
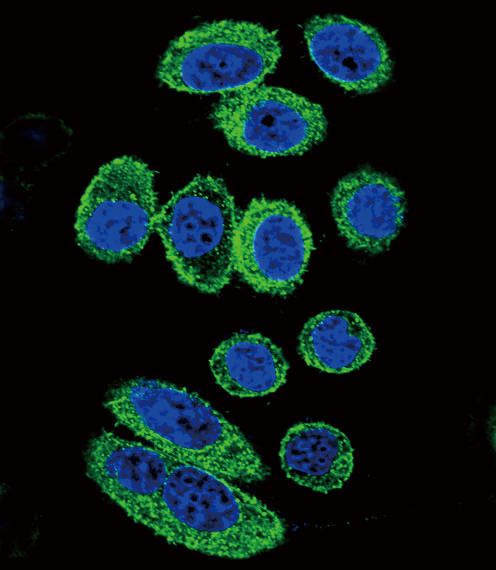
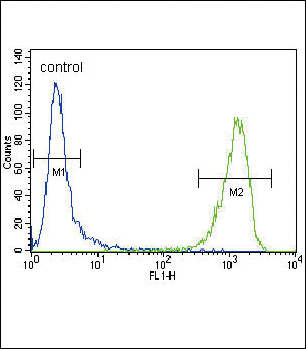
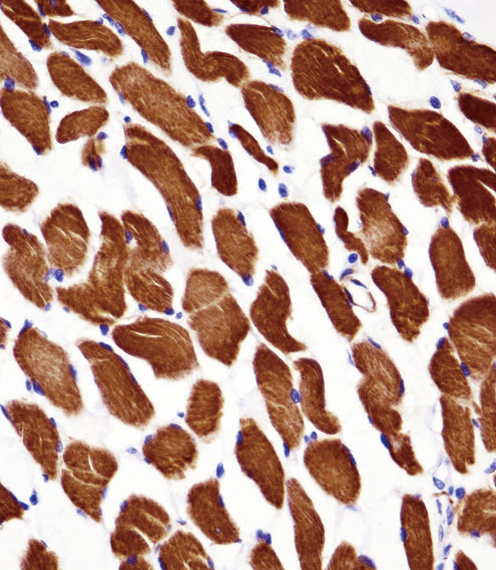
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Actin, alpha skeletal muscle, Alpha-actin-1, ACTA1, ACTA |
| Entrez GeneID | 58 |
| WB Predicted band size | 42.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This ACTA1/Alpha-actin antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 346-375 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human ACTA1/Alpha-actin. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于ACTA1/Alpha-actin抗体的代表性文献摘要:
1. **文献名称**:*Mutations in the skeletal muscle α-actin gene (ACTA1) cause congenital nemaline myopathy*
**作者**:Nowak KJ. et al. (1999)
**摘要**:首次报道ACTA1基因突变与线状肌病的关联,通过抗体免疫染色发现患者肌肉中α-actin异常聚集,建立了ACTA1突变与肌肉功能障碍的直接联系。
2. **文献名称**:*Alpha-actin-1 related myopathies: Pathology and mechanisms*
**作者**:Laing N.G. et al. (2009)
**摘要**:系统分析了ACTA1突变导致的肌病病理特征,利用特异性抗体揭示突变α-actin在肌纤维中的错误定位及其对肌节结构的破坏机制。
3. **文献名称**:*Antibody-based profiling of skeletal muscle actin isoforms in neuromuscular disorders*
**作者**:Feng J.J. & Marini J.F. (2014)
**摘要**:开发了针对ACTA1的特异性单克隆抗体,验证其在肌肉活检样本中的诊断价值,成功区分α-actin与其他肌动蛋白亚型,提升先天性肌病的分型准确性。
注:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用时需核对具体文献信息。如需最新研究,建议在PubMed或Web of Science以“ACTA1 antibody”、“alpha-actin skeletal muscle”为关键词检索。
The ACTA1 gene encodes alpha-skeletal muscle actin (α-actin), a critical component of the contractile apparatus in skeletal muscle. As a member of the actin protein family, α-actin polymerizes into thin filaments that interact with myosin to enable muscle contraction. Antibodies targeting ACTA1/α-actin are widely used in research and diagnostics to study skeletal muscle structure, function, and pathology. These antibodies enable visualization of α-actin distribution via techniques like immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, and Western blotting, helping assess muscle integrity in conditions such as muscular dystrophies, myopathies, or sarcopenia.
ACTA1 mutations are linked to congenital myopathies, including nemaline myopathy, actin aggregate myopathy, and congenital fiber-type disproportion. Antibodies against α-actin aid in characterizing these disorders by identifying abnormal protein aggregation, mislocalization, or reduced expression in muscle biopsies. They also serve as markers for muscle differentiation in developmental studies or regenerative research, as α-actin expression rises during myoblast fusion and maturation.
Commercially available ACTA1/α-actin antibodies are typically validated for species cross-reactivity (human, mouse, rat) and application-specific performance. Some exhibit cross-reactivity with cardiac α-actin (ACTC1) due to high sequence homology, necessitating careful experimental controls. Their utility extends to preclinical models, such as assessing muscle-specific therapies or gene editing outcomes in muscular diseases. Overall, ACTA1/α-actin antibodies remain indispensable tools for advancing neuromuscular disease research and diagnostic precision.
×