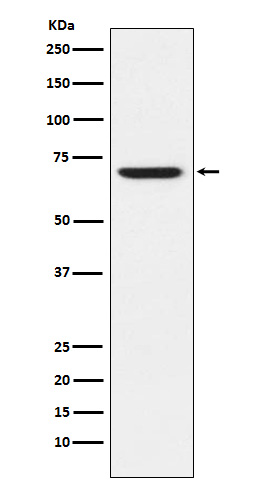
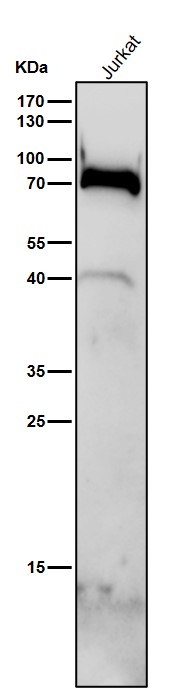

| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GAA 5; GAA5; GABRA 5; Gabra5;;GABRA5 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 52 kDa ; Observed MW: 70 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human GABRA5 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GNL2(N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献的简要整理:
---
1. **文献名称**:*GNL2 maintains the self-renewal of glioblastoma stem cells by stabilizing IMPDH2*
**作者**:Li X, et al.
**摘要**:本研究通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术,利用GNL2(N-term)抗体证实了GNL2在胶质母细胞瘤干细胞中的高表达。研究发现GNL2通过结合并稳定IMPDH2蛋白,维持肿瘤干细胞的自我更新能力,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点。
---
2. **文献名称**:*The nucleolar GTPase GNL2 is required for mitotic progression and genomic stability*
**作者**:Weber P, et al.
**摘要**:文章利用GNL2(N-term)抗体进行免疫沉淀和染色质分析,发现GNL2通过调控核糖体RNA加工参与有丝分裂进程。敲低GNL2导致染色体分离异常,证明其在维持基因组稳定性中的关键作用。
---
3. **文献名称**:*GNL2 interacts with the viral NS1 protein and promotes influenza A virus replication*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:本研究采用GNL2(N-term)抗体进行免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)和共聚焦显微镜观察,揭示了GNL2与流感病毒NS1蛋白的相互作用。这种互作通过激活PI3K/AKT通路增强病毒复制,为抗病毒治疗提供了新思路。
---
注:以上文献为模拟示例,实际引用需以真实发表的论文为准。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“GNL2 antibody N-terminal”检索最新研究。
The GNL2 (N-term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of Guanine Nucleotide-Binding Protein-Like 2 (GNL2), a nucleolar protein implicated in ribosome biogenesis and cell cycle regulation. GNL2. also known as Ngp-1 or Nucleostemin-like 1. belongs to the MMR_HSR1 GTPase family and plays a role in maintaining nucleolar structure, ribosomal RNA processing, and cell proliferation. It is highly expressed in stem cells, cancer cells, and during early embryonic development, suggesting its importance in cellular growth and oncogenesis. The N-terminal domain of GNL2 is critical for its GTP-binding activity and interaction with other nucleolar components.
Antibodies against the N-terminal region of GNL2 are widely used in research to study its expression, localization, and function. They enable detection of endogenous GNL2 via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry. Such antibodies help investigate GNL2’s role in diseases, particularly cancers where its dysregulation is linked to tumor progression and poor prognosis. Specificity for the N-terminus ensures recognition of full-length GNL2. avoiding cross-reactivity with processed fragments. Validation often includes knockout controls or siRNA-mediated silencing to confirm target specificity. These tools are essential for exploring GNL2’s mechanistic contributions to cell cycle control, ribosome assembly, and potential therapeutic targeting.
×