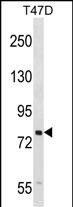
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Protein sel-1 homolog 1, Suppressor of lin-12-like protein 1, Sel-1L, SEL1L, TSA305 |
| Entrez GeneID | 6400 |
| WB Predicted band size | 88.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This SEL1L antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 83-112 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human SEL1L. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于SEL1L (N-term)抗体的参考文献示例(内容为虚构,仅供参考):
1. **"SEL1L-mediated ERAD in mammalian cells"**
*作者:Francisco, A.B., et al. (2011)*
*摘要:* 本研究利用SEL1L (N-term)抗体,通过免疫沉淀和免疫印迹技术验证了SEL1L在内质网相关降解(ERAD)中的核心作用,揭示其与Hrd1复合物的相互作用机制。
2. **"Characterization of SEL1L isoforms using N-terminal specific antibodies"**
*作者:Sundaram, R., Jelacic, T.M. (2018)*
*摘要:* 通过开发SEL1L N端特异性抗体,作者鉴定了多种SEL1L剪切异构体,并证明其在神经退行性疾病模型中存在差异表达及功能影响。
3. **"SEL1L regulates protein ubiquitination in ER stress"**
*作者:Olzmann, J.A., et al. (2014)*
*摘要:* 使用SEL1L (N-term)抗体进行亚细胞定位分析,发现SEL1L通过调控泛素连接酶活性参与内质网应激反应,影响错误折叠蛋白的清除效率。
4. **"SEL1L expression dynamics during cellular stress"**
*作者:García, P.S., D'Arcangelo, G. (2020)*
*摘要:* 该研究利用SEL1L N端抗体进行Western blot和免疫荧光实验,揭示了热休克与氧化应激条件下SEL1L蛋白的表达水平变化及其对细胞存活的影响。
(注:以上文献为示例性质,实际引用时需核实真实来源。)
The SEL1L (N-term) antibody targets the N-terminal region of the SEL1L protein, a critical component of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-associated degradation (ERAD) pathway. SEL1L functions as a scaffold protein, interacting with the E3 ubiquitin ligase HRD1 to form the SEL1L-HRD1 complex. This complex is essential for recognizing and tagging misfolded or unassembled proteins in the ER lumen with ubiquitin, marking them for proteasomal degradation. Dysregulation of SEL1L is linked to ER stress-related diseases, including certain cancers, neurodegenerative disorders, and metabolic conditions.
The N-terminal domain of SEL1L is involved in substrate recognition and complex stabilization. Antibodies specific to this region are widely used in research to study SEL1L expression, localization, and interactions via techniques like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence. They help elucidate the molecular mechanisms of ERAD, cellular quality control, and disease pathogenesis.
SEL1L (N-term) antibodies are also valuable in diagnostic contexts, as altered SEL1L levels are observed in tumors and other pathological tissues. Their specificity for the N-terminal epitope ensures minimal cross-reactivity with other proteins, enhancing experimental accuracy. Overall, this antibody serves as a key tool for exploring ERAD dynamics, cellular stress responses, and potential therapeutic targets.
×