致纯红细胞再生障碍性贫血(PRCA),阐明了抗体通过阻断EPO-EPOR结合抑制红细胞生成的病理机制。
4. **文献名称**: *Targeting EPOR in leukemia through antibody-mediated inhibition*
**作者**: Sinclair AM 等.
**摘要**: 研究证明EPOR在某些白血病细胞中异常激活,使用特异性抗体阻断EPOR信号可抑制癌细胞增殖,为白血病靶向治疗提供了实验依据。
The erythropoietin receptor (EPOR) is a transmembrane protein that mediates the biological effects of erythropoietin (EPO), a glycoprotein hormone essential for red blood cell production. Belonging to the type I cytokine receptor family, EPOR activates intracellular signaling pathways, primarily JAK-STAT, upon EPO binding, promoting erythroid progenitor cell survival, proliferation, and differentiation. EPOR is predominantly expressed in erythroid tissues but has also been detected in non-hematopoietic cells, including neurons, endothelial cells, and certain cancer cells, suggesting roles beyond erythropoiesis.
EPOR antibodies are critical tools for studying receptor expression, localization, and function in both physiological and pathological contexts. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry to investigate EPOR's involvement in diseases such as anemia, myeloproliferative disorders, and cancers. Some tumors aberrantly express EPOR, potentially contributing to cell survival and therapy resistance, making EPOR a biomarker of interest in oncology research. Additionally, EPOR-targeting antibodies have therapeutic potential, though their clinical application remains limited due to complexities in receptor signaling and tissue-specific effects. Research continues to clarify EPOR's dual roles in health and disease, emphasizing the importance of high-specificity antibodies for accurate experimental and diagnostic outcomes.
×