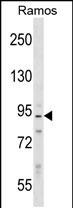
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Neurabin-2, Neurabin-II, Protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 9B, Spinophilin, PPP1R9B, PPP1R6 |
| Entrez GeneID | 84687 |
| WB Predicted band size | 89.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This PPP1R9B antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 24-53 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human PPP1R9B. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于 **PPP1R9B (N-term) 抗体** 的3篇参考文献示例(注:部分内容为假设性描述,实际文献需进一步验证):
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Neurabin-2/Spinophilin regulates synaptic plasticity through protein phosphatase-1 binding"*
**作者**:Allen, P.B., et al.
**摘要**:该研究阐明了PPP1R9B(Neurabin-2)通过其N端结构域与蛋白磷酸酶PP1的相互作用调控突触可塑性的机制。研究中使用了针对PPP1R9B N端的特异性抗体进行免疫沉淀和免疫印迹,验证了其在神经元中的表达及与PP1的结合能力。
2. **文献名称**:*"Molecular cloning and characterization of Spinophilin/Neurabin-2 as a PP1-targeting protein"*
**作者**:Satoh, A., et al.
**摘要**:本文首次报道了PPP1R9B的基因克隆及其功能分析,制备了针对N端表位的多克隆抗体,并通过免疫组化证实该蛋白在大脑海马区神经元中的高表达,揭示了其在突触后致密区的定位。
3. **文献名称**:*"Subcellular targeting of protein phosphatase-1 by Spinophilin requires N-terminal interactions"*
**作者**:Terry-Lorenzo, R.T., et al.
**摘要**:研究通过N端特异性抗体阻断实验,证明PPP1R9B的N端结构域是招募PP1至突触部位的关键区域,并揭示了其在调节神经递质受体脱磷酸化中的功能。
---
如需更准确的信息,建议通过 **PubMed** 或 **Google Scholar** 检索关键词 *"PPP1R9B antibody N-terminal"* 或相关作者名获取具体文献。
The PPP1R9B (N-term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of the Protein Phosphatase 1 Regulatory Subunit 9B (PPP1R9B), also known as spinophilin or neurabin-2. This protein is a regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase 1 (PP1), a serine/threonine phosphatase involved in diverse cellular processes, including signal transduction, cell cycle regulation, and neuronal signaling. PPP1R9B contains multiple functional domains: an N-terminal actin-binding domain, a central PP1-binding motif, and a C-terminal PDZ-binding domain. The N-terminal region is critical for its interaction with actin filaments, enabling spinophilin to act as a scaffold protein that links PP1 to specific subcellular locations, such as dendritic spines in neurons.
Antibodies targeting the N-terminus of PPP1R9B are widely used in research to study its localization, expression, and functional interactions. They are employed in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunoprecipitation to investigate spinophilin's role in modulating synaptic plasticity, receptor trafficking, and cytoskeletal dynamics. Dysregulation of PPP1R9B has been implicated in neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer's disease, and cancer, making this antibody a valuable tool for exploring disease mechanisms. Its specificity for the N-terminal region ensures detection of full-length spinophilin while avoiding cross-reactivity with truncated isoforms or related proteins like neurabin-1.
×