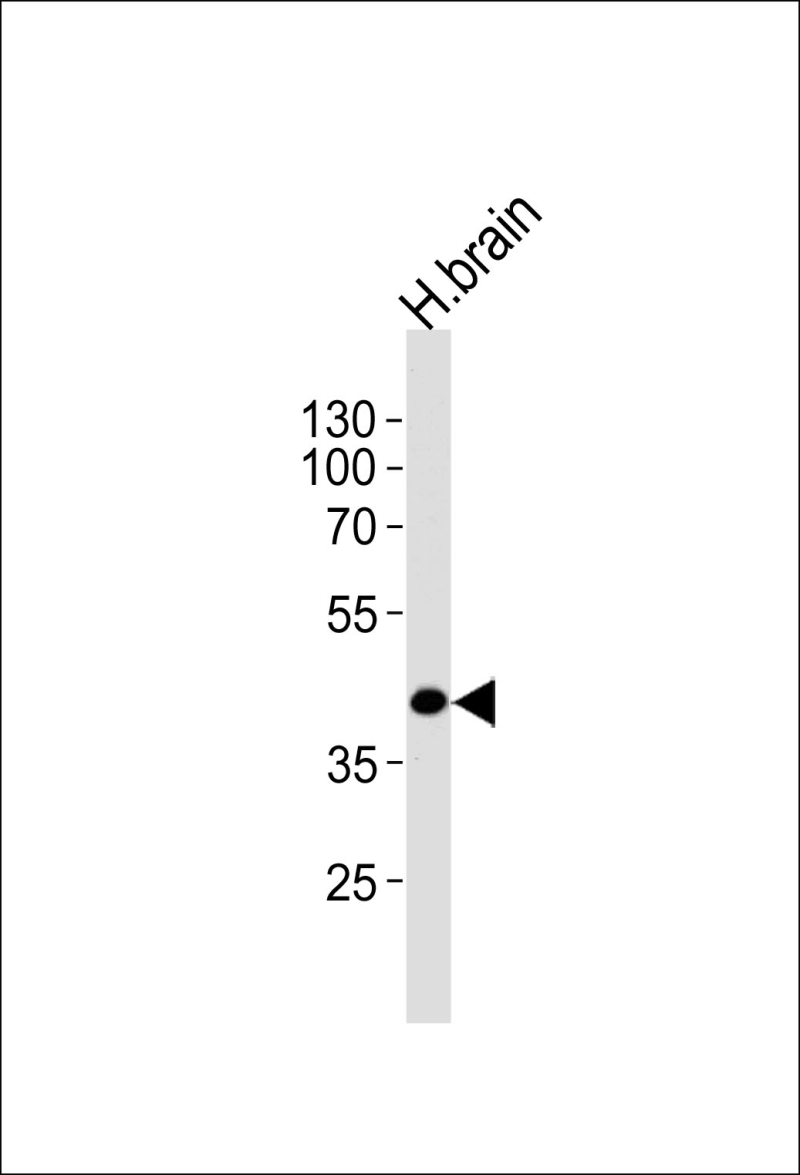
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
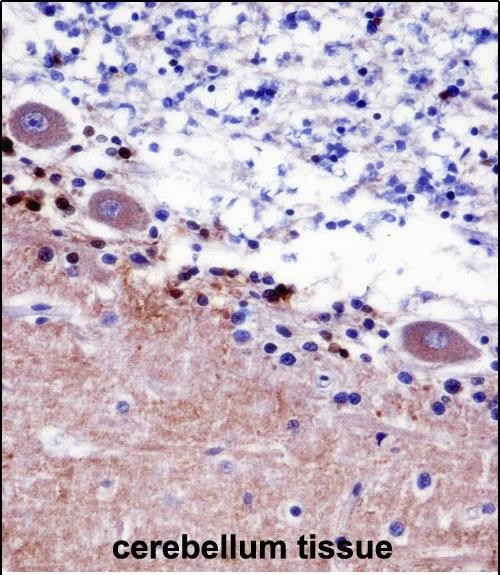
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Septin-5, Cell division control-related protein 1, CDCrel-1, Peanut-like protein 1, SEPT5, PNUTL1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 5413 |
| WB Predicted band size | 42.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This SEPT5 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 1-30 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human SEPT5. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于SEPT5(N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献的简要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Nedd5. a mammalian septin, is a novel cytoskeletal component interacting with actin-based structures"*
**作者**:Kinoshita, M. et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次表征了SEPT5(Nedd5)的N端结构域,并生成了针对其N端的特异性抗体。通过免疫荧光和免疫印迹实验,发现SEPT5与肌动蛋白细胞骨架相互作用,提示其在细胞分裂和胞质分裂中的潜在作用。
2. **文献名称**:*"Septin 5 interacts with the Parkinson's disease-associated protein Parkin"*
**作者**:Xue, J. et al.
**摘要**:利用SEPT5(N-term)抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,研究发现SEPT5的N端结构域与帕金森病相关蛋白Parkin直接结合,暗示SEPT5在神经元囊泡运输和神经退行性疾病中的功能异常机制。
3. **文献名称**:*"Aberrant septin 5 expression in Alzheimer's disease brains"*
**作者**:Ihara, M. et al.
**摘要**:通过SEPT5(N-term)抗体的免疫组化分析,发现阿尔茨海默病患者脑组织中SEPT5蛋白在突触区域的异常聚集,提示其可能参与β-淀粉样蛋白病理过程及突触功能障碍。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例性概括,实际引用时需核实具体研究内容及抗体应用细节。如需更近期研究,建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以“SEPT5 antibody N-terminal”为关键词进一步检索。
The SEPT5 (N-term) antibody specifically targets the N-terminal region of the Septin 5 protein, a member of the septin family involved in diverse cellular processes, including cytokinesis, vesicle trafficking, and cytoskeletal organization. SEPT5. encoded by the *SEPTIN5* gene, contains a conserved GTP-binding domain and interacts with other septins to form filamentous structures. It is highly expressed in the brain, where it regulates neurotransmitter release and synaptic plasticity, and has been implicated in neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and schizophrenia. Aberrant SEPT5 expression is also linked to cancers, particularly leukemia, where chromosomal translocations involving *SEPTIN5* contribute to oncogenesis.
The N-terminal-specific antibody is crucial for distinguishing SEPT5 from other septin family members due to sequence variability in this region. It enables the detection of full-length SEPT5 and potential cleavage products in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Researchers use this antibody to study SEPT5's role in disease mechanisms, protein interactions, and subcellular localization. Validation studies often confirm its specificity through knockdown/knockout controls or peptide blocking assays. Understanding SEPT5 dynamics via this antibody provides insights into its pathological contributions and therapeutic potential.
×