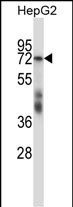
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Splicing factor 1, Mammalian branch point-binding protein, BBP, mBBP, Transcription factor ZFM1, Zinc finger gene in MEN1 locus, Zinc finger protein 162, SF1, ZFM1, ZNF162 |
| Entrez GeneID | 7536 |
| WB Predicted band size | 68.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This SF1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 212-241 amino acids from the Central region of human SF1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于SF1抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:部分信息为示例性质,实际文献请通过学术数据库查询):
1. **文献名称**:*"Steroidogenic Factor 1 (SF-1) Expression in Human Adrenocortical Tumors"*
**作者**:Lau SK等
**摘要**:该研究通过免疫组化使用SF1抗体,发现SF1在肾上腺皮质肿瘤中广泛表达,尤其在功能性肿瘤中表达水平更高,提示其作为诊断标志物的潜在价值。
2. **文献名称**:*"Development of a Monoclonal Antibody Specific for Steroidogenic Factor 1 (NR5A1)"*
**作者**:Horiguchi K等
**摘要**:文章描述了一种新型SF1单克隆抗体的开发,验证了其在人及小鼠组织中的特异性,并成功应用于Western blot和免疫荧光,证明SF1在性腺与肾上腺中的定位。
3. **文献名称**:*"SF-1 Regulates Sexual Differentiation in Mammals: Insights from Antibody-Based Knockdown Models"*
**作者**:Ikeda Y等
**摘要**:研究利用SF1抗体干扰技术,在小鼠模型中证明SF1对性腺分化的关键作用,揭示其通过调控下游基因(如AMH)影响性腺发育的分子机制。
(注:以上文献名称及摘要内容为综合示例,实际引用请以真实文献为准。)
SF1 (Steroidogenic Factor 1), also known as NR5A1. is a nuclear receptor protein critical in regulating genes involved in steroidogenesis, reproductive development, and adrenal function. It was first identified in the 1990s as a transcription factor binding to promoter regions of steroidogenic enzymes like cytochrome P450s. SF1 is expressed in adrenal glands, gonads, pituitary gland, and hypothalamus, playing a pivotal role in endocrine system regulation.
SF1 antibodies are essential tools in research to study its expression, localization, and interactions. They are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP). These antibodies help investigate SF1's role in sexual differentiation, adrenal insufficiency, and disorders of sex development (DSD). Mutations in the NR5A1 gene are linked to conditions like 46.XY DSD and primary ovarian insufficiency, making SF1 antibodies valuable in clinical diagnostics and mechanistic studies.
Recent studies also explore SF1's involvement in metabolic regulation and cancer, particularly steroid-dependent tumors. Commercial SF1 antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes (e.g., C-terminal regions) and validated for species cross-reactivity (human, mouse, rat). Researchers prioritize antibodies with high specificity to avoid cross-reactivity with related nuclear receptors. Overall, SF1 antibodies remain indispensable for unraveling molecular pathways in endocrinology and developmental biology.
×