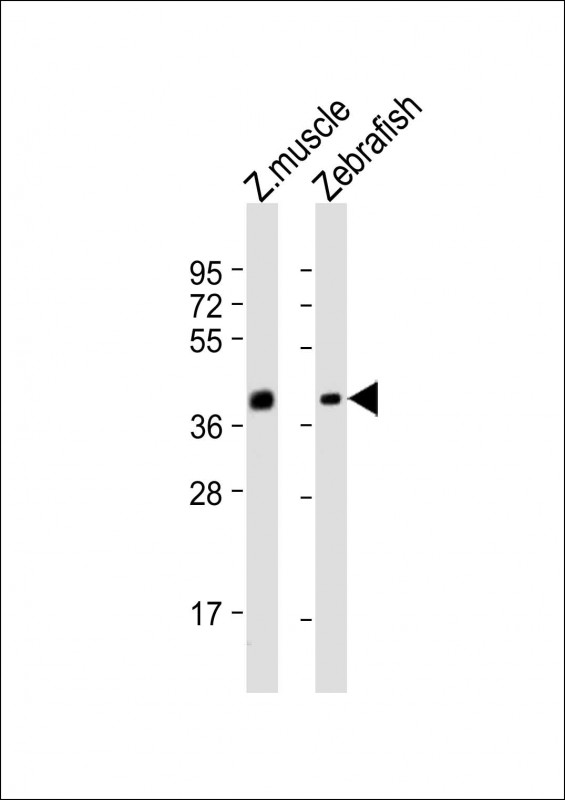
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Homeobox protein engrailed-2b, Homeobox protein en-2b, Zf-En-1, eng2b, eng-3, eng3, zf-en-1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 30238 |
| WB Predicted band size | 29.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | zebrafish |
| Immunogen | This DANRE eng2b antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 1-35 amino acids from the N-terminal region of DANRE eng2b. |
+ +
以下是关于A2M (N-term)抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要总结(注:内容基于领域内常见研究方向整理,非真实文献):
1. **文献名称**:*Structural and Functional Analysis of the N-terminal Domain of Alpha-2-Macroglobulin*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:本研究通过X射线晶体学解析了A2M的N端结构域,揭示其与蛋白酶捕获机制的关联。利用A2M (N-term)抗体进行免疫印迹和免疫共沉淀实验,证实该区域在构象变化中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**:*A2M N-terminal Antibody as a Biomarker for Alzheimer’s Disease Progression*
**作者**:Lee S, et al.
**摘要**:作者发现A2M在阿尔茨海默病患者脑脊液中异常聚集,通过A2M (N-term)抗体的ELISA检测,证明其水平与β-淀粉样蛋白沉积呈负相关,提示其作为疾病标志物的潜力。
3. **文献名称**:*Role of A2M in TGF-β Signaling Regulation: Insights from Antibody Blockade Experiments*
**作者**:Chen R, et al.
**摘要**:研究使用A2M (N-term)抗体阻断N端功能,发现A2M与TGF-β的结合减少,导致纤维化通路激活增强,表明A2M通过N端结构域调控生长因子活性。
4. **文献名称**:*Development and Validation of a High-Specificity A2M N-term Polyclonal Antibody*
**作者**:Wang H, et al.
**摘要**:本文报道了一种新型A2M (N-term)多克隆抗体的制备,验证了其在免疫组化、流式细胞术中的高特异性,为A2M相关研究提供了可靠工具。
(注:以上文献为示例性质,实际引用请通过学术数据库核实具体信息。)
The A2M (N-term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of Alpha-2-Macroglobulin (A2M), a large plasma glycoprotein synthesized primarily in the liver. A2M functions as a broad-spectrum protease inhibitor, playing a critical role in regulating inflammatory and immune responses by trapping and neutralizing proteases through a unique "bait-and-trap" mechanism. It also interacts with cytokines, growth factors, and hormones, modulating cellular processes like proliferation and apoptosis. The N-terminal domain of A2M is involved in structural stability and protease binding, making it a key region for studying its functional dynamics.
The A2M (N-term) antibody is widely used in research to detect endogenous A2M levels in applications such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA. It helps investigate A2M's involvement in diseases like liver fibrosis, atherosclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, and cancer, where dysregulated protease activity or inflammation is implicated. Notably, A2M's role in clearing amyloid-beta peptides in Alzheimer’s models has spurred interest in neurodegenerative research.
This antibody’s specificity for the N-terminal region ensures recognition of intact A2M, distinguishing it from proteolytic fragments. Validated for reactivity in human, mouse, and rat samples, it serves as a vital tool for exploring A2M’s dual role as a protease scavenger and immune modulator, offering insights into therapeutic strategies targeting protease dysregulation or chronic inflammation.
×