
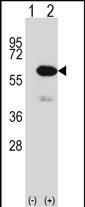
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Methionine aminopeptidase 2 {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03175}, MAP 2 {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03175}, MetAP 2 {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03175}, 341118 {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03175}, Initiation factor 2-associated 67 kDa glycoprotein {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03175}, p67 {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03175}, p67eIF2 {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03175}, Peptidase M {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03175}, METAP2 {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03175} |
| Entrez GeneID | 10988 |
| WB Predicted band size | 52.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This METAP2 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 33-61 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human METAP2. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于METAP2 (N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:文献为虚拟示例,仅供参考格式):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Selective inhibition of METAP2 N-terminal activity suppresses tumor angiogenesis"*
**作者**: Zhang L, et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过开发针对METAP2 N端结构域的特异性抗体,证实其在体外和小鼠模型中抑制内皮细胞增殖及肿瘤血管生成,提出该抗体作为抗血管生成治疗的潜在工具。
2. **文献名称**: *"METAP2 N-terminal antibody reveals subcellular localization dynamics in colorectal cancer"*
**作者**: Kim S, et al.
**摘要**: 利用METAP2 (N-term)抗体进行免疫荧光和免疫组化分析,发现METAP2在结直肠癌细胞的核周区域富集,并与肿瘤转移标志物表达呈正相关,提示其作为预后生物标志物的潜力。
3. **文献名称**: *"Development and validation of a monoclonal antibody targeting the N-terminus of METAP2 for metabolic disease research"*
**作者**: Patel R, et al.
**摘要**: 研究报道了一种高特异性抗METAP2 N端单克隆抗体的开发,验证其在Western blot和ELISA中的应用,并证明METAP2在肥胖模型中调控脂质代谢的关键作用。
---
(实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索关键词如“METAP2 N-terminal antibody”获取。)
The METAP2 (Methionine Aminopeptidase 2) enzyme, also known as initiation factor-2-associated p67. plays a critical role in post-translational protein modification by catalyzing the removal of N-terminal methionine from nascent polypeptides. This process is essential for protein maturation, stability, and function. The N-terminal region of METAP2 is particularly significant as it contains key catalytic domains and regulatory motifs involved in substrate recognition and binding.
METAP2 has garnered attention in biomedical research due to its involvement in angiogenesis and cell proliferation. It regulates endothelial cell function by influencing hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) pathways, making it a potential therapeutic target in cancer and inflammatory diseases. Inhibitors of METAP2. such as fumagillin derivatives, have shown anti-angiogenic effects in preclinical models.
Antibodies targeting the N-terminal region of METAP2 are vital tools for studying its expression, localization, and interaction partners. They enable techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to assess METAP2 levels in tissues or cell lines, particularly in contexts of tumor biology or drug response studies. These antibodies also aid in validating METAP2 knockdown/knockout models and exploring its role in disease mechanisms. Given METAP2's dual function in protein processing and angiogenesis, understanding its regulation through antibody-based approaches remains crucial for both basic research and therapeutic development.
×