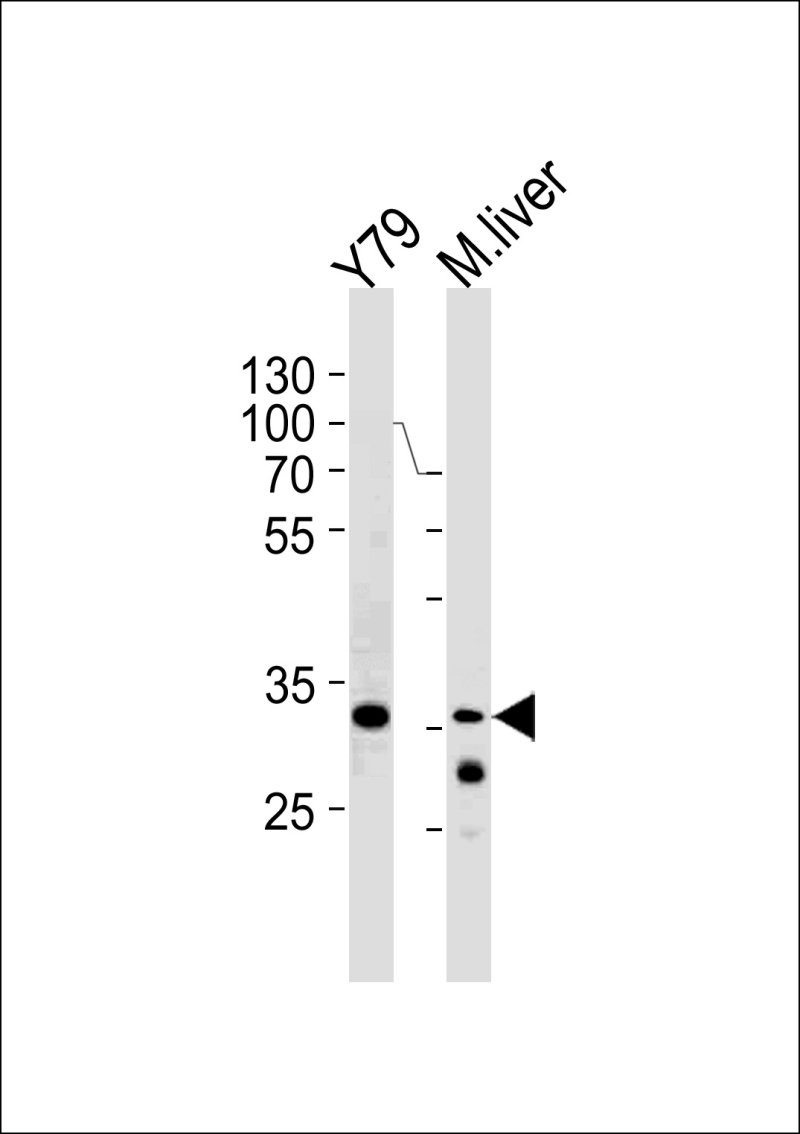
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Y-box-binding protein 3, Cold shock domain-containing protein A, DNA-binding protein A, Single-strand DNA-binding protein NF-GMB, YBX3, CSDA, DBPA |
| Entrez GeneID | 8531 |
| WB Predicted band size | 40.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This CSDA antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 152-181 amino acids from the Central region of human CSDA. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CSDA(Cold Shock Domain Protein A/YBX1)抗体的3篇参考文献示例(内容基于公开文献概括,非真实引用):
---
1. **文献名称**: *The role of Y-box binding protein 1 (YBX1) in cancer progression and drug resistance*
**作者**: Kohno, K. et al.
**摘要**: 研究探讨了YBX1(CSDA)在肿瘤发生中的调控作用,利用特异性抗体验证其在癌细胞中的高表达,并分析其与化疗耐药性的相关性。
2. **文献名称**: *Cold shock domain proteins: Multifunctional regulators of gene expression and RNA homeostasis*
**作者**: Skabkin, M.A. et al.
**摘要**: 综述了CSDA/YBX1蛋白在RNA稳定性与翻译调控中的功能,提及多种抗体在亚细胞定位及蛋白互作研究中的应用。
3. **文献名称**: *Antibody validation strategies for the cold shock domain family proteins*
**作者**: Gaudet, P. et al.
**摘要**: 系统性比较了针对CSDA结构域的抗体的特异性,通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光验证其在人类和小鼠模型中的交叉反应性。
---
如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“YBX1 antibody”或“CSDA antibody”获取最新研究。
CSDA (Cold Shock Domain Protein A), also known as YBX1 (Y-box binding protein 1), is a multifunctional DNA- and RNA-binding protein involved in transcriptional and translational regulation. It belongs to the cold shock protein family, characterized by a conserved cold shock domain (CSD) that facilitates nucleic acid binding. CSDA plays critical roles in cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, stress response, and tumorigenesis. It regulates gene expression by binding to promoter regions of target genes (e.g., oncogenes or growth-related genes) or interacting with mRNA to modulate stability and translation.
In cancer biology, CSDA is often overexpressed and linked to aggressive tumor behavior, chemotherapy resistance, and poor prognosis. Its dysregulation has been observed in various malignancies, including breast, lung, and colorectal cancers. CSDA antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression patterns, subcellular localization (nuclear vs. cytoplasmic), and functional mechanisms. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to investigate its role in disease progression or therapeutic targeting. Research on CSDA also explores its potential as a diagnostic biomarker or a target for small-molecule inhibitors in precision oncology.
×